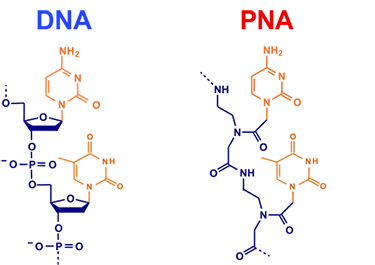
PNAs, or peptide nucleic acids, is an analogue of oligonucleotide in which sugar-phosphate backbone has been replaced by a polyamide chain. Due to the unique backbone of PNA, it can be used in same applications as conventional DNA/RNA. Comparing with DNA, PNAs are neutral in charge, chemically more stable and resistant to DNases and proteases, as well as remaining high sequence specificity, binding activity and lower salt sensitivity. PNAs have been widely used in molecular diagnostics and therapeutics, such as fluorescent in situ hybridization (Fish), single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) detection and antisense therapy.
Creative Peptides can provide a number of PNA related products, such as Gamma PNA or Fmoc/Boc PNA Monomers etc.
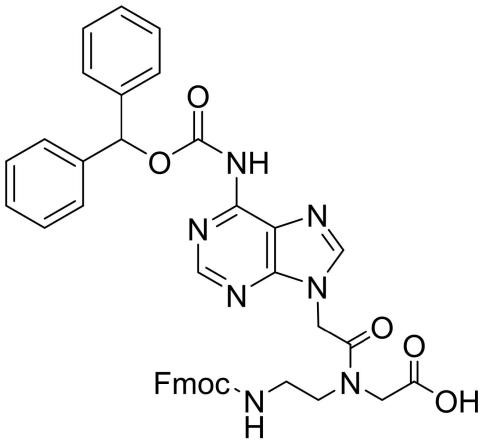
Fmoc-PNA-A(Bhoc)-OH
CAS: 186046-82-2
Chemical Formula: C40H35N7O7
Molecular Weight: 725.76
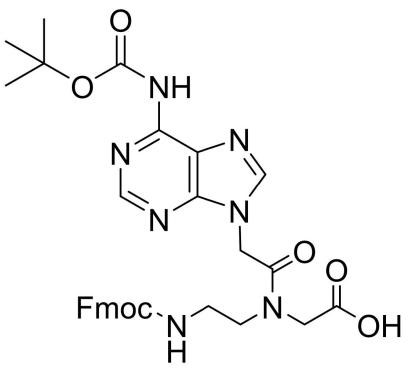
Fmoc-PNA-A(Boc)-OH
CAS: 511534-99-9
Chemical Formula: C31H33N7O7
Molecular Weight: 615.65
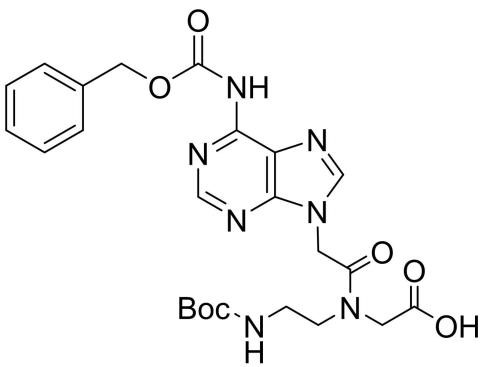
Boc-PNA-A(Z)-OH
CAS: 149376-69-2
Chemical Formula: C24H29N7O7
Molecular Weight: 527.54’
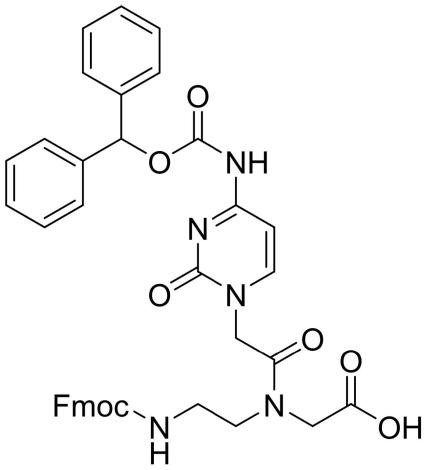
