Cardiovascular disease (CVD) refers to diseases related to the heart or blood vessels, also known as circulatory system diseases, circulatory system diseases. Common cardiovascular diseases include coronary artery syndrome, stroke, hypertensive heart disease, rheumatic heart disease, aneurysm, cardiomyopathy, atrial fibrillation, congenital heart disease, endocarditis, and peripheral artery obstructive disease. The pathogenesis of different diseases is different. Ischemic heart disease, stroke and peripheral artery occlusion are all associated with atherosclerotic atherosclerosis. It may be caused by high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, hyperlipidemia, poor eating habits and excessive drinking. Among the deaths caused by cardiovascular diseases, 13% were caused by hypertension, 9% by smoking, 6% by diabetes, 6% by lack of exercise and 5% by obesity. Other possible factors include rheumatic heart disease, which is caused by a lack of proper treatment after streptococcal infection of the throat.
Inflammatory conditions up-regulate the production of vascular adhesion molecule-1 on the surface of vascular endothelial cells, attracting and binding leukocytes. Highly proliferating monocytes gather around endothelial cells, adhere to inflammatory leukocytes and secrete proinflammatory cytokines to promote chemotaxis in the intima. Once the monocytes fully infiltrate the intima, monocyte colony stimulating factor-1 (M-CSF-1) binds to MCP-1 to promote the differentiation of monocytes into macrophages. At this point, macrophages show high expression of scavenger receptors, which are closely related to oxidized lipoprotein and integrate them into the cytoplasm. In vivo and in vitro, when macrophages devour lipoprotein, the accumulation of cholesterol ester stimulates the differentiation of macrophages into foam cells, indicating early atherosclerotic lesions.
In recent years, proteins and peptides with unique biological activity and metabolism have aroused great interest because of their strong ability to resist inflammatory cell reaction. At the same time, more and more attention has been paid to how bioactive peptides prevent and reduce the occurrence of CVD and the intracellular and intracellular interactions of inflammatory and bioactive peptides. Some studies have shown that regulatory pathways of CVD potentially modulated by dietary proteins and peptides. In addition, further studies have shown that RGD peptides regulate a variety of inflammatory pathways in macrophages. CVD risk factors stimulate the release of integrin ligand activators and initiate inflammatory cascade through MAPK/NF-kB-dependent pathways.
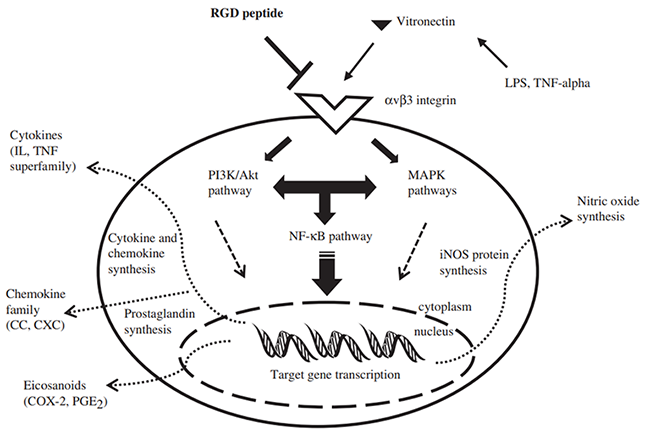
At present, more and more attention has been paid to the development of peptide therapy. In the later stage, researchers should further explore the mechanism of ischemic activity in patients with cardiovascular disease, and how to induce ischemic activity through polypeptide drugs, so as to better treat cardiovascular disease.
References