| CAT# | Product Name | M.W | Molecular Formula | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A05002 | Adrenomedullin (16-31), human, pig | 1865.2 | ||
| A05003 | Adrenomedullin (1-12), human | 1514.7 | ||
| A05005 | Adrenomedullin (1-52), porcine | 5971.7 | ||
| A05008 | Adrenomedullin (26-52), human | 3119.5 | ||
| A05009 | Prepro-adrenomedullin (153-185), human | 3219.6 | ||
| A05010 | Prepro-adrenomedullin (45-92), human | 6028.9 | ||
| A05011 | Pro-Adrenomedullin (12-20) human | 1187.4 | ||
| A05013 | Pro-Adrenomedullin (N-20), porcine | 2444.9 | C112H178N36O26 | |
| A05014 | Pro-Adrenomedullin (N-20), rat | 2477.9 | C111H177N37O28 | |
| A05015 | Proadrenomedullin N-terminal 20 Peptide (Human, 9-20) | 1619.1 | C77H119N25O14 | |
| A05017 | Adrenomedullin 5 (primate) | 5784.55 | C253H394N82O71S2 | |
| A05021 | Adrenomedullin (porcine) trifluoroacetate salt | 5971.77 | C264H406N80O77S3 | |
| A05022 | Adrenomedullin (rat) trifluoroacetate salt | 5729 | C242H381N77O75S5 | |
| A05023 | Adrenomedullin 5 (primate) trifluoroacetate salt | 5784.55 | C111H177N37O28 | |
| A05024 | Pro-Adrenomedullin(N-20), rat | 2477.86 | C253H394N82O71S2 |
It was in 1993 that Kitamura's group discovered the peptide hormone adrenomedullin (ADM, or AM). In order to bind to ADM receptors, the 52-amino acid peptide ADM must have a ring structure and an amide at its C-terminus. Chromosome 11 is home to the ADM gene, which has four exons. The family of receptor activity-modifying proteins (RAMP) is an important factor in ADM's biological action. In order to express ADM, it is necessary for the calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CRLR) to be coupled with either RAMP 2 or 3, which in turn makes the receptor ADM specific. The adrenal medulla is the original site of ADM discovery (thus the name "adrenomedullin"). However, additional research has shown that many other tissues and cells, notably endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells, produce ADM as well. Its small size (6 kDa) allows it to diffuse freely between the blood and interstitium. Enzymatic conversion of ADM-glycine to the physiologically active ADM-amide occurs after proteolytic fragmentation of the pro-hormone (pro-ADM) forms a glycine-extended, inactive ADM. There are many ADM receptors and binding sites throughout the body, but the density is greatest in the lungs and cardiovascular systems. After 22 minutes in the body, ADM has half its initial concentration. Based on the recent promising results with sacubitril/valsartan as a new therapy for heart failure, practitioners may be familiar with the molecule neprilysin, which is thought to primarily metabolize ADM. Since sacubitril is a neprilysin inhibitor, it is believed that it will prevent the breakdown of ADM and other peptide hormones. Binding with its receptors and then being internalized and degraded is another way that ADM is eliminated.
There are 52 amino acids in ADM, with 6 forming a ring and an amide bond at the C-terminus. To function biologically, they must have these two structural characteristics. Amylin, calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), and adrenomedullin 2/intermedin (ADM2/IMD) are all members of the same calcitonin peptide superfamily with which it has similarity.
The bigger precursor molecule known as preproadrenomedullin (preproADM) is the building block of adrenomedullin. During its transit across the cell membrane, the 185-amino-acid precursor of proAM—a prohormone consisting of 164 amino acids—is cleaved at the 21-amino-acid N-terminal signal peptide. ADM), proadrenomedullin N-terminal 20 peptide (PAMP), mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin (proADM 45–92), and adrenotensin (proADM 153–185) are the four peptides that result from further processing of proAM by endopetidases. Plasma levels of PAMP, ADM, and ProADM 45–92 are known, and among them, PAMP, ADM, and Adrenotensin are peptides with biological activity. Plasma contains both the active form, which is created following enzymatic amidation, and the inactive form, which is both PAMP and ADM peptides. The inactive form is characterized by a glycine (Gly) extension.