Fmoc-PNA-C(Bhoc)-OH
CAS: 186046-81-1
Chemical Formula: C39H35N5O8
Molecular Weight: 701.74
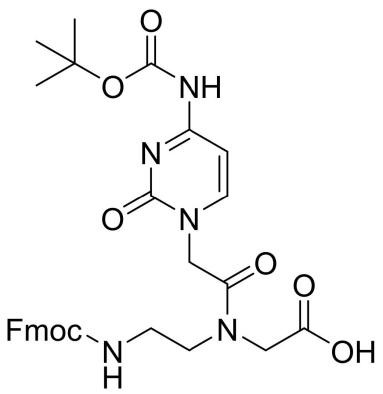
Fmoc-PNA-C(Boc)-OH
CAS: 172405-61-7
Chemical Formula: C30H33N5O8
Molecular Weight: 591.62
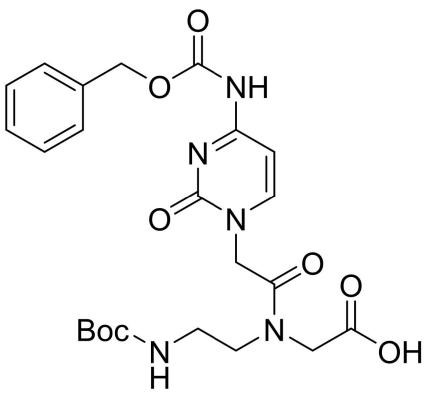
Boc-PNA-C(Z)-OH
CAS: 144564-94-3
Chemical Formula: C23H29N5O8
Molecular Weight: 503.51
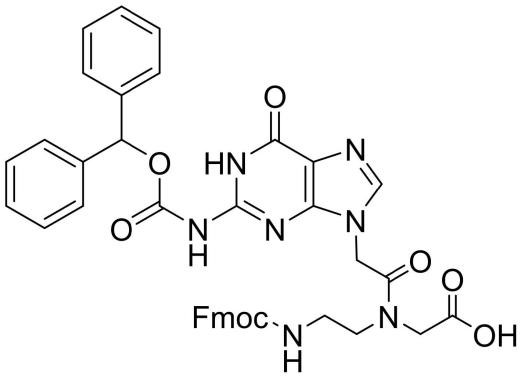
Fmoc-PNA-G(Bhoc)-OH
CAS: 186046-83-3
Chemical Formula: C40H35N7O8
Molecular Weight: 741.76
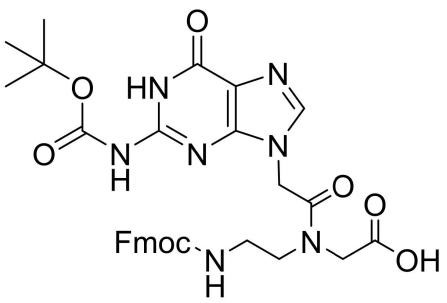
Fmoc-PNA-G(Boc)-OH
CAS: 1052677-90-3
Chemical Formula: C31H33N7O8
Molecular Weight: 631.65
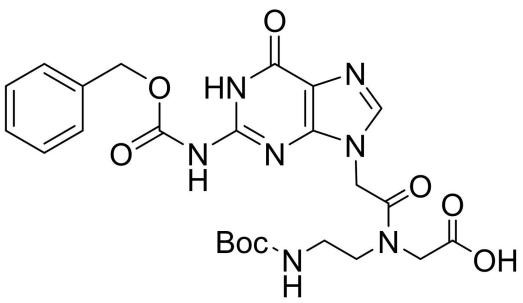
Boc-PNA-G(Z)-OH
CAS: 169287-77-8
Chemical Formula: C24H29N7O8
Molecular Weight: 543.54
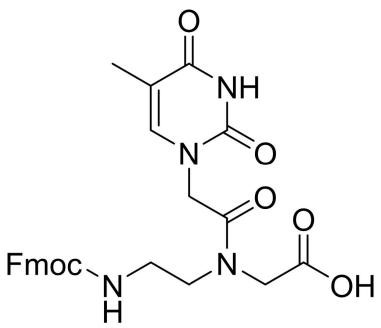
Fmoc-PNA-T-OH
CAS: 169396-92-3
Chemical Formula: C26H26N4O7
Molecular Weight: 506.52
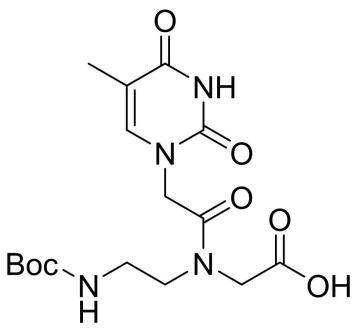
Boc-PNA-T-OH
CAS: 139166-80-6
Chemical Formula: C16H24N4O7
Molecular Weight: 384.39
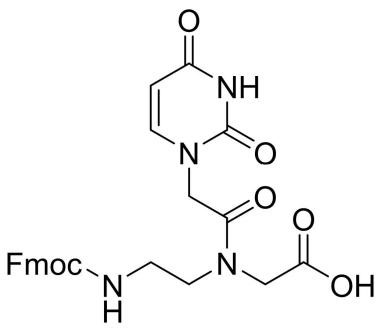
Fmoc-PNA-U-OH
CAS: 959151-70-3
Chemical Formula: C25H24N4O7
Molecular Weight: 492.49
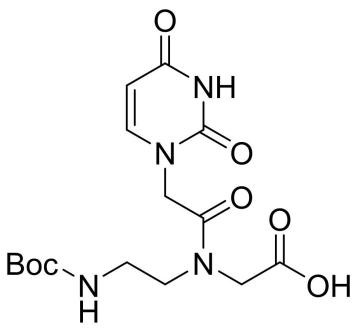
Boc-PNA-U-OH
CAS: 149500-74-3
Chemical Formula: C15H22N4O7
Molecular Weight: 370.36
