Peptide nucleic acid (PNA) is an artificial oligonucleotide mimetic with a peptidic backbone in lieu of a phosphoribosyl backbone. As such, it combines the properties of both peptides and nucleic acids. Remarkably, it forms more stable duplexes with DNA or RNA than either of the DNA or RNA homoduplexes and is metabolically stable. These advantageous features instigated tremendous interest in PNAs as antisense and antigene agents. However, unmodified PNAs have poor cellular permeability.
Despite the advantageous features of classic PNA, its low water solubility, poor cellular uptake, propensity to self-aggregate, and orientational ambiguity in recognizing nucleic acid targets, limits the effectiveness of PNA in its applications. Furthermore, high salt concentrations encountered in the cellular environments increase the stability of the DNA/DNA duplexes, making it challenging for PNA to invade duplex DNA under physiological conditions. However, these issues can be overcome by the chemical flexibility of PNA that allows for the insertion of modifications on its backbone and nucleobases.
Recently PNAs, because of their excellent affinity to DNA/RNA and the scope to be modified as per the application, have attracted a wide range of researchers for the development of new PNA molecules by a simple backbone or nucleobase modifications.
A randomly folded peptide nucleic acid has been transformed into a right-handed helix by simple modification at the γ-position of the backbone. The conformationally preorganized helical PNA has an excellent affinity and high sequence selectivity to bind the DNA and RNA.
Because of its antigene, antisense, anti-miR, and the scope to be labeled with various fluorophores, PNA finds application in gene expression modulation in-vivo, and development of nucleic acid-based biosensors which are useful in biotechnology researches and clinical diagnostics.
It is also used as tools for genome mapping, hybridization technologies in genetic detection, FISH technology, PCR analysis, and many more.
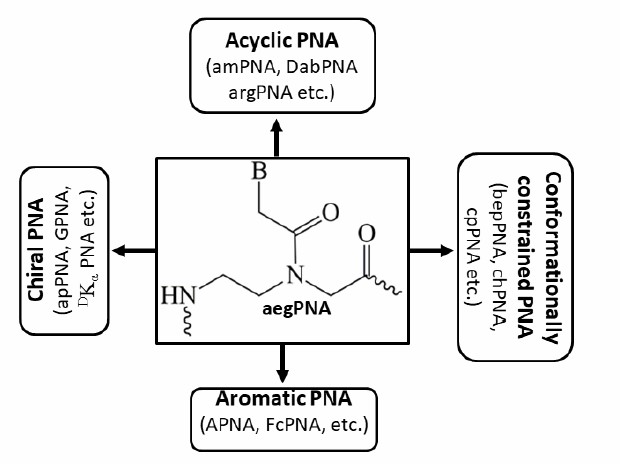 Examples of various strategies for backbone modifications of PNA (Das A, et at. 2021)
Examples of various strategies for backbone modifications of PNA (Das A, et at. 2021)
Acyclic Backbone modifications: Aminoethyl glycine PNA; N-(3-aminopropyl)glycine PNA; N-(2-aminoethyl)-β-alanine PNA; Arginine- derived PNA; Aminopropyldimethyl glycyl PNA; Aminopropyl glycinyl PNA; Amino methylene PNA; Diaminobutyryl PNA; Guanidine- based PNA; D- Lysine α- PNA; (R)- MiniPEG γ- PNA; L- Serine γ- PNA; Amino ethyl dimethyl glycyl PNA
