Enhanced SelectivityImproved PharmacokineticsEnhanced Drug DeliveryReduced Drug Dosage
We provide comprehensive Peptide–Drug Conjugate (PDC) development services designed to accelerate your targeted drug discovery and delivery programs. Our end-to-end platform integrates custom peptide design, linker chemistry, conjugation synthesis, and biological validation, delivering fully characterized PDC candidates ready for preclinical or clinical advancement. Whether you are developing oncology therapeutics, precision imaging agents, or targeted delivery systems, we offer flexible, high-quality solutions tailored to your scientific and regulatory goals.
Peptide-drug conjugates (PDCs), a subset of drug conjugates, are composed of carrier peptides ranging from 5 to 30 amino acid residues, toxic payloads, and linkers that connect the payload to the peptide. PDCs are further broken down into cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) and cell-targeting peptides (CTPs), each having their own differences in the delivery of cytotoxic payloads. The efficacity of PDCs lies in their ability to deliver drugs to targeted cells without affecting healthy cells. The peptide in the PDCs attaches to specific receptors or proteins on the disease-causing cells' surfaces. In this state, the medicine is released to the diseased cells alone, reducing the side effects commonly associated with traditional therapies. Generally, compared to antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), PDCs have advantages in tumor penetration, ease of synthesis and cost, and reduced off-target effects. Further, as compared to traditional cancer treatments (e.g., chemotherapy and radiation), PDCs have higher specificity for the target cancer with generally less toxic side effects in smaller doses.
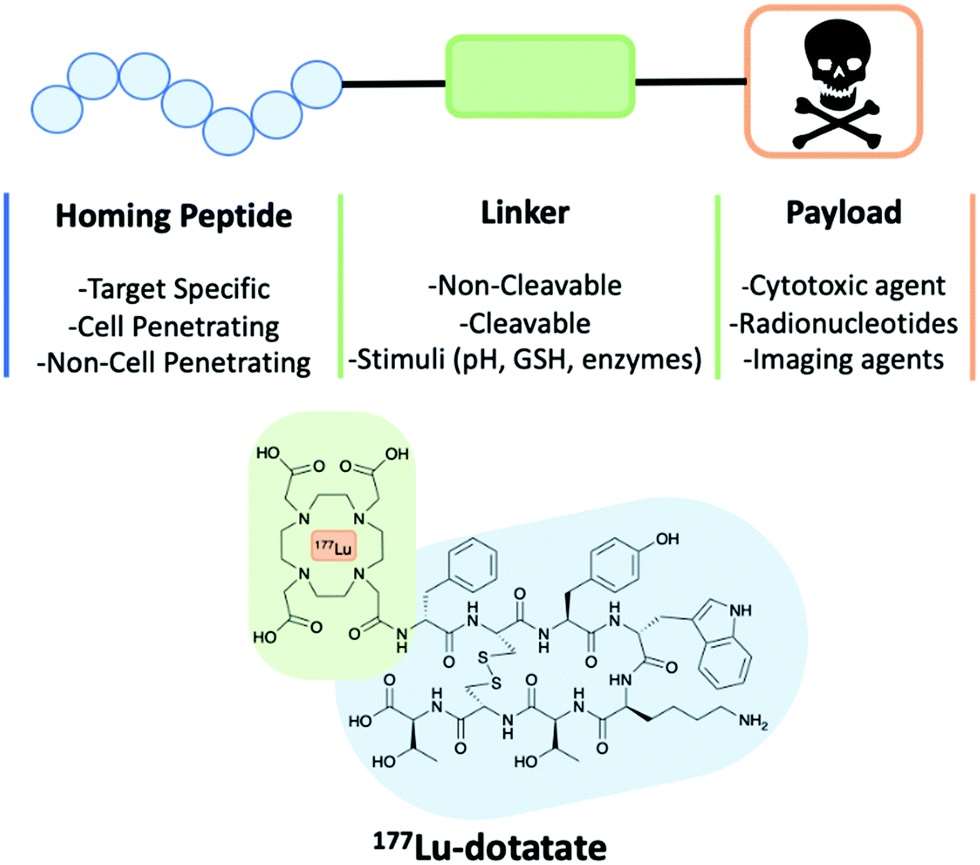 Fig. 1 A schematic of a peptide-drug conjugate construct consisting of a homing peptide, linker and payload. The structure of 177Lu-dotatate an FDA approved peptide-drug conjugate. (Cooper, B. M., 2021)
Fig. 1 A schematic of a peptide-drug conjugate construct consisting of a homing peptide, linker and payload. The structure of 177Lu-dotatate an FDA approved peptide-drug conjugate. (Cooper, B. M., 2021)
Developing effective targeted drug conjugates involves multiple challenges — and our expertise helps you overcome each of them:
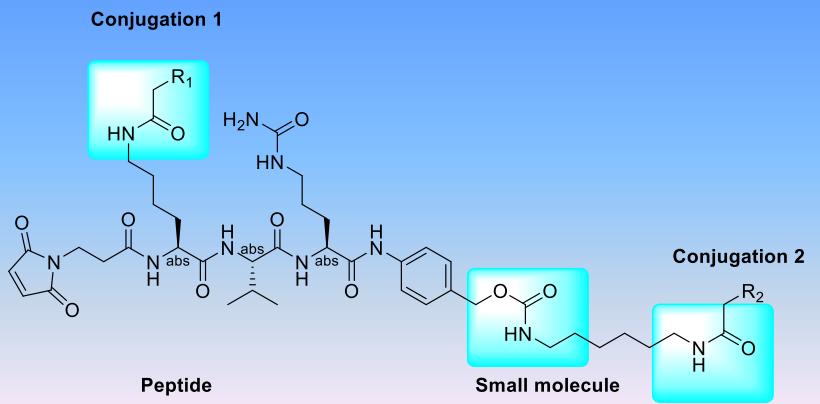 Fig. 2 Mal-K-V-R-PABC small molecule-peptide conjugate
Fig. 2 Mal-K-V-R-PABC small molecule-peptide conjugate
Peptides play a critical role in Peptide Drug Conjugates (PDCs), functioning as the targeting ligand, delivery enhancer, or therapeutic effector. Advanced peptide engineering significantly improves selectivity, stability, tumor penetration, and payload delivery efficiency. Our platform provides all major classes of targeting and functional peptides, allowing seamless integration into next-generation PDC design and optimization.
