Lipidation is a post-translational modification of peptides and proteins. Some nonribosomally synthesized bacterial antibiotics and ghrelin are naturally-occurring lipidated peptides. Peptide lipidation is a process in which a peptide molecule is attached to a lipid molecule. This modification can occur naturally in living organisms or can be performed artificially in the laboratory.
Peptide drugs offer many desirable drug properties such as potent bioactivity, high receptor binding affinity and specificity, and relatively low toxicity. However, most peptides are quickly degraded in serum and exhibit rapid clearance in vivo. Many strategies have been employed in an attempt to overcome these apparent disadvantages including lipidation, glycosylation, cyclization, backbone modification, unnatural or D-amino acid conjugation and PEGylation. Among these chemical modification methods, lipidation has proven to be one of the most robust strategies for the generation of new therapeutic peptide.
Four lipidized peptide drugs are currently approved for use in humans: two long-acting anti-diabetics human glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogue liraglutide and insulin detemir, and two antibiotics daptomycin and polymixin B. A number of lipidated peptides, lipoproteins and lipidated peptide vaccines are at different phases of clinical trials. As indicated in Table 1, lipidation was extensively exploited in the drug developments.
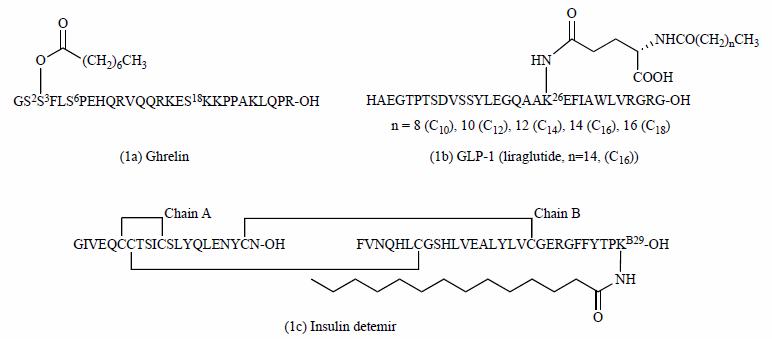 Structures of ghrelin, GLP-1 (liraglutide) and insulin detemir (Zhang L, et,al. 2012)
Structures of ghrelin, GLP-1 (liraglutide) and insulin detemir (Zhang L, et,al. 2012)
Table 1
| Type | Peptides |
| Fatty acid | Enkephalin, Galanin, GIP, GLP-1 (liraglutide), hPP, IGF1R JM inhibitor, Insulin; Leuteinizing hormone releasing hormone (LHRH), NPW, NPY, NT, RC-160, STAT3, Tetragastrin, Thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) |
| Amino fatty acid | Conotoxin SIIIA, Ghrelin, Liraglutide, Met-Enkephalin, TAN-1511A, Tenecin-1 |
| Acidic fatty acid (dicarboxylic acid) | Growth hormone-releasing hormone antagonists (GHRH) |
| Halo-fatty acid | Ghrelin |
| Lipoamino acid | Core peptide, Thymopentin TP5, Peptide A2, Polycationic lipophilic core dendron excipient |
| Alkyl ether (O-, S-) | Angiotensin |
| Alkyl amine | Compound 3 |
| Adamantylation | Ghrelin |
| Cholesterol | C34, Insulin |
Lipidation can be classified into three types based on lipid bond formation methods with peptide chain or side chains: amidation, esterification (S- or O-) and S-bond (ether or disulfide) formation. Amidation and O-esterification are strong and irreversible covalent bonds, whereas S-esterification and disulfide bond formation are weak and reversible covalent bonds.
Peptide lipidation is a chemical modification that covalently attaches a lipid moiety to a peptide chain. This modification alters physicochemical properties such as hydrophobicity and molecular interaction behavior.
Lipidation is used to improve peptide stability and enhance interaction with biological membranes. It also supports optimization of molecular distribution and functional performance in research systems.
Common lipidation sites include the N-terminus, lysine side chains, cysteine residues, and hydroxyl-containing amino acids. Site selection depends on peptide structure and functional requirements.
Peptide lipidation can involve amide, ester, thioester, or disulfide bond formation. These bond types differ in stability and reversibility under experimental conditions.
Lipidated peptides can form organized structures such as micelles, vesicles, or nanofibers through hydrophobic interactions. This property is useful for studying molecular aggregation and membrane-related behavior.
Peptide lipidation can be customized by selecting lipid chain length, attachment position, and linkage chemistry. This flexibility allows precise control over molecular properties and experimental performance.

References