Adrenomedullin is a broad phrase that could lead people astray. It is essential to differentiate among three principal forms of ADM: the biologically active 52-amino acid form (bio-ADM), and its two biosynthetic precursors derived from the same propeptide, pro-Adrenomedullin: midregional pro-Adrenomedullin (MR-proADM) and the 53-amino acid C-terminally glycine-extended form (ADM-Gly).
A highly researched predictive, prognostic, and diagnostic biomarker for a variety of clinical conditions, including cardiovascular diseases (CVD) and cv-mortality, sepsis and septic shock, pneumonia, COVID-19 complications, and Alzheimer's disease, MR-proADM is produced by a multi-step processing of pro-Adrenomedullin. It also has a relatively long plasma half-life. Although its physiological role is yet unknown, MR-proADM serves as a surrogate marker for bio-ADM since it is stable in circulation and originates biosynthetically from the same propeptide.
ADM-Gly, with a glycine residue at its C-terminus, is the inert glycine-extended precursor of the active bio-ADM. A catalytic event called C-terminal amidation transforms inactive ADM-Gly into its fully physiologically active form, bioADM. The enzyme peptidyl-glycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase (PAM) uses this glycine residue as a recognition signal. In humans, it has been found in individuals with obesity, heart failure, essential hypertension, chronic renal failure, sepsis, before and after cardiac surgery, and as a reaction to LPS injection; however, it does not seem to have any function when taken alone. Additionally, ADM-Gly is the predominant circulation type in healthy persons.
By activating the CRLR + RAMP receptor complex, the mature version of ADM, known as Bio-ADM, performs the physiological activities of Adrenomedullin. And much like MR-proADM, bio-ADM is a great biomarker for most medical issues. So, in cases of acute and chronic heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, sepsis, septic shock, and as a predictor of shock and organ failure in intensive care units, supranormal levels of bio-ADM were linked to illness severity and outcomes. Based on this knowledge, bio-ADM was studied and developed as a potential treatment for various medical conditions.
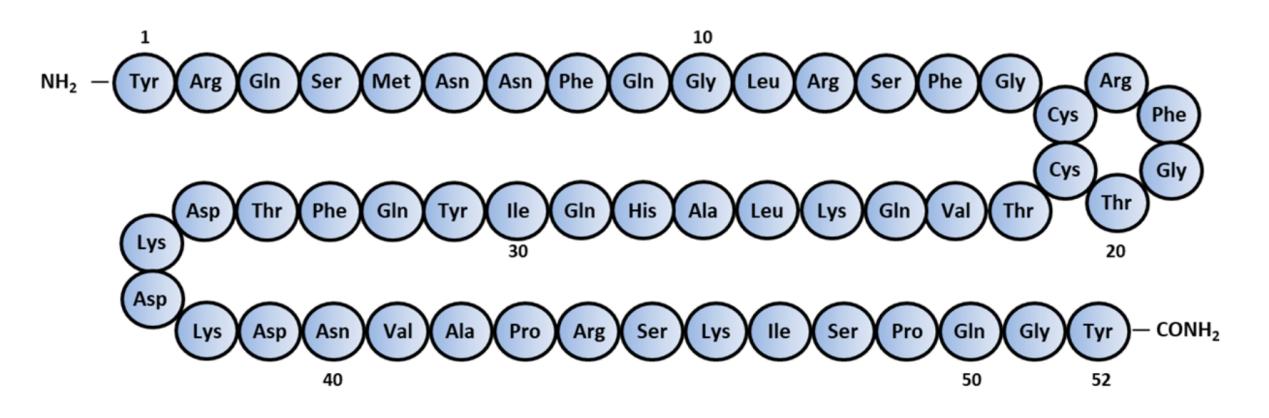
Amino-acid sequence of human Adrenomedullin. (Ashizuka S., et al., 2021)
