Creative Peptides has advanced peptide synthesis abilities and provides more than 40 types of N-terminal modifications to meet your needs in different research fields.
The N-terminal of a peptide is the end of the amino acid chain where the amino group (-NH2) is not involved in peptide bond formation. This is generally the start of any polypeptide or protein chain.
Peptide N-terminal modification refers to the chemical alteration of the N terminus, or the start, of a peptide or protein. Proteins can undergo this process after they are formed to allow them to fulfill different biological functions.
Although many of the most widely recognized post-translational modifications are characteristic of secretory or cell-surface proteins, most proteins, whatever their ultimate cellular desination, undergo some modification. For proteins synthesized completely within the cytoplasm, the earliest and most widespread are removal or modification of the N-terminal residue. In many proteins the N-terminal α-ammonium group (PK=8) undergoes secondary modification.
N-terminal modification reduces overall solubility of the peptide by reducing its overall charges. However, the stability of the peptide could also be increased because N-terminal modification generates a closer mimic of the native protein. Therefore, these modifications might increase the biological activity of a peptide and prevent degradation by enzymes. The following are common peptide N-terminal modifications.
Methionine excision: This modification occurs when the initiating methionine amino acid is cut off by a protease upon the completion of protein synthesis.
N-terminal acetylation: This is one of the most common modifications, where an acetyl group is added to the N-terminus of a peptide or protein.
N-terminal alkylation: N-alkylated amide bonds can often change the intramolecular or intermolecular hydrogen bond interaction of peptides, thus affecting the spatial structure of peptides and changing their physical and chemical properties. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding in flexible peptides is the decisive factor in passive diffusion. By alkylation at a specific amide bond, peptide molecules can cross the cell membrane in the most dominant conformation.
N-myristoylation: A myristoyl group is covalently linked to the N-terminal glycine residue of specific proteins, typically involved in signal transduction and apoptosis.
N-formylation: In bacterial and mitochondrial proteins, formylation of the N-terminal methionine is common preceding translation.
N-terminal phosphorylation: It is the addition of a phosphate group to the N-terminal residue of a protein.
N-terminal carbamylation: It is a non-enzymatic modification leading to the addition of a carbamyl group at the N-terminus or on lysine side chains.
N-pyroglutamate: Pyroglutamate forms via modification of a glutamine or glutamate residue on the N-terminus, which blocks the N-terminus against degradation and proteolytic cleavage.
N-succinylation: A succinyl group is added to the N-terminus or lysine side chains of proteins, affecting their structure and function.
N-propionylation: In this, a propionyl group is added to the N-terminal residue of a protein.
Increases stability: Peptides are often unstable and can be quickly degraded by enzymes in the body. N-terminal modifications can increase their stability and lifespan, enhancing their therapeutic efficacy.
Enhances absorption: Certain modifications such as acetylation can increase peptides' ability to cross cell membranes, thereby increasing their absorption.
Increases resistance to protease degradation: Various proteases in the body target the N-termini of proteins and peptides for degradation. Modifications can create resistance to these enzymes and extend the peptide's lifespan.
Provides chemical versatility: N-terminal modification enables researchers to add different chemical groups to peptides, opening up a wide variety of potential applications.
Reduces immunogenicity: In some cases, modifications can lower a peptide's immunogenicity, reducing the immune system's response to it and increasing the peptides' therapeutic potential.
Increases solubility: Some modifications can enhance the solubility of peptides in water or other solvents, which can be helpful in peptide development and synthesis.
Target specificity: Modification at the N-terminus can increase the specificity of the peptide for its target, which can improve effectiveness and reduce side effects.
Enhances bioactivity: Some modifications can enhance peptides' activity, resulting in increased potency.
Produces fluorescent markers: Some N-terminal modifications introduce a fluorescent marker into the peptide, which allows for easy tracking and visualization of the peptide in biological systems.
Drug development: Modification of the N-terminal of peptides can increase their stability, cellular uptake, and bioactivity, which can be beneficial in the development of peptide-based drugs.
Disease treatment: Modifying the N-terminal of peptides can aid in the treatment of various diseases. For example, protease-resistant peptide analogs can be developed for treating diabetes or obesity.
Protein engineering: N-terminal modifications are often used in protein engineering to enhance protein expression and folding.
Diagnostic tools: Modified peptides can be used in diagnostic tools, such as biomarkers for particular diseases.
