Creative Peptides provides high-quality, customizable peptide C-terminal modification scheme to meet the diversified needs of medical research. We use advanced technology and complex analytical tools to ensure the accuracy, repeatability and high yield of peptide modification. These peptide modifications can be used to create synthetic peptide with the exact conformation of characteristics needed for specific applications.
The C-terminus and N-terminus are the ends of a peptide or protein molecule. The difference between them lies in their structure and the type of group that is present at each terminal.
N-Terminus: This is the start of a peptide or protein molecule where the amino group (-NH2) is free and is not attached to any other amino acid. It is referred to as the N-terminus because of the presence of this Nitrogen-containing group.
C-Terminus: This is the end of a peptide or protein where the carboxyl group (-COOH) is free and is not attached to the other part of the molecule. It is referred to as the C-terminus due to the presence of this Carbon-containing group.
These terms become important when speaking about the direction or orientation of a protein, as well as in the process of protein synthesis (which occurs from the N-terminus to the C-terminus).
Peptides are molecules that are made up of two or more amino acids. During their synthesis, these peptides often undergo various types of modifications at their C-terminus, or the end of the peptide chain that contains a carboxyl group. C-terminal modification of peptides has significant effects on their biological properties. The ability to selectively introduce functional groups, such as a fluorescent reporter or a synthetic polymer, onto a peptide under mild conditions would allow a broad array of peptide biophysical studies and applications. There are several types of C-terminal peptide modifications:
Amidation: This is a common modification where a carboxyl group at the C-terminus is converted into an amide. This modification improves the stability of the peptide and can increase its biological activity.
Prenylation: Addition of a prenyl group to a cysteine residue near the C-terminus.
GPI anchoring: The protein is linked to a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor, which can become attached at the C-terminus.
Glycosylation: Addition of sugar molecules to the C-terminus, this can help the protein to fold correctly or improve its stability.
Phosphorylation: Addition of phosphate groups, altering the charge and potentially the function of the protein.
Methylation: Addition of a methyl group, which can change the protein activity.
Acetylation: Addition of an acetyl group, commonly at the N-terminus but can also occur at the C-terminus.
Carboxylation: Addition of a carboxyl group, this can bind calcium ions and is found in blood clotting proteins.
Lipidation: Addition of lipid groups (like myristoyl or palmitoyl groups) at the C-terminus can serve to anchor proteins to membranes.
Ubiquitination: Attachment of ubiquitin, a small protein, to the C-terminus can mark the protein for degradation.
Conjugation: The C-terminus of the peptide can be conjugated to various groups or other peptides to improve stability, target specificity, or delivery. An example of this is the conjugation of a peptide to polyethylene glycol (PEG) to increase its stability and solubility.
The classical peptide structure is not stable to protease in vivo, and will be degraded soon after entering the body. In addition, most bioactive peptides have poor bioavailability and cannot be taken orally, so it is necessary to change the dosage form and then develop a suitable route of administration. C-terminal modified peptides can improve the properties of peptides, including improving the affinity and selectivity between peptides and receptors, enhancing the pharmacokinetic stability of peptide molecules, reducing the degradation or elimination of active peptides in vivo, improving the membrane permeability of active peptides and improving the water solubility of hydrophobic peptides.
C-terminal modification finds extensive applications in therapeutic peptide design, drug delivery, and medical research, among other areas.
With C-terminal modification, therapeutic peptides can be designed to resist the catalyzing action of enzymes in the body. This action improves the therapeutic peptide’s stability and lifespan within the body, enhancing the peptide drug's effectiveness.
Peptide C-terminal modification often plays a pivotal role in peptide drug delivery. The process can modify peptides to enable targeted drug delivery, improve drug absorption, or enhance other pharmacokinetic properties.
C-terminal modifications like biotinylation, fluorescent tagging or radiolabeling can be used for protein detection, protein-protein interaction studies and for tracking proteins in cells or organisms.
In medical research, C-terminal modification assists researchers in studying peptides' roles and understanding their behavior in different biological contexts. For instance, fluorescent labels can be added to peptide C-terminals to track peptide interactions by controlling the interaction sites within the protein.
