Peptides are a kind of promising molecules with the potential protein-anchoring/modulating property, due to their large chemical diversity and the existence of well-established methods for library synthesis. There is a growing realization that it is possible to create synthetic structures with affinities and specificities comparable to natural antibodies, by using peptides as building blocks.
Enzymes often detect proteins by direct or indirect antibody detection strategies or as nucleic acid hybridization probes in sensitive assays. Reported enzyme molecules are widely used in biology due to their special properties. Although the detection of fluorescent and luminescent tags has made great progress, but enzyme conjugates can detect immune complexes by visual or spectrophotometry as sensitive probes. Enzyme labels provide the best overall performance, high sensitivity, low background, and can achieve fast detection.
Horseradish peroxidase and alkaline phosphatase are commonly used to linked to peptides or proteins.
For the detection of proteins, horseradish peroxidase (HRP) substrates are designed to produce signals for chromogenic, chemiluminescent or fluorescent oxidation. HPR has a molecular weight of 40,000. This molecular weight is lower than other enzyme conjugates, allowing for greater tissue and cell permeability and reducing the possibility of interfering with protein coupling.
Synthetic peptide-alkaline phosphatase conjugates, which was developed with alkaline phosphatase (AP) as the detector enzyme, permits epitopespecific analysis of antibody responses in experimentally or clinically derived lymphoid tissue.
Two reaction mechanisms are involved in peptide-enzyme conjugation:
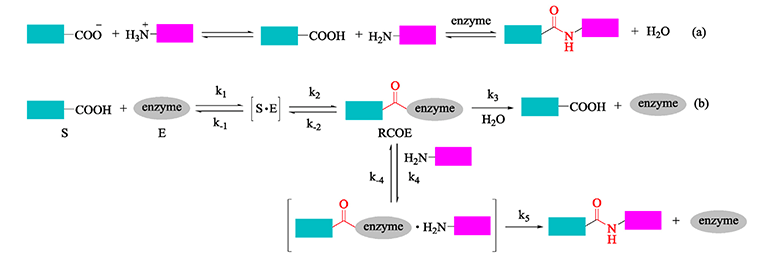 Fig.1 Reaction mechanisms of Peptide-enzyme Conjugation (Xu et al. 2018)
Fig.1 Reaction mechanisms of Peptide-enzyme Conjugation (Xu et al. 2018)
Creative Peptides offers custom peptide-enzyme coupling and modification services, as well as services such as experimental method development and testing for our customers. Our strengths in enzymatic engineering and peptide manufacturing will provide you with a specialized peptide-enzyme conjugate custom synthesis service, customizing proprietary peptide-enzyme conjugate products using different coupling methods.
Peptide-enzyme conjugation involves attaching enzymes like horseradish peroxidase (HRP) or alkaline phosphatase (AP) to peptides to enhance detection sensitivity in various assays. This technique combines the specificity of peptides with the catalytic properties of enzymes, offering high sensitivity and low background for applications such as protein detection.
Peptide-enzyme conjugates are primarily used in assays for detecting proteins, such as chromogenic, chemiluminescent, or fluorescent assays. They are also useful in epitope-specific analysis and immunological studies due to their high sensitivity and fast detection capabilities.
The enzyme selected for conjugation, such as HRP or AP, influences the conjugate's performance in assays. For instance, HRP has low molecular weight, allowing for better tissue and cell permeability, while alkaline phosphatase is widely used for its stability and efficiency in immunoassays.
Peptide-enzyme conjugation typically uses two methods: direct reaction via protease-catalyzed peptide hydrolysis or aminolysis of N-protected peptide esters. Both approaches allow for precise attachment of enzymes to peptides, ensuring functionality and stability in assays.
Yes, Creative Peptides offers custom peptide-enzyme conjugation services, tailored to specific research requirements. We provide different coupling methods to create proprietary peptide-enzyme conjugates, ensuring compatibility and performance for various experimental setups.

References