| Peptide Strategy | Key Benefits | Core Characteristics | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor-Homing Peptides (THPs) | Highly selective targeting; enables precise payload delivery | Recognize tumor-specific receptors or microenvironment markers | Solid tumors, metastatic cancer, high-specificity targeting |
| Cell-Penetrating Peptides (CPPs) | Enhances intracellular delivery; overcomes membrane barriers | Positively charged or amphipathic sequences; efficient endocytosis | Difficult-to-penetrate tumors, intracellular targets, oligonucleotide payloads |
| Receptor-Specific Peptides | Binds defined receptors with high affinity | Often derived from natural ligands or optimized sequences | GPCR targets, integrins, RTKs, disease-specific surface proteins |
| Enzyme-Responsive Peptides | Activated or cleaved by disease-specific enzymes | Cleavable motifs triggered by MMPs, cathepsins, or proteases | Tumor microenvironment targeting; conditional activation |
| pH-Responsive Peptides | Preferential activation under acidic tumor conditions | Conformational switch or charge change at low pH | Tumor microenvironment delivery; improved endosomal escape |
| Peptide Ligands from Phage Display / Screening | High screening flexibility; strong optimization potential | Selected via in vitro / in vivo biopanning; customizable specificity | Any disease requiring novel or unique targeting ligands |
| Cyclic Peptides | Greatly improved stability; resistant to proteolysis | Rigid conformation increases affinity and half-life | Systemic PDCs, long-circulation applications, harsh biological environments |
| Stapled / Helical Peptides | Enhanced structural stability and cell permeability | Hydrocarbon-stapling maintains α-helix structure | Intracellular protein–protein interaction (PPI) targets |
| Peptide–Antibody Hybrid Ligands (Peptide Mimetics) | Combines antibody-level specificity with peptide size advantages | Smaller, more stable, lower immunogenicity than antibodies | High-specificity PDCs, where antibody size is limiting |
| Bioinspired / Natural-Derived Peptides | Balanced affinity and safety; often lower immunogenicity | Derived from hormones, antimicrobial peptides, or natural ligands | Broad applicability from oncology to inflammation |
| Computationally Designed Peptides | Tunable binding affinity and selectivity | AI/ML-guided optimization; de novo sequence design | Rapid pipeline generation; customized targeting strategies |
The linker is a critical component of every Peptide-Drug Conjugate (PDC), determining how securely the drug is attached to the peptide and how precisely it will be released at the target site. An optimized linker ensures controlled drug release, enhances therapeutic index, and minimizes off-target toxicity, making it essential for developing effective targeted medicines. We provide customized linker design, synthesis, and validation services to ensure optimal stability, controlled drug release, and seamless compatibility across all peptide-drug conjugate (PDC) projects.