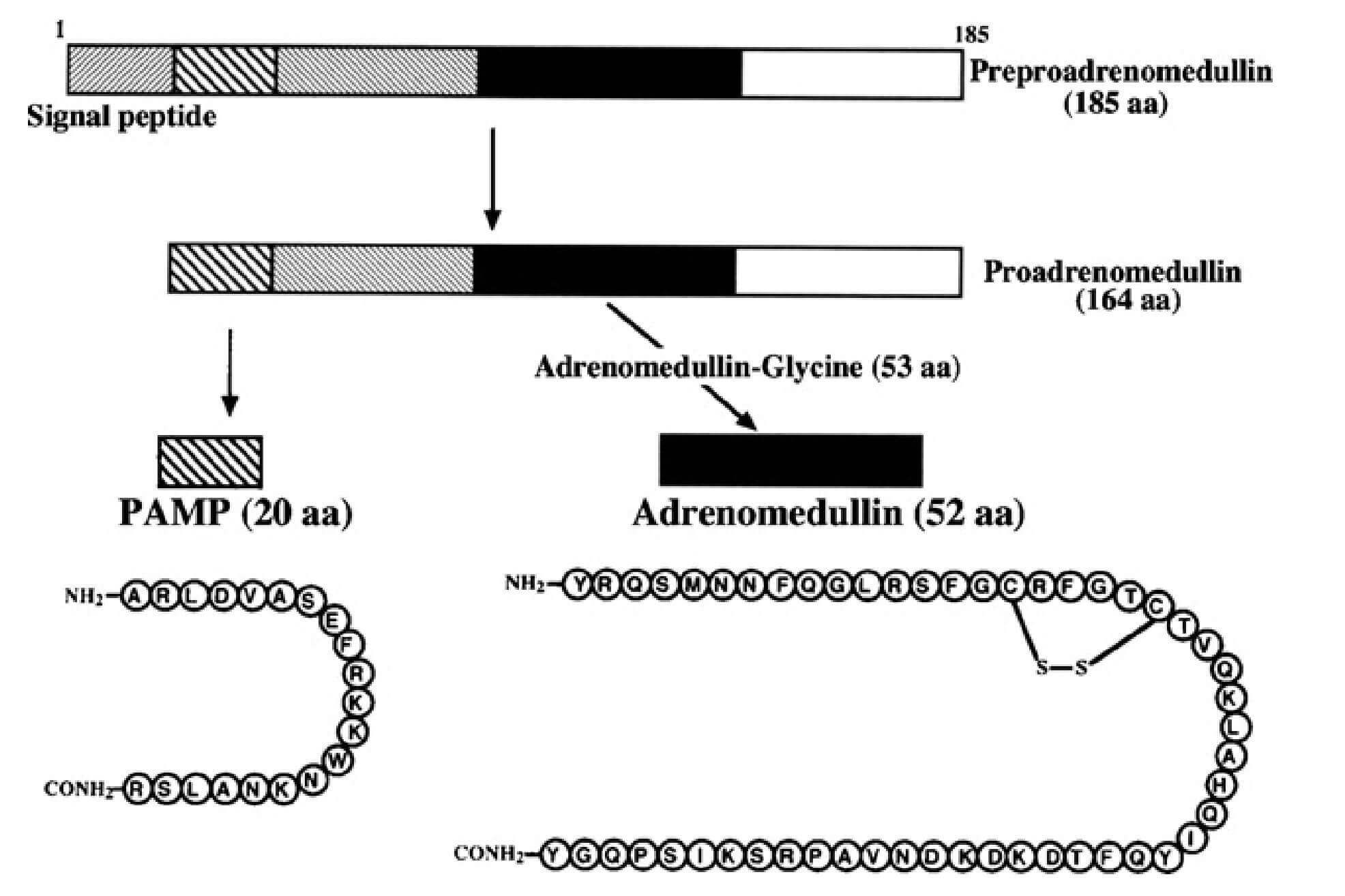
Schematic representation of the human adrenomedullin. (Li Y., et al., 2007)
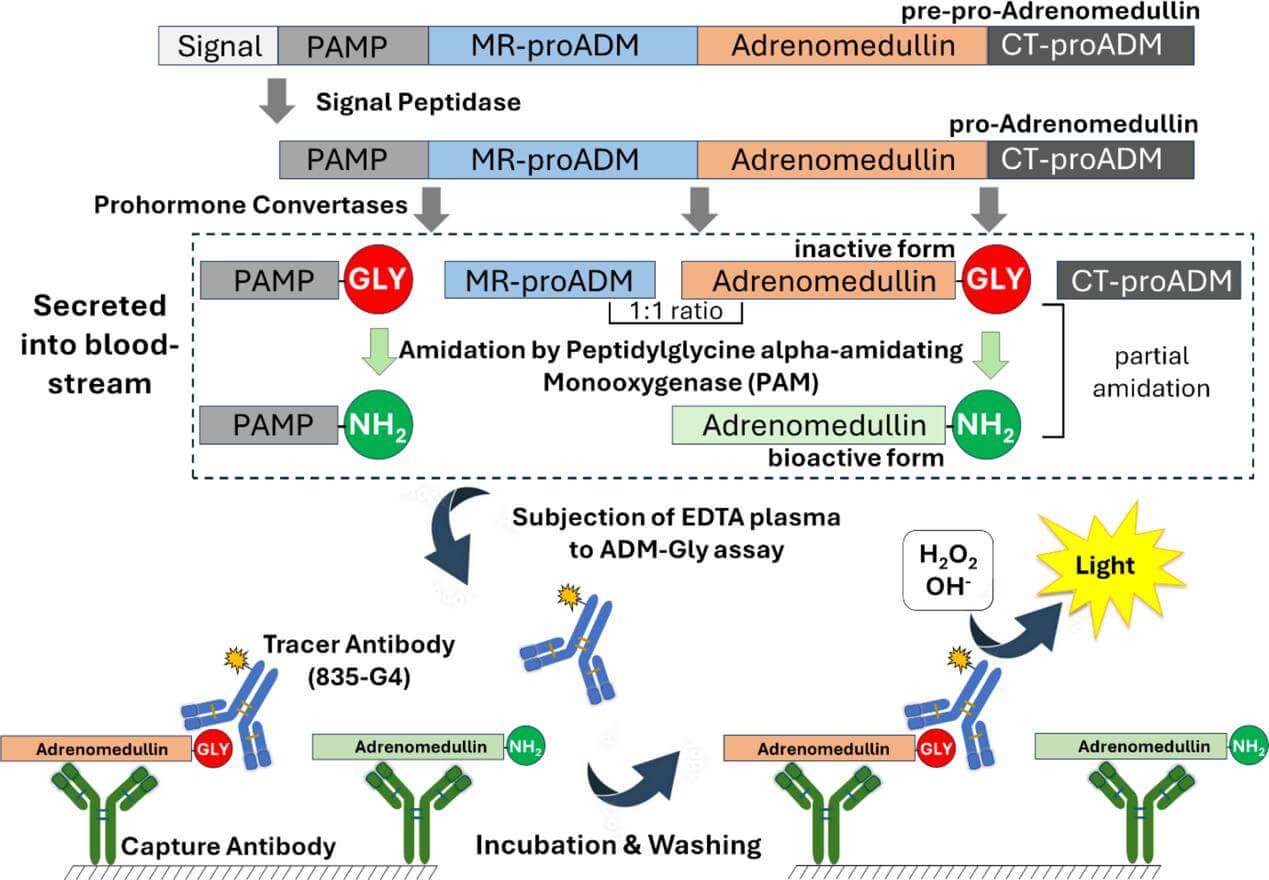
Schematic representation of Adrenomedullin processing. (Kaufmann P., et al., 2024)
In order for ADM to regulate human adrenocortical cells, its six-membered ring structure and C-terminal amino acid sequence are crucial. To be more specific, ADM segments without the ring structure or C-terminus, such as ADM sequences 22-52, 15-22, or 16-3l, do not have any impact on mineralocorticoids, while ADM (13-52) does. Research on calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), a 37-amino acid vasodilator peptide with a distinct amino acid sequence similarity to ADM and a six-membered ring created by a disulfide bridge in the 2-7 position, lends credence to this claim.
Nevertheless, ADM fragments lacking the ring structure, such as ADM-(22-52), have no vasodilator action. A new paper indicates that ADM-(22-52) competitively inhibits ADM binding and, in a dose-dependent way, suppresses ADM-induced cAMP buildup in rat vascular smooth muscle cells, indicating that ADM-(22-52) may function as an ADM receptor antagonist.