Peptide vaccines: N-terminal modification can be used to increase the potency and efficacy of peptide vaccines.
Probe synthesis: Modified peptides can also be used in the synthesis of molecular probes for biological research and drug discovery.
Enhancing the selective delivery of drugs: N-terminal modifications can be used to modify a drug's selectivity to specific tissues or cells, increasing its efficacy and reducing side effects.
Imaging agents: N-terminal modified peptides can be used in medical imaging to enhance visualization of certain tissues or biological processes.
Target drug discovery: N terminal modifications can help in targeted drug discovery when specific binding or uptake is needed.
Protein-protein interactions: These modifications can help to understand protein-protein interactions by controlling the interaction sites within the protein.
| 3-Mercaptopropyl (Mpa) | D (+) Glucose | Lauric acid |
| 5-FAM | Dansyl | Lipoic acid |
| 5-FAM-Ahx | Dansyl-Ahx | Maleimide |
| Abz | Decanoic acid | MCA (7-Methoxycoumarinyl-4-acetyl) |
| Acetylation | DNP (2, 4-Dinitrophenyl) | Myristoyl |
| Acryl | DTPA | Octanoic acid |
| Alloc | Fatty Acid | OVA (-NH2 of N terminal) |
| Benzoyl | FITC | Palmytoyl |
| Benzyloxycarbonylation (CBZ) | FITC-Ahx | Pentinoic Acid |
| Biotin | Fmoc | Propiolic Acid |
| Biotin-Ahx | Formylation | Pyroglutamyl (pGlu) (Pyr) |
| Boc (Tertbutoxycarbonyl) | Hexanoic acid | Stearic acid |
| Br-Ac- | HYNIC | Succinylation |
| BSA (-NH2 of N terminal) | HPP (4-Hydroxyphenylpropionic acid) | Thioester |
| Chenodeoxycholic acid | KLH (-NH2 of N terminal) | TMR |
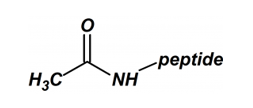
Acetylation
Acetylation (N-terminus) will remove the positive charge and help peptides imitate its natural structure. In addition, this modification makes the resulting peptide more stable towards enzymatic degradation resulting from exopeptidases.
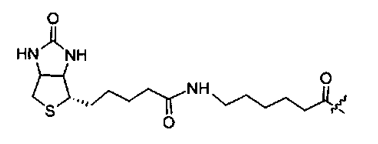
Biotin
Biotin has a very strong affinity for streptavidin and avidin, so the biotinylation of peptides is an effective method for specifically binding peptides to streptavidin-coated surfaces.
Peptide biotinylation can be performed at the N-terminus or C-terminus. Biotin is directly coupled to the N-terminal primary amino group. Biotin-labeled peptides are commonly used in immunoassays, histocytochemistry, and fluorescence-based flow cytometry.
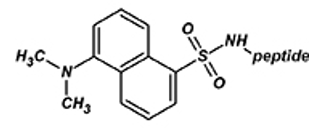
Dansyl (5-(Dimethylamino) naphthalene-1-sulfonyl)
Dansyl labeled peptides are used in fluorescence-based assays. The excitation/emission wavelengths are about 342 nm/562 nm.
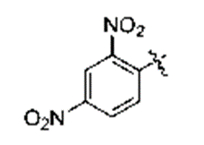
DNP (2, 4-Dinitrophenyl)
DNP can be used as a quencher for MCA sometimes tryptophan. This modification can be attached to the N-terminus of the peptide, or it can be used as an internal modification via the lysine side chain. its excitation wavelength is 354-400 nm.
Fatty Acid
Fatty acids bind to peptides at their N-terminus, increase their cell permeability, and help peptides bind to cell membranes. Peptide fatty acid modifications include caprylic acid (C8), capric acid (C10), lauric acid (C12), myristic acid (C14), palmitic acid (C16) or stearic acid (C18), etc.
Hashizume et al. modified the side chain of insulin molecule with palmitic acid, and the lipophilicity of palmitoyl insulin was improved. The researchers labeled insulin with isotopes and inferred the content of insulin in plasma by measuring the radioactivity in plasma within 6 hours after administration. The results showed that the content of dipalmitoyl insulin was 6 times as high as that of natural insulin, and that of monopalmitoyl insulin was 3 times as high as that of natural insulin.
