Biotinylated peptides are compounds that covalently bind biotin to a peptide molecule. Creative Peptides utilizes our expertise in peptide technology, which allows us to establish a stable, efficient and high-throughput peptide synthesis platform to provide a wide range of labeled peptides for our customers. In addition to biotin-labeled peptides, our peptide synthesis business also covers various long peptides, short peptides, cyclic peptides and various types of modified peptides, such as fluorescence and dye labeling, functional group modified peptides, isotope labeled peptides, stapled peptides, fatty acid modified peptides, phosphorylated modified peptides, PEG modified peptides, methylated modified peptides, etc.
 Fig. 1 Biotinylated peptides. (Kosako, H., 2022)
Fig. 1 Biotinylated peptides. (Kosako, H., 2022)
Biotinylation is a process that attaches biotin or Vitamin B7 to peptides, proteins, and other targeted molecules. This technique aimed at covalent modification helps in research areas like molecule detection and purification, probe capture, and cell imaging. Biotinylated peptides are those peptides that have been chemically modified to carry a biotin molecule. This link can be leveraged for multiple protein studies due to the avidin-biotin bond, known for its exceptional strength and stability, varying from cellular imaging and microscopy to protein interaction studies and diagnostic assays. Biotin labeling is often attached to the side chain or N-terminal of lysine. Usually, 6- aminocaproic acid is used as a bond between peptide and biotin, which can flexibly bind to substrate, and can bind better when there is steric hindrance.
The most common modification site of biotin is the N-terminal of peptide.
Biotin is labeled at the C-terminal, and usually a lysine is added at the C-terminal, and then biotin is labeled at the side chain amino group of lysine.
Enhanced Detection and Visualization: Biotinylated peptides can easily bind to streptavidin or avidin-labeled entities, making them excellent tools for detection in a variety of biomedical assays, as well as for visualization in fluorescent or electron microscopy.
High Binding Affinity: Biotin has an extraordinarily high binding affinity for avidin or streptavidin, making these interactions extremely stable even under tough conditions. This ensures the biotinylated peptides remain attached during experiments, resulting in more reliable results.
Versatility: Biotinylated peptides can be employed in a variety of research settings, including enzyme activity measurements, protein interactions studies, immunoassays, and cellular targeting research.
Customizable: Biotinylated peptides can be precisely tailored to meet specific research needs. The peptide sequence, biotin attachment point, peptide length, purity grade, and other parameters can all be customized.
Easy to Use: Unlike radio-labeled or fluorescently labeled peptides, biotinylated peptides do not require special handling or storage conditions, making them easy to use.
Increases the Efficiency of Drug Delivery: In some cases, biotinylated peptides have been used for targeted drug delivery, potentially boosting their effectiveness while minimizing side effects.
Non-immunogenic: Biotinylated peptides are non-immunogenic, which means they do not trigger an immune response. This is an important characteristic for many research applications and potential therapeutic uses.
Biotinylation is also named as biotin tagging or labeling, which is helpful in protein studies and can be applied in multiple fields, involving enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and Western blot analysis, as well as immunohistochemistry, immunoprecipitation, cell surface labeling, and flow cytometry.
Peptide nucleic acid (PNA) is a DNA or RNA synthetic variant. When biotinylated, it can attach itself more accurately to a corresponding nucleic acid sequence, enhancing its functionality. Biotinylated PNA is beneficial in identifying specific DNA or RNA sequences, which could be useful in treating genetic disorders and cancer.
Biotinylated peptides can be discerned using techniques such as western blotting, fluorophore-assisted light inactivation, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), due to the strong bond of biotin and streptavidin. This detection method could help in understanding interactions and processes at the molecular level.
In this assay, a biotin-bound peptide of interest is introduced to a cellular or tissue extract. After this, streptavidin-linked beads "pull down" the biotinylated peptide and any proteins that interact with it. It's a handy technique for studying protein-protein interactions and signaling pathways in cells.
These peptides are attached to target proteins and immobilized, interacting with other proteins in a specific way.
Biotinylated peptides can be rapidly purified and enriched by taking advantage of the high affinity between biotin and affinities.
By attaching biotinylated peptides to target proteins, they can be immobilized on solid phase materials and specifically interact with other proteins. This method is widely used in fields such as affinity chromatography, proteomic analysis and protein interaction network studies.
By introducing biotinylated peptides into cells, visual localization and study of target proteins can be achieved by binding to fluorescent dyes or fluorescently labeled affinities.