| Linker Type | Trigger / Release Mechanism | Typical Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH-Sensitive Linkers (e.g., hydrazone, cis-aconityl) | Cleaved in acidic environments such as tumors or endosomes | Tumor-targeted chemotherapy, intracellular drug delivery | Selective release inside tumor tissue; minimal release in bloodstream |
| Enzyme-Cleavable Linkers (e.g., MMP-sensitive, cathepsin B-sensitive, peptide linkers) | Cleaved by overexpressed enzymes in tumor microenvironment | Oncology PDCs, tumor-penetrating systems | High specificity; compatible with a wide range of peptides and drugs |
| Redox-Sensitive Linkers (e.g., disulfide linkers) | Cleaved in high-glutathione intracellular environments | Targeted cytotoxic drug release inside cancer cells | Rapid intracellular release; well-studied mechanism |
| Non-Cleavable Linkers (e.g., stable thioether bonds) | Remain intact; payload is released only after peptide degradation | Durable payload delivery, imaging agents, stable conjugates | High plasma stability; predictable PK/PD profile |
| Self-Immolative Linkers | Undergo cascade breakdown after initial trigger | Smart drug-delivery systems, controlled release PDCs | Highly customizable; fine-tuned release kinetics |
| PEG-Based Linkers | Provide steric flexibility and stability | Improving solubility, serum stability, reducing immunogenicity | Enhanced circulation time; improved physicochemical properties |
In Peptide Drug Conjugates (PDCs), the payload is the therapeutic engine that ultimately determines potency, selectivity, and clinical performance. A well-engineered payload strategy ensures the ideal balance among efficacy, safety, stability, and controlled release, making it a critical differentiator for next-generation targeted therapies.
| Payload Strategy | Key Benefits | Core Features | Ideal Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Potency Cytotoxic Payloads | Enables rapid and efficient tumor cell elimination with minimal dosing | Extremely potent; designed to minimize off-target toxicity when delivered via peptides | Highly expressed tumor targets; oncology applications requiring strong cytotoxic action |
| Pathway-Modulating Payloads (e.g., epigenetic modulators) | Achieves precise pathway control with moderate toxicity | Mechanism-driven; suitable for combinational or long-term therapy | Chronic cancer therapy, drug-resistant tumors, or patient groups sensitive to toxicity |
| Immunomodulatory Payloads | Reprograms the tumor microenvironment to enhance immune response | Low toxicity; strong synergy with immuno-oncology agents | "Cold" tumors, immune-evasive cancers, combination immunotherapy |
| RNA / Oligonucleotide Payloads | Targets diseases at the genetic level for highly selective intervention | Highly customizable sequences; requires enhanced stability via conjugation | Gene-driven cancers, precision medicine, rare genetic disorder pipelines |
| Photo- or Sono-Activated Payloads | Allows spatiotemporal control for highly localized therapeutic activity | Inactive during circulation; activated only by external stimuli | Localized solid tumors, therapies requiring minimal systemic exposure |
| Dual-Modality Payloads | Simultaneously targets multiple disease pathways to reduce resistance | Synergistic multi-mechanism design; modular combination options | Hard-to-treat cancers, multi-pathway disease models |
| Next-Generation Natural-Product-Derived Payloads | Combines high biological potency with improved safety profiles | Unique chemical architecture; offers strong innovation value | Differentiated oncology pipelines, high-value proprietary drug portfolios |
| Low-Toxicity "Enhanced-Delivery" Payloads | Transforms moderately potent molecules into clinically valuable therapeutics through targeted delivery | Optimized for safety; suitable for broader dosing and long-term treatment | Metabolic diseases, inflammatory disorders, non-oncology therapeutic areas |
Comprehensive PDC Platform
End-to-end capability covering peptide design, linker chemistry, conjugation, and biological evaluation in one integrated workflow.
Targeted Drug Delivery Expertise
Proven experience in developing tumor-targeting peptides (RGD, NGR, iRGD) for oncology, imaging, and precision therapy applications.
Advanced Linker Design
Expertise in cleavable linkers for controlled drug release, enhancing efficacy while minimizing systemic toxicity.
High-Purity Peptide Synthesis
State-of-the-art solid-phase synthesis and HPLC/MS quality control ensure reproducibility and analytical accuracy.
Integrated Analytical Support
Comprehensive LC-MS, NMR, DLS, and PK/PD testing for precise conjugate characterization and stability evaluation.
Scalable Manufacturing
Flexible production from milligram to gram scale for research and preclinical development.
Rapid Turnaround & Project Transparency
Efficient communication, milestone-based reporting, and real-time project updates shorten development timelines.
Confidentiality & IP Protection
Full intellectual-property security and customizable NDAs to safeguard client innovations.
