Peptide Sulfation is a common post-translational modification of tyrosine residues in eukaryotes that is known to have a widespread occurrence among proteins of multicellular eukaryotic organisms. Studies on tyrosine-sulfated proteins have shown a major role in enhancing protein-protein interactions, and it is found to be implicated in multiple biological processes. Due to sulfation plays a role in strengthening protein-protein interactions, so types of human proteins known to undergo tyrosine sulfation include G-protein-coupled receptors, adhesion molecules, serine protease inhibitors, coagulation factors, hormones and extracellular matrix proteins. Meanwhile, tyrosine O-sulfate is a stable molecule and is excreted in urine in animals. In addition, studies have shown that it may be observed that tyrosine sulfation has effects on the growth of the mice, such as fecundity, body weight and postnatal viability by knock-out of TPST (tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase) genes in mice.
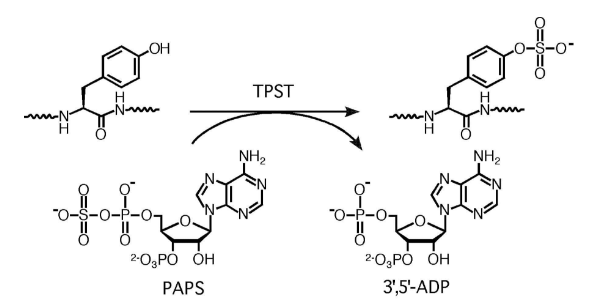 Fig.1 The tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase reaction (Moore K. L. 2003)
Fig.1 The tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase reaction (Moore K. L. 2003)
It is well known that in their N-terminal regions, many receptors of chemokine contain sulfated tyrosine. Meanwhile, these residues can affect the interactions of chemokines with their receptors. Due to highly flexible chemokine receptors, this type of sulfur peptide may be a reasonable mimic of the N-terminal region of chemokine receptors.
A complex network was formed by chemokines and their receptors in which most receptors can respond to most chemokines and several cognate chemokines, and then can activate more than one receptor. Differently sulfated states of a receptor peptide can have distinct selectivity profiles among cognate chemokines. However, tyrosine sulfation is one possible mechanism that could regulate the responses of receptors among possible ligands.
Due to inhibition of sulfation or mutation of receptor tyrosine residues may be causes a reduction in chemokine binding affinity, so it is normal that sulfated peptides derived from chemokine receptors bind to the cognate chemokines of those receptors with higher affinity than their non-sulfated analogues. The sulfopeptides homogeneity has made it possible to determine the specific affinity enhancements resulting from each individual tyrosine residue sulfated. A key finding is that chemokine binding affinity can have a markedly different with sulfation of the same receptor peptide at different positions.
Creative Peptides has developed a reliable procedure for the synthesis of sulfated peptides, we can provide global customers with sulfated peptides based on our excellent technology. Creative Peptides has extensively developed sulfated peptides structures and is the company of choice to manufacture your sulfated peptides requirements, providing a confidential and efficient service at competitive prices. Our experienced scientists will tailor the most appropriate methods and 100% guaranteed service for customers. Every step of peptide synthesis is subject to Creative Peptides’ stringent quality control. Typical delivery specifications include:
Peptide sulfation involves adding a sulfate group to the tyrosine residue, playing a vital role in enhancing protein-protein interactions. It is crucial in various biological processes, such as receptor binding and signal transduction.
Tyrosine sulfation enhances the binding affinity of receptors to their ligands, especially in chemokine receptors. This modification improves receptor selectivity and interaction with target molecules.
Sulfated peptides are used extensively in studying chemokine receptor functions and receptor-ligand interactions. They help determine the impact of different sulfation patterns on receptor selectivity and binding affinity.
Sulfation significantly increases the binding affinity of receptor peptides for chemokine ligands, especially when applied at specific tyrosine residues. The position of sulfation can alter the binding strength and receptor activity.
Creative Peptides offers customized peptide sulfation services, including modification and purification. We ensure high-quality synthesis with detailed analysis reports, including HPLC and mass spectrometry results.

References