Peptides-Metal Chelates Conjugation is a kind of compound with cyclic structure which is formed by chelation reaction between peptide and metal ions. It has many special biological activities. It can improve the bioavailability of metal ions by means of the absorption mechanism of peptides in the body, and has physiological and biochemical characteristics that inorganic metal ions do not have. At present, the chelate prepared by chelating peptide (Fig1)with the essential trace element (Fe3+, Ca2+, Zn2+) has become a new metal ion supplement, offer an attractive approach for both imaging of cancer tissues and as therapies that deliver cytotoxic cargo to cancer cells, which has attracted more and more attention. Therefore, Peptides-Metal Chelates Conjugation not only has the activity of promoting the absorption of metal ions, but also may have high biological activities, such as antioxidant, antibacterial and so on, and has great R & D value.
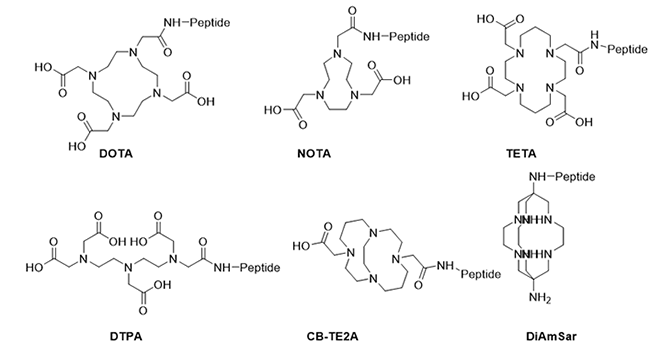 Fig1. Peptides conjugated to metal chelates
Fig1. Peptides conjugated to metal chelates
Molecular imaging has become an indispensable tool in modern diagnostics in biomedical research and therapeutic fields. Cancer cells that express or overexpress specific receptors has lead to the development of synthetic peptides that target these receptors. Peptides conjugated to metal chelates (e.g, DOTA, NOTA, etc.) offer an attractive approach for both imaging of cancer tissues and as therapies that deliver cytotoxic cargo to cancer cells.
Promoting metal ion absorption is one of the most important functions of Peptides-Metal Chelates Conjugation. In organism, the bioavailability of chelate iron is higher than that of inorganic iron. The reason is that the chelates in the form of carriers enable iron ions located at the center of the ring structure to pass smoothly through the brushing edge of the intestinal mucosa, thus promoting the absorption, transport and utilization of iron.
After chelating peptides from different sources with metal ions, the chelates obtained were higher than those of unchelated peptides in antioxidation, antimicrobial activity or other special biological activities, or the chelates obtained some biological activities which were not found in unchelated peptides. Since peptides, one of the raw materials of chelates, come from natural animal and plant proteins, there is almost no safety problem. Therefore, chelates as antioxidants or bacteriostatic agents have great advantages and prospects in food, cosmetics and other industries.
Creative Peptides has developed a reliable method for peptides-metal chelates conjugation. Creative Peptides has a large number of researchers who will tailor the most appropriate methods to suit your needs and 100% guaranteed service for customers. Besides, the all-round literature database has been set up, which provides the technical support for products. Our company guarantees peptides-every step of metal chelates conjugation synthesis is subject to strict quality control.
Peptides-metal chelates conjugation involves binding peptides to metal ions through chelation. This enhances peptide bioavailability and activity for applications in imaging and metal ion supplementation.
These conjugates help visualize cancer tissues by targeting specific receptors in cancer cells. Metal chelation improves stability and functionality for precise imaging.
Peptides-metal chelates enhance the absorption of essential trace metals like iron, zinc, and calcium. They facilitate metal transport and utilization in the body more efficiently than inorganic forms.
Yes, peptides-metal chelates exhibit improved antioxidant and antibacterial activities. These properties are useful in industries like food preservation and cosmetics.
Industries such as biomedical research, food, cosmetics, and agriculture benefit from these conjugates. They are used for metal supplementation, molecular imaging, and enhancing product efficacy.
We apply stringent quality control to every step of the conjugation process. Customers receive detailed synthesis reports, HPLC chromatograms, and mass spectrometry analysis for verification.

References