Aldosterone and corticosterone concentrations in the culture medium, together with the presence or absence of 10−8 M ACTH, were evaluated using a radioimmunoassay for ADM (22-52). ACTH-stimulated aldosterone production remained unaffected, but ADM and/or ADM (22-52) elevated baseline aldosterone secretion after 3 hours, but not after 24 hours of exposure. After three hours, corticosterone secretion remained unchanged. After 24 hours of administration, both ADM(22-52) and ADM independently decreased baseline corticosterone secretion; ADM elicited a minor rise in ACTH-stimulated corticosterone synthesis, which was antagonized by ADM(22-52). The following elucidations are presented to clarify these enigmatic outcomes: i) the cultures comprised a mixture of ZG, ZF/R, and medullary chromaffin cells; ii) ADM induces adrenomedullary cells to release catecholamines, which may enhance aldosterone secretion from ZG cells; and iii) Prolonged exposure to ADM can alter the phenotype of ZF/R cells in vitro, rendering them more responsive to the compound. Our study concerns the selectivity of ADM(22-52) as an ADM receptor antagonist and underscores the need for caution when comparing adrenal secretion outcomes obtained via different in vitro approaches.
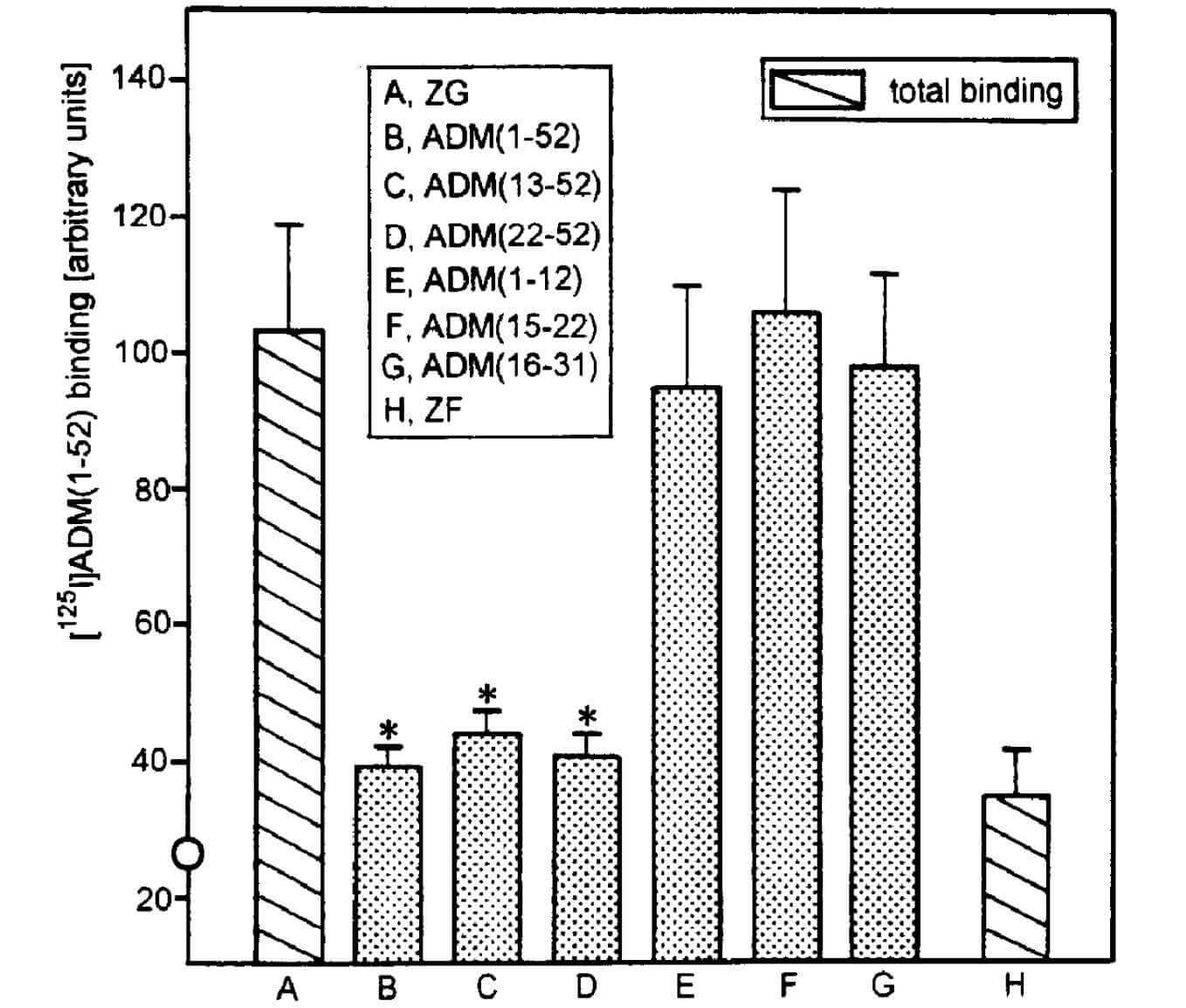
Binding assay of ADM fragments. (Belloni A S., et al., 1998)
The primary function of ADM is vasodilation in both resistance and capacitance vessels. ADM reduces blood pressure by enhancing blood flow. Even little dosages provoke vasodilation, suggesting that plasma concentrations of ADM in circumstances like heart failure are sufficient to directly influence vascular tone. In addition to vasodilation, ADM seems to significantly contribute to the maintenance of endothelial integrity. ADM expression may be stimulated by several factors, including volume overload, and elevated plasma ADM indicates excessive fluid volume. This is presumably a result of a counteractive reaction, since the ADM-induced stability of endothelial barrier function is believed to mitigate tissue fluid excess. Disruption of the ADM system leads to vascular leakage and systemic and pulmonary edema. The function of the ADM–RAMP 2 system has also been examined. Mice deficient in the gene for RAMP 2 exhibited increased vascular permeability and systemic edema. Mice having a conditional knock-out of ADM in endothelial cells exhibited heightened vascular permeability relative to wild-type littermates.