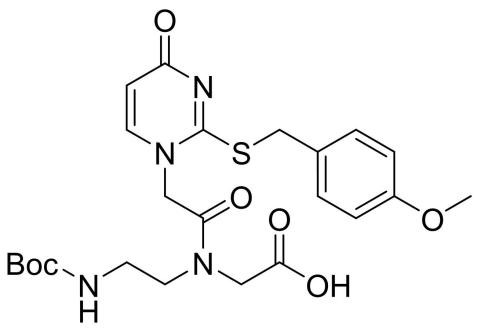
Boc-PNA-thioU(PMB)-OH
CAS: 253438-99-2
Chemical Formula: C23H30N4O7S
Molecular Weight: 506.57
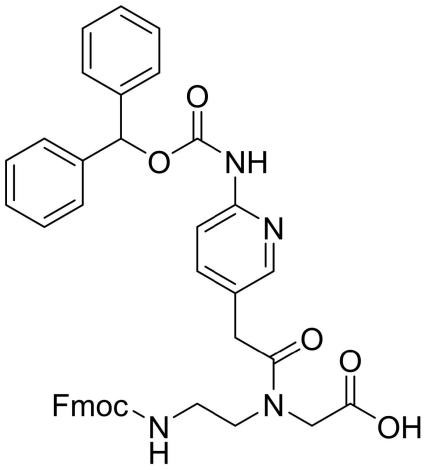
Fmoc-PNA-M(Bhoc)-OH
CAS: NA
Chemical Formula: C40H36N4O7
Molecular Weight: 684.75
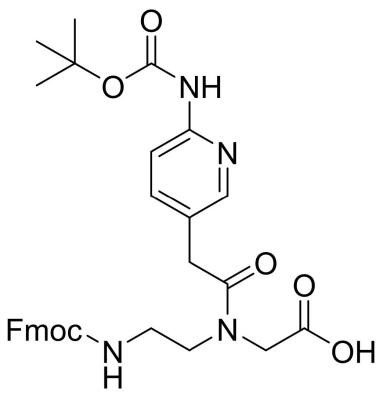
Fmoc-PNA-M(Boc)-OH
CAS: 1417611-27-8
Chemical Formula: C31H34N4O7
Molecular Weight: 574.63
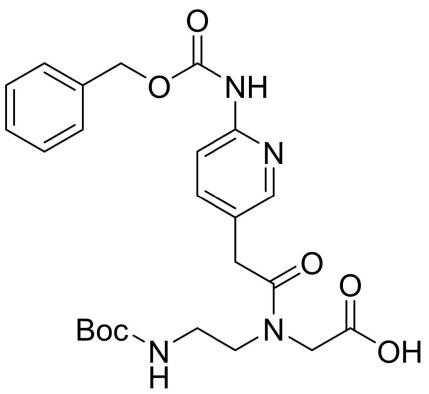
Boc-PNA-M(Z)-OH
CAS: NA
Chemical Formula: C24H30N4O7
Molecular Weight: 486.53
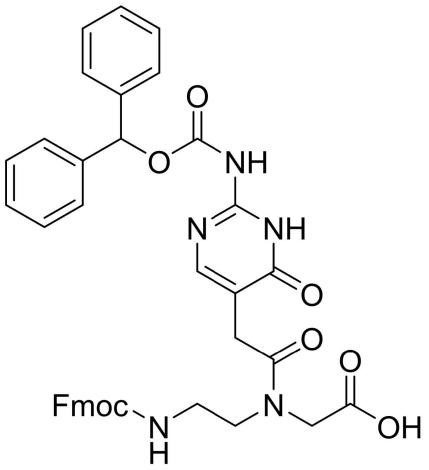
Fmoc-PNA-J(Bhoc)-OH
CAS: NA
Chemical Formula: C39H35N5O8
Molecular Weight: 701.74
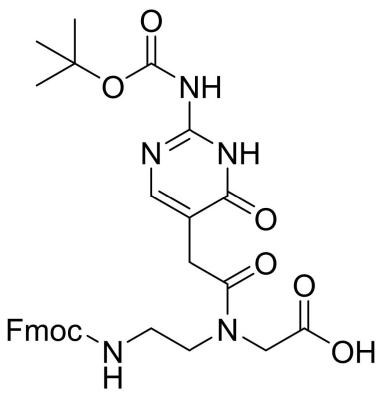
Fmoc-PNA-J(Boc)-OH
CAS: 1095275-70-9
Chemical Formula: C30H33N5O8
Molecular Weight: 591.62
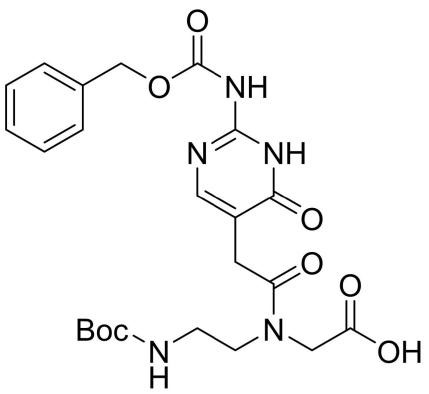
Boc-PNA-J(Z)-OH
CAS: 163081-03-6
Chemical Formula: C23H29N5O8
Molecular Weight: 503.51
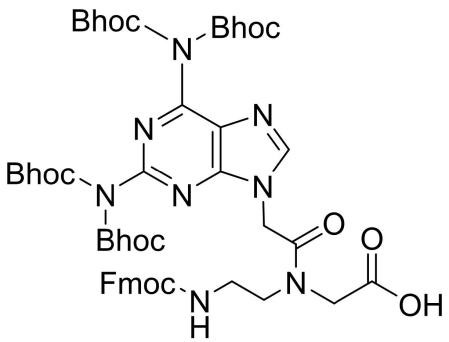
Fmoc-PNA-D(tetraBhoc)-OH
CAS: NA
Chemical Formula: C82H66N8O13
Molecular Weight: 1371.47
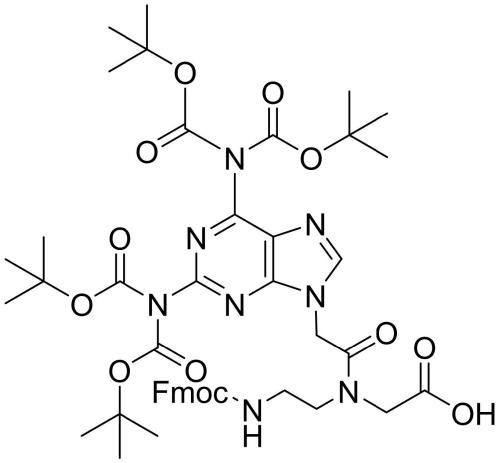
Fmoc-PNA-D(tetraBoc)-OH
CAS: 2101661-88-3
Chemical Formula: C46H58N8O13
Molecular Weight: 931.01
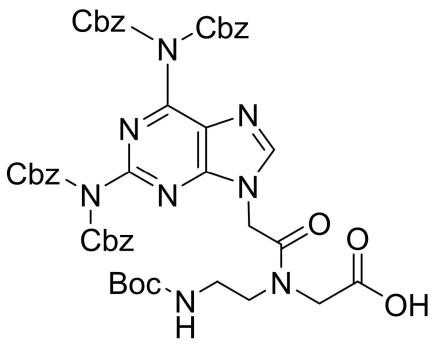
Boc-PNA-D(tetraZ)-OH
CAS: NA
Chemical Formula: C48H48N8O13
