The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) is an important regulatory mechanism for electrolyte levels, fluid balance, and blood pressure, and angiotensin I is a precursor hormone in this system. The angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), which is mainly found in the lungs, converts it from an inactive form of angiotensin to an active version called angiotensin II. Renin, an enzyme secreted by the kidneys and located in the juxtaglomerular cells of the afferent arterioles, is responsible for the synthesis of angiotensin I. Activation of the sympathetic nervous system, low sodium levels, and low blood pressure are among the variables that cause the release of renin. The liver continually secretes a protein called angiotensinogen into the bloodstream, and once released, renin acts on this protein. The enzyme renin breaks down the alpha-globulin angiotensinogen into the decapeptide angiotensin I, which consists of 10 amino acids. Lungs are the primary sites of ACE activity, which converts angiotensin I to the active form angiotensin II. However, other tissues, such as the brain, kidneys, and endothelium, also participate in this process, albeit to a lesser degree.
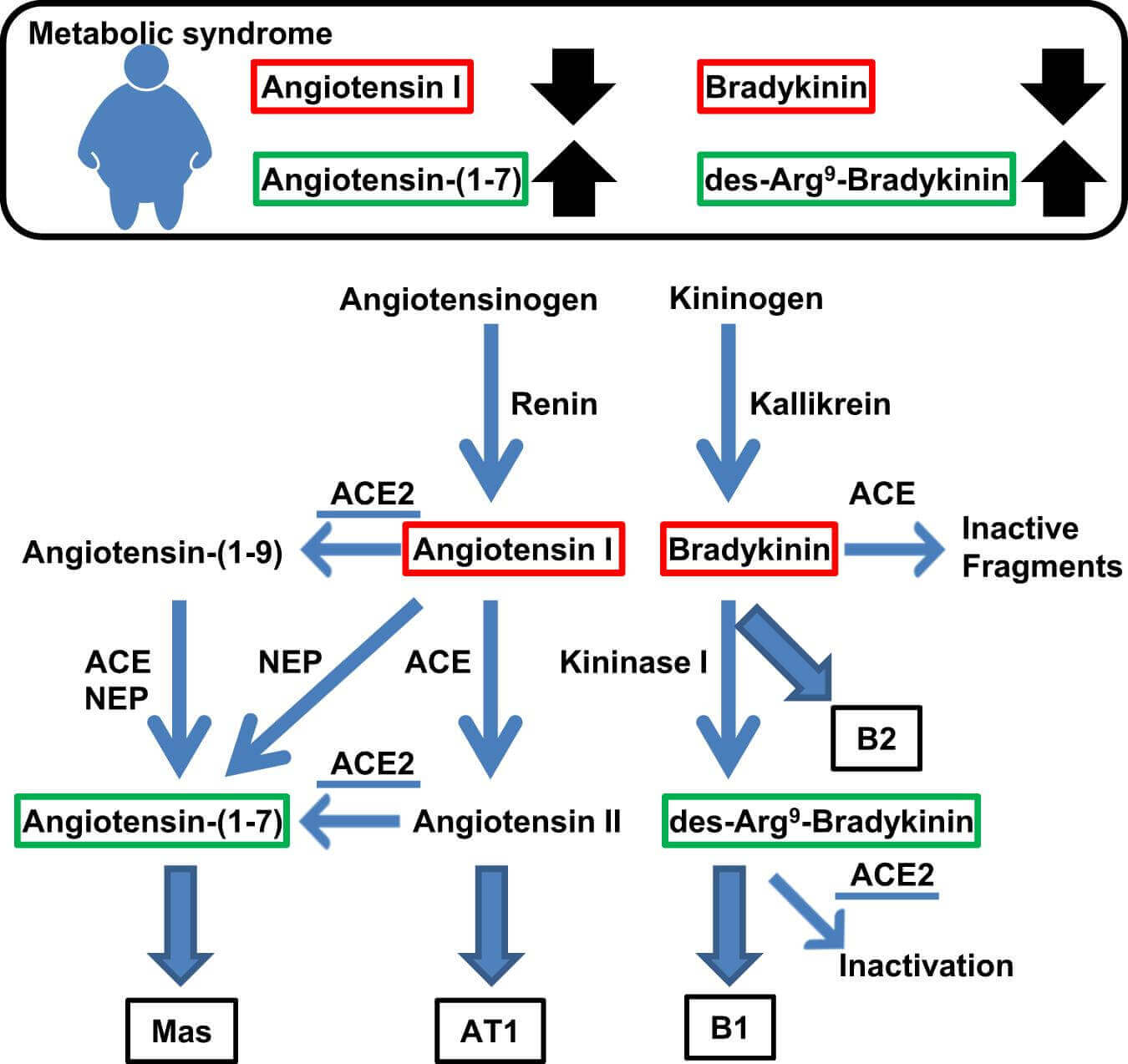
Possible biomarkers for metabolic syndrome. (Sugawara A., et al., 2021)