In protein expression, C-terminal modifications can increase protein stability and improve purification techniques.
| Acryl | Ester (OEt) | NHEt |
| AFC | Ester (OMe) | NHisopen |
| AMC (7-Amino-4-Methylcoumarin) | Ester (OtBu) | NHMe |
| Amidation | Ester (OTBzl) | OBzl |
| BSA (-COOH of C terminal) | FMK (Fuoro-methylketones) | OSU |
| Bzl | KLH (-COOH of C terminal) | OVA (-COOH of C terminal) |
| CMK (Chloro-methylketones) | MAPS Asymmetric 2 branches | p-Nitroanilide (pNA) |
| C-terminaleaters | MAPS Asymmetric 4 branches | tBu |
| Cysteamide (Mercaptoacetamide) | MAPS Asymmetric 8 branches | TBzl |
| Ethylamine | Me | Thioester |
AMC (7-Amino-4-Methylcoumarin)
Enzyme substrates based on the AMC (7-amino-4-methyl coumarin) fluorophore are very popular tools for studying protease activity and specificity. In such substrates, AMC is usually linked to the peptide by forming an amide bond between the coumarin amine and the carboxyl group of the C-terminal amino acid residue.
The proteolysis of the amide bond releases free AMC, resulting in a greatly increased fluorescence. The excitation/emission wavelengths are about 342 nm/441 nm.
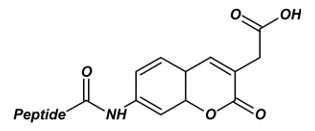
Amidation
Terminal amidation (C-terminus) will remove the positive charge and help peptides imitate its natural structure. In addition, this modification makes the resulting peptide more stable towards enzymatic degradation resulting from exopeptidases.
Hepatitis C virus NS3/4A protease is a serine protease. At present, most serine protease inhibitors contain electrophilic groups, which form covalent bonds with serine hydroxyl groups in catalytic triad. Based on decapeptide substrate, active peptide aldehyde was obtained by simplifying peptide chain and modifying carboxyl terminal structure. Its binding constant to HCVNS3/4A protease was 12 μmol·L-1, but the chemical and metabolic stability of aldehyde group was poor. Therefore, the researchers modified the end of the aldehyde group and replaced the aldehyde group with α-halogenated ketone, heterocyclic ketone, α-diketone and α-ketoamide, and the binding constant of the ketoamide compound to serine protease NS3/4A was increased by 12 times. By analyzing the interaction between ketoamide compounds and serine protease, the researchers found that ketoamide structures can form covalent bonds with serine at position 139, and hydrogen bonds with nearby glutamic acid at position 137 and serine residues at position 138, thus enhancing the combination of the compounds with NS3/4A protease, thus enhancing their antiviral activity.
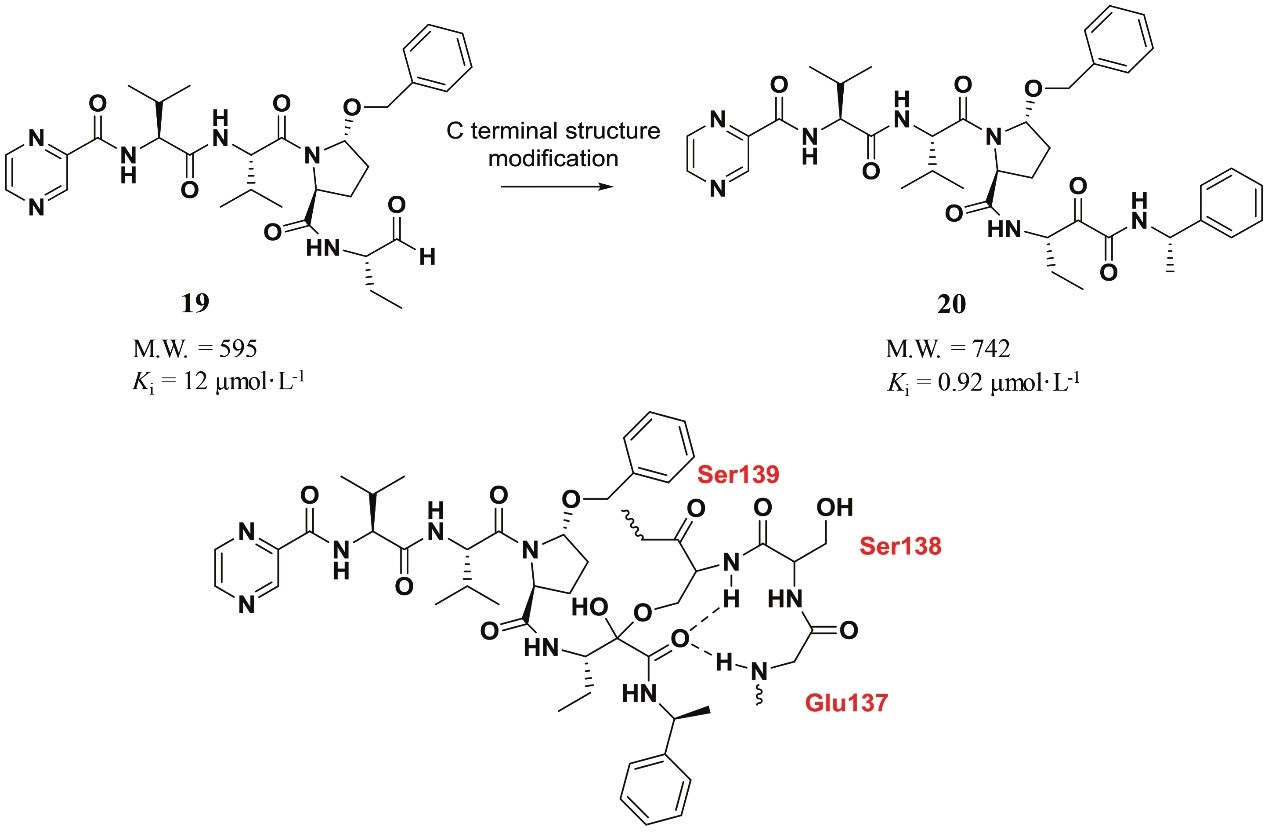 Fig. 1 C-terminal structure modification to improve activity against serine protease. (Peng, J. J., 2020)
Fig. 1 C-terminal structure modification to improve activity against serine protease. (Peng, J. J., 2020)
Biotin
Biotin has a very strong affinity for streptavidin, so the biotinylation of peptides is an effective method of specifically binding peptides to streptavidin-coated surfaces.
Peptide biotinylation can be performed at the N-terminus or C-terminus. At the C-terminus, the first-order epsilon amino group on the lysine inserted at the C-terminus is biotinylated to remove the positive charge of lysine.
KLH, BSA, OVA
After peptide synthesis, the peptide can be coupled to carrier proteins, OVA, KLH or BSA. The carrier protein can be conjugated to the N- or C-terminal of the peptide through the inserted N- or C-terminal cysteine. OVA, KLH or BSA-coupled peptides are mainly used for immunization and can significantly increase the cell-mediated immune response.