Molecular Weight: 944.96
PNAs are synthetic analogs of oligonucleotides where the sugar-phosphate backbone is replaced by a polyamide chain. Unlike DNA or RNA, PNAs are neutral in charge, more chemically stable, and resistant to nucleases and proteases. They exhibit higher sequence specificity and binding activity, making them ideal for various molecular applications.
PNAs have superior binding affinity and specificity to DNA and RNA compared to conventional oligonucleotides. They are more stable, less sensitive to salt concentrations, and resistant to nucleases, making them excellent for applications like antisense therapy, diagnostics, and microarrays.
PNAs are widely used in molecular diagnostics, including applications like PNA-FISH (fluorescent in situ hybridization) probes, PCR blockers, miRNA inhibitors, and antisense therapy. They are also useful in detecting genetically modified organisms and in the development of PNA arrays for high-throughput screening.
PNA-FISH uses PNA probes conjugated with fluorescent dyes to detect DNA or RNA sequences. Due to PNA's high specificity, shorter probes can be used, resulting in less background noise and quicker hybridization, even under low-salt conditions, compared to traditional DNA probes.
PNAs bind more strongly to complementary RNA sequences than DNA or RNA, making them highly effective miRNA inhibitors. When conjugated with cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs), PNA miRNA inhibitors can enter cells without the need for transfection reagents, providing a powerful tool for gene regulation studies.
PNAs can bind to complementary mRNA sequences, preventing gene expression by forming PNA/DNA triplexes or double duplexes. This ability to block transcription and translation of target genes makes PNAs a valuable tool in gene silencing therapies and research.
PNAs can inhibit PCR amplification by binding directly to one of the PCR primer sites, preventing the elongation of primers during PCR reactions. This method, known as PNA-directed PCR clamping, is particularly effective in detecting single base pair mutations by outcompeting the conventional PCR primers.
Creative Peptides offers a wide range of PNA synthesis services, including automated solid-phase synthesis, custom PNA scales from 5 mg to multi-grams, specialized modifications, PNA-peptide and PNA-protein conjugations, and PNA arrays. We also provide high-quality purification with HPLC and mass spectrometry analysis.