Angiotensin II is an octapeptide resulting from ACE-mediated cleavage of angiotensin I. Angiotensin II is a short-lived molecule (half-life = 15 seconds), the actions of which are mediated through membrane receptors. Angiotensin II regulates blood pressure and fluid and electrolyte homeostasis through various actions. Most notably, angiotensin II is an extremely potent vasoconstrictor; intravenous infusion results in a pressor response within 15 seconds that lasts for 3 to 5 minutes. Several peptidases rapidly degrade angiotensin II into several active and inactive metabolites. Although the fates and actions of these metabolites largely remain unknown, it has been shown that angiotensin (1-7) exerts regulatory effects on both vasculature and the kidney. In contrast to the vasoconstrictor and growth-promoting actions of angiotensin II, angiotensin (1-7) inhibits cell growth and causes diuresis and natriuresis.
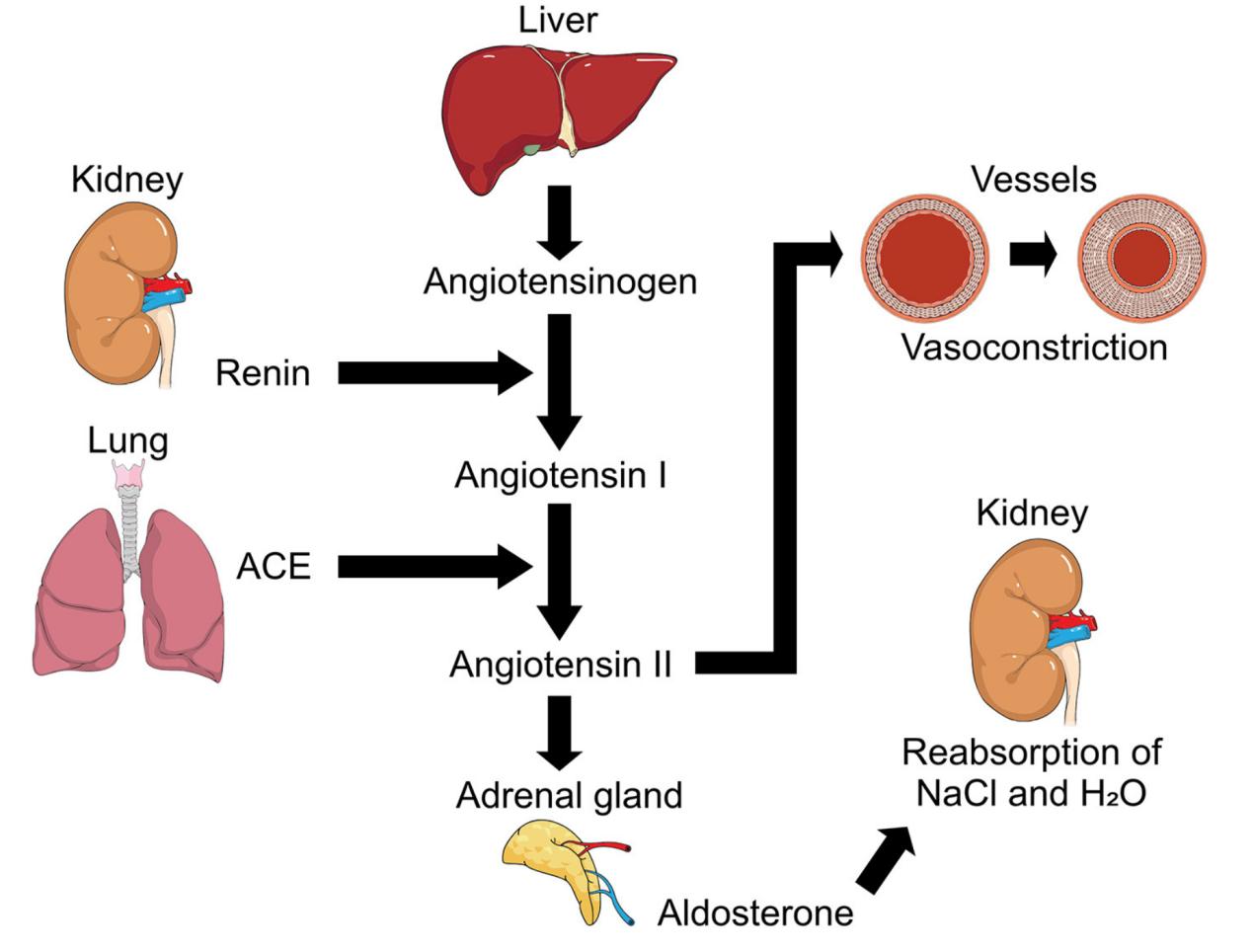
Representation of Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS). (Vargas-Rodriguez J R., et al., 2022)
In the RAS, the main distinction between Angiotensin I and Angiotensin II is their biological activity and function. The active form of angiotensin, Angiotensin II, has substantial physiological effects, particularly on the control of blood pressure and fluid balance, in contrast to the largely inert precursor, Angiotensin I. Arg-Val-Tyr-Ile-His-Pro-Phe-His-Leu is the sequence of the decapeptide Angiotensin I, which is 10 amino acids long; the octapeptide Angiotensin II, which is 8 amino acids long, has the following sequence: Asp-Arg-Val-Tyr-Ile-His-Pro-Phe. Neither blood pressure nor vascular tone are directly impacted by angiotensin I. Angiotensin II is produced when it binds to specific receptors on different tissues, such as those found in the brain, adrenal glands, blood vessels, and kidneys. This binding sets off a cascade of reactions, including vasoconstriction and fluid retention.
The complex, divergent, and multi-modal signaling pathway is enhanced when angiotensin II activates AT1R. Key signaling components required for angiotensin II -dependent physiological and pathophysiological pathways have, however, been identified by scientific research. Simply put, the interaction between AT1R and heterotrimeric G proteins, such as Gq/11, G12/13, and Gi, is triggered when angiotensin II binds to AT1R. Inositol trisphosphate, diacylglycerol, arachidonic acid, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) are later involved in second messenger signaling, which activates phospholipases C, A, and D, which are downstream effectors. Such components normally regulate contraction in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) via Gq/11 Ca2+-sensitive myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) activation and G12/13 Rho/Rho kinase-mediated inhibition of myosin light chain phosphatase (MLCP), but the reaction may vary depending on the tissue in which these signals are activated. Significantly, angiotensin II-mediated AT1R triggers the activation of a number of intracellular protein kinases, including as receptor and non-receptor tyrosine kinases, as well as serine/threonine kinases, such as Akt, PKC, and members of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family.