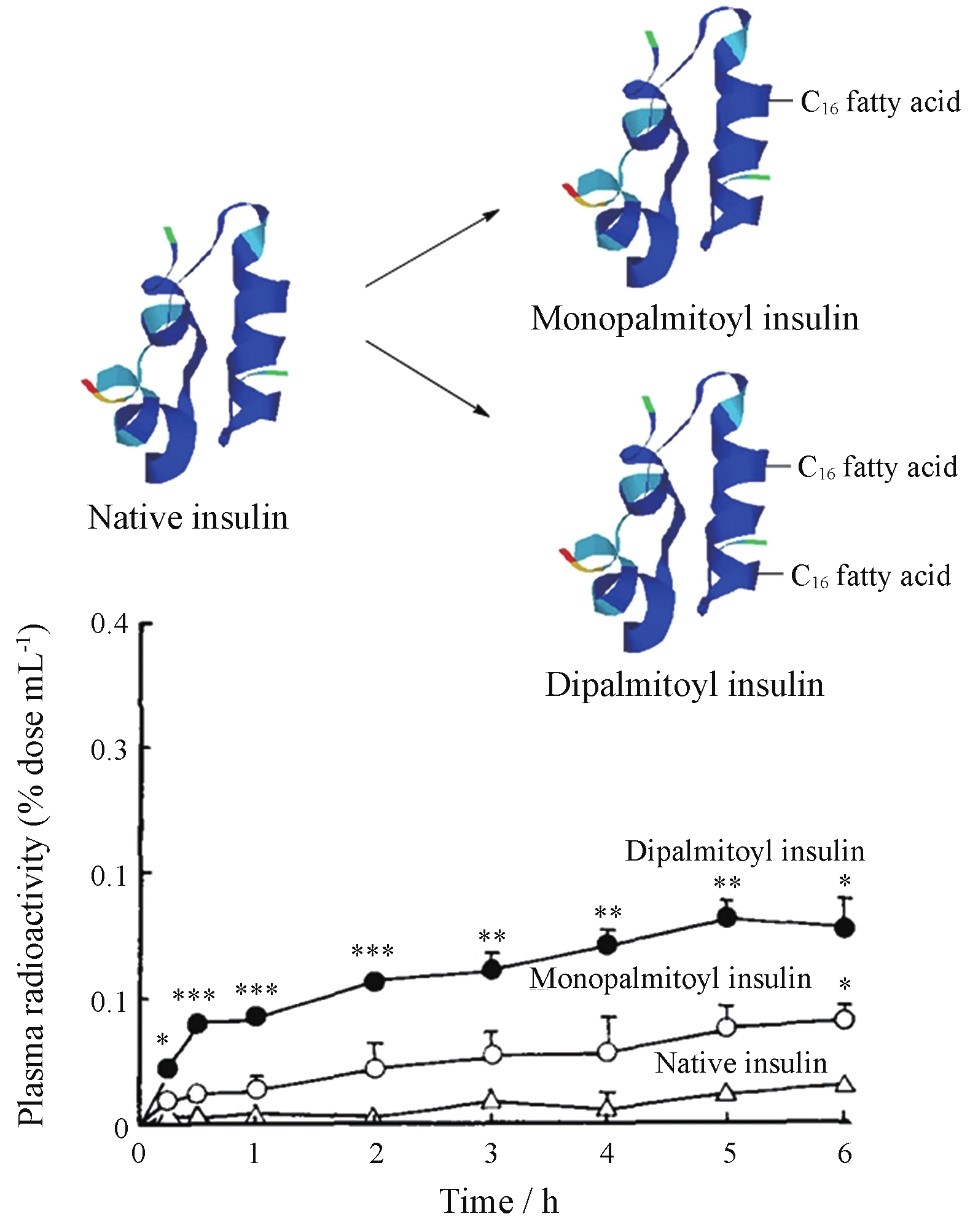 Fig. 1 Introduction of fatty acid to improve the permeability of insulin. Figure derived from Hashizume M, et al. (Peng, J. J., 2020)
Fig. 1 Introduction of fatty acid to improve the permeability of insulin. Figure derived from Hashizume M, et al. (Peng, J. J., 2020)
FITC (Fluoresceinisothiocyanate)
During peptide synthesis, the peptide can be directly conjugated to the fluorophore at the N-terminus (FITC always passes through the aminocaproic acid (Ahx) linker). For effective N-terminal labeling, a seven-atom aminohexanoyl spacer (NH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-COOH) is inserted between the fluorophore (fluorescein) and the N-terminal of the peptide. The excitation/emission wavelengths are about 490 nm/520 nm.