Collaborative Development Partnership
Support for co-development, technology transfer, and IND-enabling documentation to accelerate market translation.
1
Project Assessment & Strategy Design
We evaluate your therapeutic goals, target receptors, and payload requirements to define the optimal peptide-drug conjugation strategy.
2
Targeted Peptide Design & Synthesis
Custom peptides are developed using phage display, AI modeling, or rational design, followed by high-purity SPPS synthesis and analytical confirmation.
3
Linker Engineering & Payload Integration
We design cleavable or stable linkers and select compatible payloads to ensure controlled release, high stability, and efficient conjugation.
4
Conjugation & PDC Construction
Your peptide and drug molecules are conjugated using precision chemistries such as click reactions, maleimide-thiol coupling, or amide linking.
5
Purification & Analytical Characterization
PDCs undergo multi-step purification (HPLC/SEC) and full analytical testing (LC-MS, NMR, stability profiles) to confirm structure and purity.
6
In-Vitro & In-Vivo Validation
We evaluate cellular uptake, drug-release kinetics, cytotoxicity, and in-vivo biodistribution/PK/PD to identify high-value PDC candidates.
Our PDC technology platform can be applied across multiple therapeutic and research domains.
Each application benefits from targeted delivery, controlled release, and enhanced efficacy while reducing systemic toxicity.
PDCs and ADCs both represent advanced targeted drug delivery modalities, but they differ significantly in size, targeting mechanisms, manufacturability, tissue penetration, safety profile, and development scalability. Understanding these differences is essential for selecting the right modality for specific therapeutic applications.
| Category | PDCs (Peptide Drug Conjugates) | ADCs (Antibody–Drug Conjugates) |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Size | Small (typically<5 kDa) | Large (~150 kDa) |
| Tumor Penetration | Excellent; easily diffuses into solid tumors | Limited due to large size; slower tissue penetration |
| Targeting Precision | High-peptides can target receptors, microenvironment markers, or internalizing motifs | High-driven by antibody–antigen specificity |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Simple, fully chemical synthesis; scalable | Complex biological/chemical hybrid production; costly |
| Production Cost | Low to moderate | Very high |
| Immunogenicity Risk | Generally low | Higher; antibodies can trigger immune responses |
| Circulation Half-Life | Shorter; can be extended via modification | Long natural antibody half-life |
| Payload Capacity | Lower payload load; typically 1–2 molecules | High drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR up to ~8) |
| Linker Compatibility | Highly flexible with chemical linkers | Bioconjugation constraints with amino acids/cysteines |
| Specificity Drivers | Peptide sequence, receptor selectivity, tumor homing | Monoclonal antibody binding to specific antigens |
| Biodistribution | Broad distribution due to small size; rapid clearance | More restricted; prolonged systemic presence |
| Stability | Requires optimization (cyclization, stapling) | Generally very stable in plasma |
| Best Use Cases | Solid tumors, intracellular targets, rapid iteration pipelines, emerging targets | Hematologic cancers, high-antigen-expression tumors |
| Discovery Speed | Fast; peptides can be screened or designed rapidly | Slow; antibody discovery, validation, cell line development required |
| Scalability & Cost Efficiency | Excellent; ideal for large-scale or rapid development programs | Limited; expensive and resource-intensive |
Ready to bring your peptide-based therapeutics from concept to reality?
Our expert scientists specialize in Peptide–Drug Conjugate (PDC) development, offering integrated solutions for targeted drug delivery, oncology therapeutics, CNS applications, and diagnostic imaging. We combine advanced peptide design, linker chemistry, and pharmacological validation to deliver PDC candidates that meet your scientific and regulatory needs. Contact us now to discuss your project — and discover how our custom PDC development services can accelerate your innovation and reduce time-to-market.
A PDC is a targeted therapeutic composed of a bioactive peptide linked to a drug molecule via a chemical linker. The peptide ensures specific binding to target cells, while the linker controls drug release at the desired site.
We can conjugate small molecules, cytotoxic agents, imaging probes, or biologics to peptides, depending on your therapeutic or diagnostic goal.
Typical tumor-targeting peptides include RGD, NGR, iRGD, and CREKA, which recognize integrins, CD13, and fibrin-fibronectin complexes on tumor vasculature.
Each conjugate is characterized by HPLC, LC-MS, NMR, and stability assays to confirm purity, structure, and reproducibility.
Yes. We offer in-vitro (cell uptake, cytotoxicity) and in-vivo (biodistribution, efficacy, PK/PD) testing to validate therapeutic potential.
We provide milligram- to gram-scale synthesis, suitable for research, preclinical, and early IND-enabling studies.