A novel phenomenon known as AT1R-dependent growth factor receptor transactivation has just been discovered. The transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is triggered by intermediary signals such as Ca2+, ROS, and the downstream activation of A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase (ADAM). The ADAM17 protein in cultured VSMCs is responsible for generating the ligands required for EGFR transactivation by cleaving heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF). Angiotensin II increases EGFR transactivation, which in turn activates Ras-GTP and the MARK/ERK and Akt/mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR)/p70 S6 kinase (p70S6K) cascades. This leads to increased protein synthesis, which in turn contributes to cell migration and hypertrophy. Despite claims to the contrary, ADAM17-mediated HB-EGF shedding by angiotensin II is dependent on Gq activation, even though Gq is not required for EGFR transactivation in some studies. Phosphorylation of ADAM17 at Tyr702 by an as-yet-unidentified tyrosine kinase in response to angiotensin II stimulation activates ADAM17 in VSMCs. Further, screening of siRNA libraries has revealed that BMX, CHKA, and TRIO are upstream signaling molecules necessary for angiotensin II-induced EGFR transactivation.
In VSMCs, angiotensin II is also recognized for transactivating the PDGFR and IGF-IR receptors, which are responsible for PDGF and insulin-like growth factor I, respectively. Responsibilities for vascular hypertrophy, fibrosis, and ERK activation have been attributed to PDGFR transactivation. It seems that activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and p70S6K, but not of ERK, requires the angiotensin II-induced IGF-IR transactivation. In response to angiotensin II, cytoskeletal rearrangement and Src kinase-mediated cortactin phosphorylation are both facilitated by IGF-IR transactivation. In VSMC, IGF-IR plays a mediating role in the creation of ROS by angiotensin II, which in turn activates p38MAPK and ERK5. In contrast to the EGFR, however, little is known about how angiotensin II -induced transactivation of PDGFR and IGF-IR contribute to the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease.
As a rule, it is thought that angiotensin II enhances ROS generation through the Nox family of proteins by raising both their expression and catalytic activity. To illustrate the point, it seems that in rat aortic VSMCs, angiotensin II increases superoxide via Nox1, which in turn increases H2O2 synthesis, whereas Nox4 keeps basal H2O2 production constant. Angiotensin II activates Nox1 in VSMC, and Ezrin-radixin-moesin (ERM) binding phosphoprotein 50 is a positive regulator of this process. Multiple Nox proteins and subunits have been upregulated by angiotensin II. In human aortic VSMC, the induction of Nox1, Nox4, p67phox, p47phox, and p22phox is dependent on AP-1 and c-Jun activation. Despite the fact that VSMCs cultured from Nox1-deficient animals showed no increase in angiotensin II -induced ROS production, the broad suppression of AT1R signaling in VSMCs, including the acute intracellular Ca2+ response, may be caused by Nox1 silencing. One possible explanation is that AT1R membrane expression is changed, leading to a decrease in caveolin 1 (Cav1) phosphorylation at Tyr14, which is dependent on H2O2. Thus, the physiological activity of angiotensin II is determined by the quantity of Nox1 in VSMCs. Nox1 abundance is maintained by G protein-coupled estrogen receptor activation. G protein-coupled estrogen receptor-deficient mice showed less angiotensin II-induced intracellular Ca2+ increase, superoxide generation, and hypertension.