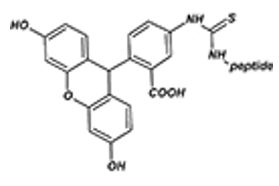
KLH, BSA
After peptide synthesis, the peptide can be coupled to two carrier proteins, KLH or BSA. The carrier protein can be conjugated to the N- or C-terminal of the peptide through the inserted N- or C-terminal cysteine. KLH or BSA-coupled peptides are mainly used for immunization and can significantly increase the cell-mediated immune response.
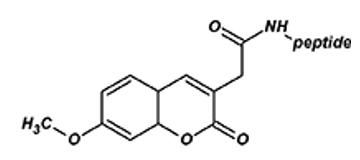
MCA (7-Methoxycoumarinyl-4-acetyl)
7-Methoxycoumarin labeled peptides in protein-protein interaction and application localization. The excitation/emission wavelengths are about 325 nm/392 nm.
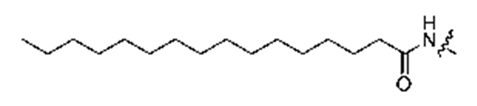
Palmytoyl
The cysteine in the peptide can be palmitoylated, thereby increasing its cell permeability and helping the peptide bind to the cell membrane.
Creative Peptides is specialized in the custom synthesis of N-terminal modification peptides, providing a confidential and efficient service at competitive prices. Every step of peptide synthesis is subject to Creative Peptides' stringent quality control.
Specialized experience: With years of expertise in the field of biomedicine, our company holds substantial understanding of the peptide N-terminal modification. Our dedicated team of experienced scientists and technologists ensure high-quality service.
Advanced technology: Our company utilizes state-of-the-art technology to provide peptide N-terminal modification services. This leading edge technology enables us to offer fast, accurate and reliable results.
Customization: We can tailor our services to match the specific needs of our clients. Our flexible approach and client-centric philosophy allow us to create specialized solutions for each project.
Quality assurance: We adhere to strict quality control standards and procedures to guarantee the accuracy and reliability of our services. Each modification is carefully monitored to ensure optimal results.
Strong research and development (R&D): Our comprehensive R&D capabilities allow us to stay up-to-date with the latest developments in peptide N-terminal modification, hence, we are always on the forefront of innovation in this field.
Customer support: We provide comprehensive customer support throughout the entire process, from initial consultation to the delivery of the final product. Our highly responsive customer service team is available to answer any queries and resolve any issues that may arise.
Competitive pricing: Despite offering top-notch peptide N-terminal modification services, our pricing remains highly competitive, providing excellent value for our clients.
Confidentiality: We fully understand the sensitive nature of the work we handle. Therefore, we take all necessary steps to ensure your data and intellectual property are kept strictly confidential.
Every step of peptide synthesis is subject to Creative Peptides' stringent quality control. Typical delivery specifications include:
We provide a wide range of modifications like acetylation, formylation, biotinylation, myristylation, addition of fluorophores and many others. Our team is able to customize the modification based on your requirements also.
Modifying the N-Terminal can change the characteristics of the peptide, but we use advanced computational design to predict and control these effects to ensure the activity of the peptide remains as desired.
N-terminal modification can increase the stability of peptides by preventing them from enzymatic degradation, thus, prolonging their biological activity. It can also help in increasing resistance to physical and chemical degradation.
The turnaround time may vary depending on the complexity and volume of the project. On average it takes us between 2-4 weeks. Our team will provide a more accurate timeline once we understand your specific project requirements.
The cost for peptide N-Terminal Modification service varies depending on the complexity and quantity of the peptides needed. Please contact our customer service team for a specific quote tailored to your project.
We have strict quality control procedures in place. Each modified peptide is subjected to rigorous testing including mass spectrometry and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to confirm its purity, composition and stability.
Absolutely, we provide full technical support and consultation regarding your peptide design, selection of the best modification strategy, and troubleshooting any issues that might arise during the process.

References