MAPS
The application of multiple antigen peptides (MAPS) is an effective method for producing high-titer anti-peptide antibodies and synthetic peptide vaccines. The system uses the α- and ε-amino groups of lysine to form a backbone that can link multiple peptide chains. Depending on the number of lysine layers, different numbers of peptide branches can be synthesized. This eliminates the need to conjugate the antigen to the protein carrier.
AMC, FMC, p-Nitroanilide (pNA).
The peptide p-nitroaniline is a useful compound for studying protease activity. In such substrates, yellow free p-nitroaniline is released through the proteolysis.
Cutting-edge expertise: Our distinguished proficiency in Peptide C-Terminal Modification positions us as a leader in the biopharmaceutical industry. Our team is composed of highly trained professionals who are passionate about delivering top-of-the-line services to our clients.
Customization: We can tailor our services to match the specific needs of our clients. Our flexible approach and client-centric philosophy allow us to create specialized solutions for each project.
Quality assurance: We adhere to strict quality control standards and procedures to guarantee the accuracy and reliability of our services. Each modification is carefully monitored to ensure optimal results.
Rapid turnaround time: We strive to deliver results in the shortest time possible without compromising on the quality of our work. This enables our clients to accelerate their research or product development processes.
Customer support: We provide comprehensive customer support throughout the entire process, from initial consultation to the delivery of the final product. Our highly responsive customer service team is available to answer any queries and resolve any issues that may arise.
Continuous innovation: We are continually investing in research and development to improve our services and stay at the forefront of the biopharmaceutical industry.
Creative Peptides specializes in the custom synthesis of C-terminal modification peptides, providing a confidential and efficient service at competitive prices. Every step of peptide synthesis is subject to Creative Peptides' stringent quality control. Typical delivery specifications include:
We can perform a variety of C-terminal modifications, including amidation, esterification, and the addition of various functional groups or labels. We can also perform more complex modifications, including the attachment of proteins, lipids, or other molecules.
The length of the process largely depends on the specific project, the complexity of the modification, and the peptide sequence. Typically, it can take anywhere from a few days to a few weeks. We will provide an estimated timeline upon assessing the individual project.
Yes, absolutely. We offer a highly customizable peptide synthesis service. You can specify the type of modification you want and we will implement it according to your requirements.
Our service cost varies depending on the type and complexity of the modification, the peptide length and sequence, and the quantity required. Please contact our service team for a detailed quote.
We have a robust QC process in place, which includes analytical HPLC and Mass Spectrometry to ensure the correct modification, purity, and identity of the peptide.

References