The Wnt/β-catenin pathway might play a role in renal fibrosis and damage caused by angiotensin II. In immortalized podocytes of mice, angiotensin II triggers the expression of Wnt1, nuclear translocation of β-catenin, and transcription of the TCF reporter gene. Decreases in podocin and nephrin production indicate that angiotensin II-induced podocyte damage is reduced when the Wnt/β-catenin pathway is blocked by β-catenin siRNA or by overexpressing the endogenous Wnt inhibitor Dickkopf1. It seems that the induction of Wnt1 mRNA is mediated by Ca2+/calmodulin kinase II (CaMKII) and CREB. The results show that angiotensin II injures the kidneys by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, which leads to the nuclear buildup of β-catenin and the induction of Wnt1/3. Furthermore, the β-catenin destabilizing reagent pyrvinium pamoate attenuates the effects of angiotensin II on β-catenin protein, fibronectin mRNA, and collagen I mRNA in the M1 mouse collecting duct cell line. In addition, there is evidence that the Wnt/β-catenin pathway plays a role in angiotensin II-dependent renal fibrosis in a rat model of renovascular hypertension, as pyrvinium pamoate therapy improves kidney induction of β-catenin, collagen I, fibronectin, and osteopontin. The fact that the Wnt/β-catenin pathway affects numerous RAS genes is intriguing as well. The AGT, renin, ACE, AT1R, and AT2R promoters are thought to contain a conserved TCF/LEF binding site, according to bioinformatics. Following this, both in vitro and in vivo studies verified that the RAS components were upregulated in the kidney and proximal tubular cells when the Wnt/β-catenin pathway was specifically activated. This means that chronic kidney illness could be a result of several feed-forward mechanisms through the RAS component amplifying the Wnt/β-catenin pathway activation by angiotensin II in vivo.
In several cell types, angiotensin II has been demonstrated to improve autophagy through AT1R. An increase in autophagy is linked to angiotensin II-induced myocardial hypertrophy in neonatal rat cardiac myocytes infected with an adenovirus that encodes the AT1R. Adding AT2R-encoding adenovirus in combination with AT1R enhances angiotensin II-induced hypertrophy, but AT2R reduces the increase of autophagy. In the HL-1 cardiomyocyte cell line, autophagy is enhanced by angiotensin II at doses ranging from 10 to 100 nM, but apoptosis and a decrease in autophagy are observed at higher concentrations, indicating that autophagy may play a protective role. Beclin-1, autophagy protein 9A (Atg9A), and microtubule-associated protein light chain 3 (LC3) are proteins that are needed for autophagosome formation, and they are all induced during angiotensin II-enhanced autophagy. The angiotensin II-induced hypertrophic response in newborn cardiac myocytes of rats is reduced when beclin-1 or Atg9A are inhibited with siRNA. Downregulation of miR-30 and miR-34a is linked to the angiotensin II-enhanced autophagy and hypertrophic responses. MiR-30 seems to control the expression of beclin-1, whereas miR-34a controls the expression of Atg9A. Also, mitochondrial malfunction, ROS generation, and the subsequent induction of autophagy in cardiac myocytes are all outcomes of AT1R activation, which promotes Nox4 activation in the mitochondria. The angiotensin (1-7)/Mas receptor signaling axis can inhibit autophagy by lowering ROS, which is an important feature of angiotensin II-induced in vivo cardiac hypertrophy as evaluated by LC3b-II and p62. Corroborating these findings, angiotensin II-induced hypertrophy and enhanced autophagy in the heart are both augmented by the loss of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10. Similarly, in a swine model of renovascular hypertension, both ARBs and non-RAS antihypertensive agents reduce blood pressure in the same way. However, ARBs alone alleviate left ventricular hypertrophy, myocardial autophagy and mitophagy, and increased mitochondrial biogenesis, while the combination does not.