Experiments demonstrating that experimental overexpression of ADM decreases pulmonary and systemic vascular leakage in animals provide more evidence for the actions of ADM in preserving vascular integrity. In a rat model of systemic inflammation caused by Staphylococcus aureus toxin and associated with significant vascular leakage, for instance, endothelial barrier function was preserved by ADM infusion via an increase in cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). Additionally, monolayers of cultivated human umbilical vein endothelial cells and swine pulmonary artery endothelial cells showed a dose-dependent reduction in experimentally generated endothelial hyperpermeability when exposed to ADM. In asthma, vascular leakage and abnormalities in epithelial healing are associated with ADM suppression. Intrathecal ADM fully reduced acutely induced airway hyper-responsiveness and mucosal plasma leakage in two animal models. In order to stabilize the endothelial barrier, ADM acts on multiple pathways. One of these is the cAMP/protein kinase A (PKA) pathway, which inhibits RhoA/ROCK and reduces the 'pulling forces' exerted on endothelial cell junctions by myosin light chain kinase-induced actomyosin contraction. Another pathway, possibly associated with the PI3K/Akt pathway, promotes the production of protective cortical actin and stabilizes the VE-cadherin/β-catenin complex, which is a part of adherens junctions. Last but not least, ADM blocks the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone pathway. Despite increasing plasma renin activity, ADM reduces aldosterone production produced by angiotensin II and lowers the aldosterone/plasma renin activity ratio. Additionally, angiotensin II protects against angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy and renal impairment by upregulating ADM. We propose that ADM compensates for renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system escalation by suppressing aldosterone production via its role as a functional antagonist to angiotensin II.
In conclusion, ADM primarily acts to widen blood vessels and prevent them from being damaged. The impacts of ADM are site dependent, which is important to note. Both the interstitium and the intravascular spaces contain ADM. Instead of acting on the interstium, it acts intravascularly. It is believed that intravascular ADM acts on endothelial cells to increase vascular integrity and reduce vascular permeability. On the other hand, it is believed that interstitial ADM causes vasodilatation via an endothelium-independent mechanism, acting on vascular smooth muscle cells. Although endothelial-dependent routes have also been established, the amount to which each pathway is implicated in vivo in people is yet uncertain.