Creative Peptides provides custom synthesis services for biotinylated peptides, which are divided into two main parts: one is the preparation and optimization of biotin, and the other is the synthesis and purification of peptides. In addition, we also provide scale-up production of biotinylated peptides and quality control. The label is usually attached to the N-terminal or C-terminal, and the N-terminal biotinylation can be carried out directly on the primary amino group, while the biotinylation is usually carried out on the ε-amino group of C-terminal lysine. In the preparation of biotinylated peptides, an important consideration is to ensure that there are sufficient spacers between the biotin groups and the amino acids expected to interact with macromolecules in the peptides. To avoid spatial barriers, a junction can be inserted between biotin and peptide sequences. Peptides are separated from peptides by various so-called connectors or spacers with different lengths and polarities.
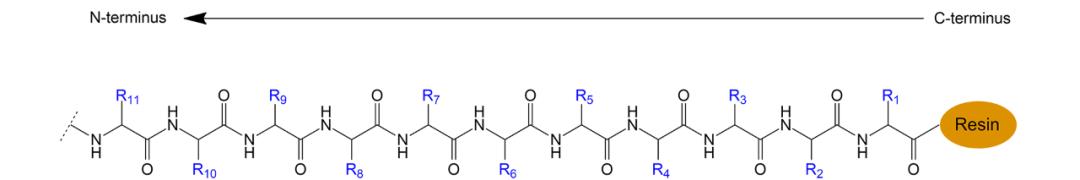 Fig. 2 Fmoc solid-phase synthesis process of biotinylated peptides.
Fig. 2 Fmoc solid-phase synthesis process of biotinylated peptides.
Before preparing biotinylated peptides, biotin customization and optimization is required. First, a suitable biotin is selected according to the customer's requirements, and then the biotin is activated. During this period, the biotin can also be chemically modified by adding specific functional groups to achieve the customer's purpose. After that, through systematic optimization experiments and parameter adjustments, the best reaction conditions are determined. Finally, according to the demand of biotinylated peptide, determine the appropriate synthesis batch.
Generally, the synthesis of biotinylated peptides involves the covalent attachment of biotin to either the N-terminus or the side-chain of a residue within the peptide. This synthesis can be accomplished using solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS), a method widely used for its speed, simplicity, and high yield of product.
Creative Peptides provides peptide design and custom synthesis services, which can establish a good foundation for the preparation of biotinylated peptides, reserving functional groups suitable for biotinylation in advance. Subsequently, our researchers will react the activated biotin molecules with the peptide to produce the target biotinylated peptide and complete the peptide modification. Finally, the resulting product is isolated and purified, and validated by mass spectrometry and other analyses to obtain the high-purity product we desire.
Quality control and analytical steps are essential in large-scale production, and Creative Peptides ensures that biotinylated peptides are produced to the required quality standards by establishing appropriate quality control standards and analytical methods.
Materials Needed:
Protocol:
Please note that all steps should be performed under sterile conditions to prevent the introduction of contaminants into the reaction mixture. Different peptides and different applications may have specific variations to this protocol, so always refer to the specific requirements of your planned assays and procedures.
Biotinylated peptides are peptides that have been covalently attached to biotin (Vitamin B7). This modification enhances their binding to streptavidin or avidin, enabling their use in various research applications like protein interaction studies, cell imaging, and protein purification due to the strong biotin-avidin bond.
Biotinylated peptides are synthesized by attaching biotin to the N-terminal or side-chain of specific amino acids within a peptide. This process typically uses solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS), where biotin is covalently linked to the peptide through chemical activation, ensuring a stable and efficient product.
Biotinylated peptides offer several benefits, including high binding affinity for streptavidin, which ensures stability in experiments. They are highly versatile, useful in protein detection, enzyme activity assays, cell surface labeling, and interaction studies. Additionally, they are non-immunogenic and easy to use without special storage or handling conditions.
Yes, biotinylated peptides can be tailored to meet specific research needs. Customization includes adjusting the peptide sequence, biotin attachment point, peptide length, purity grade, and adding spacers to enhance functionality. This flexibility allows biotinylated peptides to be optimized for various assays and experiments.
In protein interaction studies, biotinylated peptides can be immobilized on solid-phase materials and used to interact specifically with target proteins. This method is widely used in affinity chromatography, proteomic analysis, and to study protein-protein interactions and signaling pathways in cellular systems.
Biotinylated peptides can be modified in various ways, such as adding a hydrocarbon chain or polyethylene glycol (PEG) as linkers to improve flexibility and reduce steric hindrance. Modifications can also include attaching biotin at the C-terminal, or on the lysine side-chain, to optimize binding affinity and performance in assays.
Quality control is essential in the production of biotinylated peptides. At Creative Peptides, we employ rigorous analytical techniques such as mass spectrometry, HPLC, and peptide sequencing to verify the purity, molecular weight, and biotinylation efficiency of the peptides. This ensures that the peptides meet the highest standards for research applications.

References