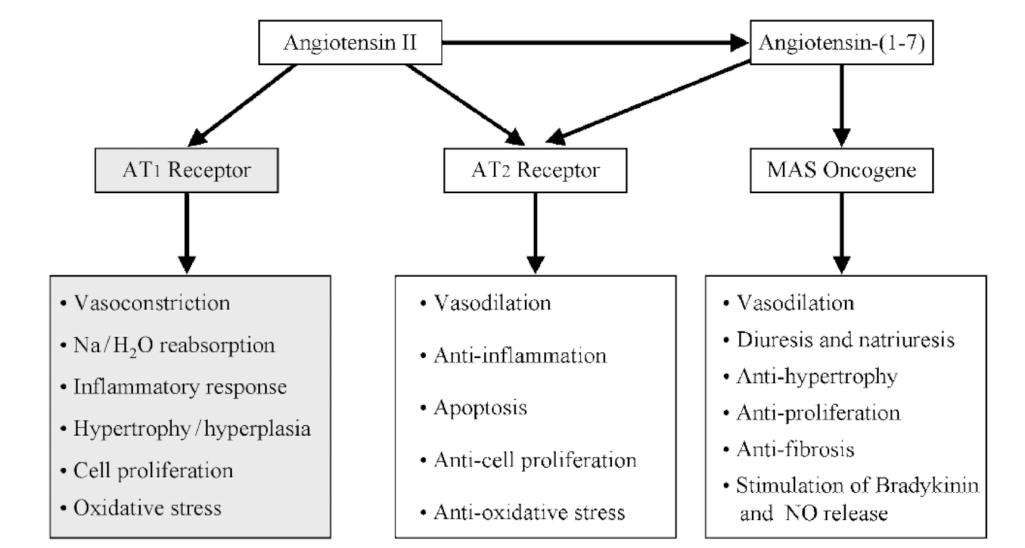
Action of Angiotensin II. (Iwai M., et al., 2009)
Among the several angiotensin peptides made by the RAS is angiotensin II. Like all peptides, angiotensin II has eight amino acids and, like all peptides, it has an N-terminus with a free amino group and a C-terminus with a free carboxyl group. One alternative notation for angiotensin II is Ang-(1-8), with the first amino acid located at the N-terminus and the eighth at the C-terminus. To produce smaller peptide fragments, the Angiotensin II molecule can have its amino acids severed at either end. Take Angiotensin II as an example; when its N-terminus amino acid is removed, a peptide called Angiotensin-(2-8) (formerly Ang III) is generated. This peptide consists of seven amino acids beginning with the second amino acid of Angiotensin II. Only three of the many possible Angiotensin II fragments have been shown to have any kind of physiological significance. Angiotensin-(1-7) (Ang-(1-7)) is one of three angiotensins; the other two, Angiotensin-(2-8) (Angiotensin III) and Angiotensin -(3-8) (Angiotensin IV), are both produced by cleavage at the N-terminus. When aminopeptidase A cleaves Angiotensin II's aspartate-arginine link, it forms Angiotensin III; when aminopeptidase B or N cleaves Angiotensin III further, it becomes Angiotensin IV. Having 40% of the pressor action and 100% of the aldosterone stimulating activity of Angiotensin II, Angiotensin III shares many of Angiotensin II's characteristics. In addition to acting in opposition to Angiotensin II and having effects on the central nervous system, Angiotensin IV has its own unique receptor (AT4). Much study has focused on Angiotensin -(1-7) since its biological activities are opposite to those of Angiotensin II, and it is produced by cleaving either Angiotensin II or Angiotensin I.