Cyclic PNA Analogues: Amino ethyl prolyl PNA; Aminoethylpyrrolidinone PNA; Amino prolyl PNA; Aminoethyl glycine -Amino ethyl pipecolyl PNA; 2- Amino cyclobutane carboxylic PNA; Amino cyclopentane carboxylic PNA; Aminomethyl thiazolidine PNA; Backbone extended pyrrolidine PNA; Cyclohexyl PNA; Cyclopentyl PNA; 1- Amino pyrrolidine carboxylic acid PNA; Prolyl glycyl PNA; Pipecolyl PNA; Pyrrolidine PNA; 2- Amino cyclohexane carboxylic PNA; Aromatic PNA; Ferrocene labeled PNA
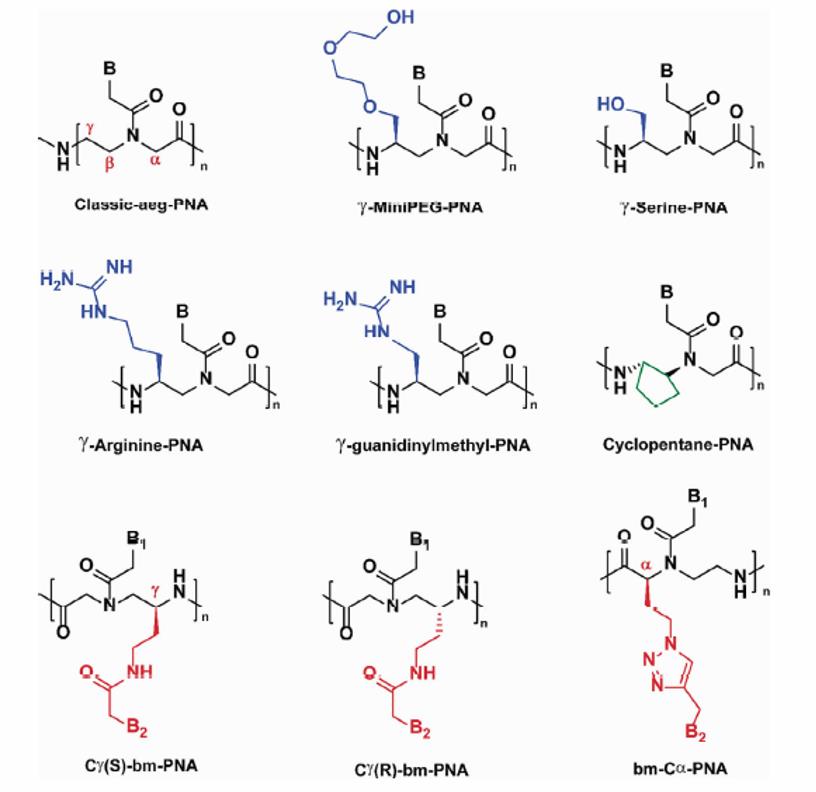 Backbone modifications of PNA (B = nucleobase) (Perera JDR, et al. 2021)
Backbone modifications of PNA (B = nucleobase) (Perera JDR, et al. 2021)
| Modification | Name |
|---|---|
| Acyclic Backbone | Aminoethyl glycine PNA |
| N-(3-aminopropyl)glycine PNA | |
| N-(2-aminoethyl)-β-alanine PNA | |
| Arginine- derived PNA | |
| Aminopropyldimethyl glycyl PNA | |
| Aminopropyl glycinyl PNA | |
| Amino methylene PNA | |
| Diaminobutyryl PNA | |
| Guanidine- based PNA | |
| D- Lysine α- PNA | |
| (R)- MiniPEG γ- PNA | |
| L- Serine γ- PNA | |
| Amino ethyl dimethyl glycyl PNA | |
| Cyclic PNA Analogues | Amino ethyl prolyl PNA |
| Aminoethylpyrrolidinone PNA | |
| Amino prolyl PNA | |
| Aminoethyl glycine -Amino ethyl pipecolyl PNA | |
| 2- Amino cyclobutane carboxylic PNA | |
| Amino cyclopentane carboxylic PNA | |
| Aminomethyl thiazolidine PNA | |
| Backbone extended pyrrolidine PNA | |
| Cyclohexyl PNA | |
| Cyclopentyl PNA | |
| 1- Amino pyrrolidine carboxylic acid PNA | |
| Prolyl glycyl PNA | |
| Pipecolyl PNA | |
| Pyrrolidine PNA | |
| 2- Amino cyclohexane carboxylic PNA | |
| Aromatic PNA | Aromatic PNA |
| Ferrocene labeled PNA |
Backbone modified PNA is a peptide nucleic acid with chemical modifications on its backbone to improve binding affinity, sequence specificity, and cellular uptake. These modifications enhance its interaction with DNA or RNA and its applicability in research.
Unmodified PNAs have poor solubility, low cellular uptake, and can self-aggregate. Backbone modification overcomes these limitations, improving duplex formation, strand invasion, and experimental efficiency.
Backbone modifications include acyclic, cyclic, chiral, extended, aromatic, and ferrocene-labeled PNAs, each offering unique structural and binding properties for nucleic acid recognition.
PNAs can be conjugated with cell-penetrating peptides, cationic amino acids, or Lys/Arg stretches, which promote entry into cells and improve access to DNA, RNA, or miRNA targets.
They are widely used in antigene, antisense, and anti-miR studies, nucleic acid-based biosensors, gene expression modulation, and hybridization technologies like FISH and PCR.
Modifications at α-, β-, or γ-positions can preorganize PNAs into helical conformations, enhancing DNA/RNA affinity and sequence selectivity while reducing structural ambiguity.

References