Amino acid sequences of the angiotensin family. (Gard P R., 2002)
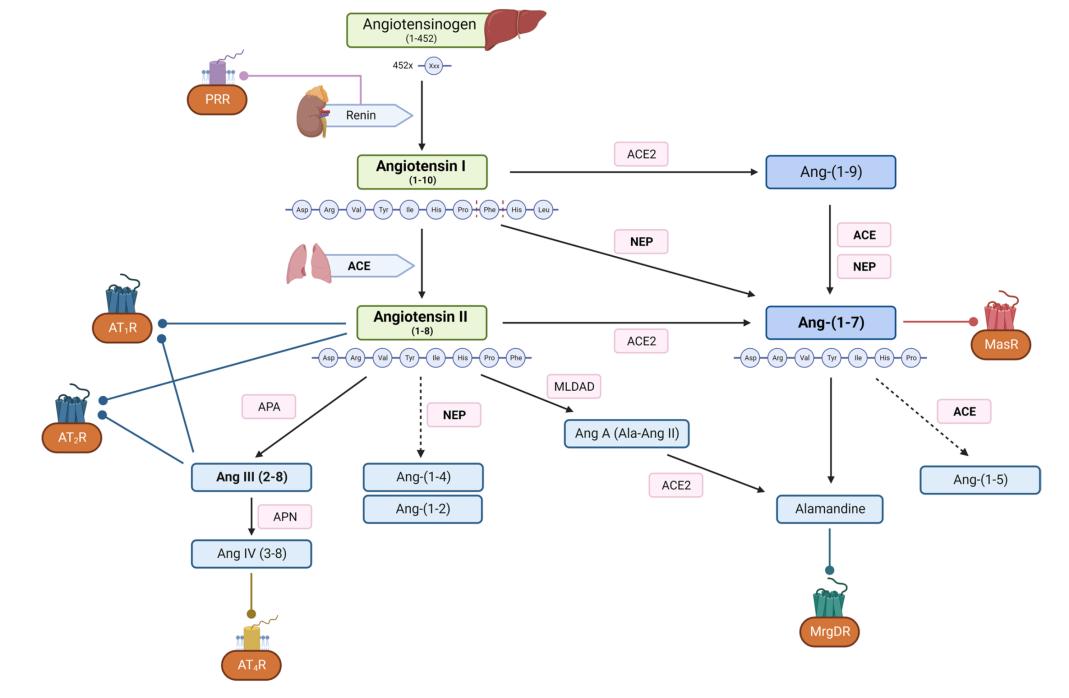
The proteolytic cascade of the RAAS. (Triebel H., et al., 2024)
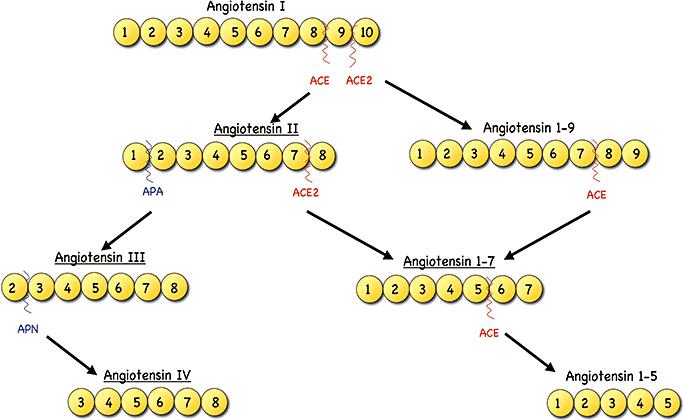
Peptide structure and fragments of angiotensin. (Lubel J S., et al., 2008)
Either Ang II can be directly converted to Ang-(1-7) by ACE2 or Ang-(1-9) can be converted to Ang-(1-7) by ACE cleaving an inactive intermediate fragment of Ang I. The kinetic favorability of the conversion of Ang II to Ang-(1-7) is 400 times higher than that of the conversion of Ang I to Ang-(1-9), the other ACE2 pathway. Research on Ang-(1-7) has mostly focused on animal models; thus far, this peptide has demonstrated anti-trophic effects in vascular endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, cardiac myocytes, and cardiac fibroblasts in addition to antihypertensive, anti-arrhythmic, and cardioprotective effects. In addition to its anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, and anti-thrombotic effects, Ang-(1-7) differs from Ang II in this regard. These investigations led to the hypothesis that Ang-(1-7) is the effector peptide of a regulatory arm of the RAS that can counteract the harmful effects of Ang II. While other receptors may exist, the G protein-coupled receptor encoded by the mas proto-oncogene14 is the putative receptor for Ang-(1-7) that has not been confirmed. An "alternative" RAS axis that may provide a counterbalance to the harmful ACE/Ang II/AT1 axis is thus represented by ACE2, Ang-(1-7) and the mas receptor. Being able to degrade Ang II and generate Ang-(1–7) at the same time places ACE2 in the center of the RAS that influences both axis.
Plasma levels of angiotensin(1-9) are elevated in rats and humans immediately following a myocardial infarction or in animals given an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. Rats with myocardial infarction who were given angiotensin-(1-9) via osmotic minipumps for a duration of two weeks showed a reduction in plasma angiotensin II levels, an inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme activity, and resistance to cardiac myocyte hypertrophy. Despite this, administering the angiotensin-(1-7) receptor antagonist A779 at the same time as the angiotensin-(1-9) reduced the attenuation of cardiac myocyte hypertrophy. In vitro studies with cultured cardiac myocytes that were exposed to norepinephrine (10 μmol/l) or insulin-like growth factor-1 (10 nmol/l) also demonstrated that angiotensin-1-9) inhibited hypertrophy. Rats with myocardial infarction were randomly assigned to receive 8 weeks of either the vehicle enalapril or the angiotensin II receptor blocker candesartan in another experimental environment. Both medications significantly elevated plasma angiotensin-(1-9) levels and inhibited left ventricular hypertrophy. Even after controlling for blood pressure lowering, there was a negative correlation between angiotensin-(1-9) levels and various left ventricular hypertrophy indicators.
In many rat models of hypertension, Ang(1-9) infusion using osmotic minipumps consistently lowers blood pressure. Additionally, end-organ damage caused by hypertension is reduced in these animals. Ang-(1-9) appears to be the endogenous ligand that activates the type-2 angiotensin II receptor (AT2R), according to multiple pieces of evidence. Att2R activation sets off distinct signaling pathways that are particular to certain tissues. One possible explanation for this observation is that AT2R can create various heterodimers with other G protein-coupled receptors. Due to the short half-life of RAS peptides and the antihypertensive and protective effects of AT2R activation by Ang-(1-9), numerous synthetic AT2R agonists have been developed and tested. Novokinin, CGP42112, and C21 are among those that have shown promise as antihypertensive agents. C21 and LP2-3, the only two synthetic AT2R agonists to far, have both failed to demonstrate antihypertensive effects in clinical trials. Ang-(1-9) is a potential antihypertensive medication since it lessens the harm that end-organs experience as a result of hypertension.
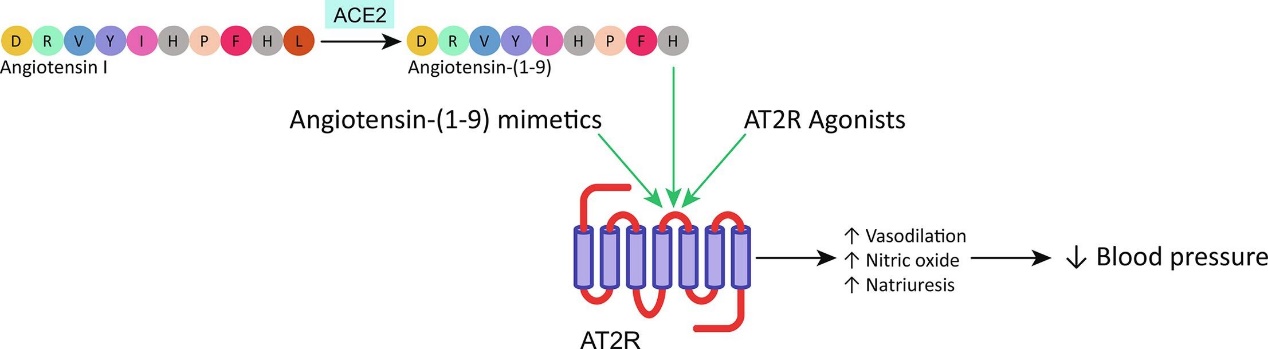
Angiotensin-(1–9) in hypertension. (Norambuena-Soto I., et al., 2022)
References