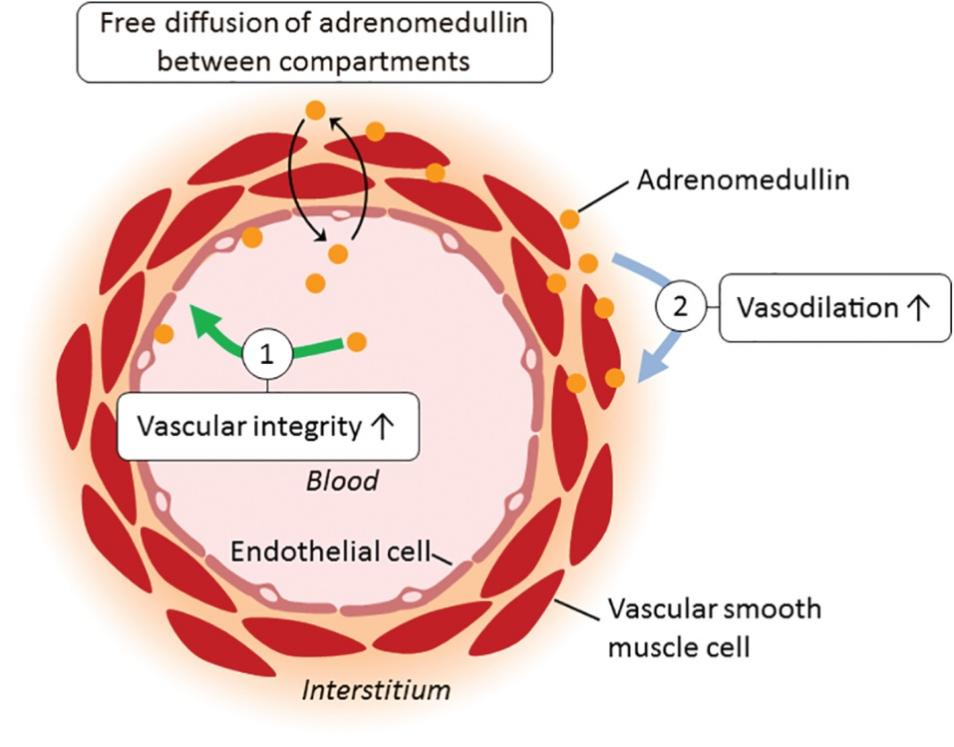
The mode of action of intravascular vs. interstitial adrenomedullin. (Voors A A., et al., 2019)
Sepsis pathophysiology relies heavily on the immune system. That is why it's important to talk about how ADM may regulate the immune system. There have been several in vitro investigations showing that ADM has anti-inflammatory properties. Researchers looked at the effects of ADM in rat alveolar macrophages triggered by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in one of the first research on the subject. The release of cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant (CINC/CXCL-1) was markedly reduced by ADM, suggesting a potential cAMP-dependent mechanism. Previous studies in Swiss 3T3 murine fibroblasts proved that ADM blocks the production of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) caused by interleukin-1 beta. These investigations also validated the significant involvement of the cAMP-PKA pathway, since a cAMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor could counteract ADMs inhibitory effects. Upon stimulation with LPS, microglia, murine RAW264.7 macrophages, and rat Kupffer cells all showed similar effects of ADM, suppressing both TNFα and interleukin (IL)-6. These results from the lab have been validated by in vivo trials. By using a mechanism involving peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma, the TNFα response was reduced in a rat endotoxemia model when ADM and ADM-binding protein-1 (AMBP-1), a protective peptide with hypothesized ADM-enhancing properties, were administered together. The use of ADM to alleviate inflammatory bowel illness is an intriguing side note. The size of the ulcerative lesions was significantly decreased, with a dose-dependent effect, and tissue IL-6 levels were lowered after intracolonic delivery of ADM in a model of acetic acid-induced colitis. Further research has verified these findings. In rats, models of dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis showed reduced amounts of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and tumor necrosis factor-α. Researchers found that seven individuals with ulcerative colitis who took ADM intravenously for eight hours every day for two weeks had significant improvements in their disease activity index scores and the appearance of their ulcers when they underwent endoscopic evaluation. With the exception of some mild changes in heart rate and blood pressure, no major side effects were noted.
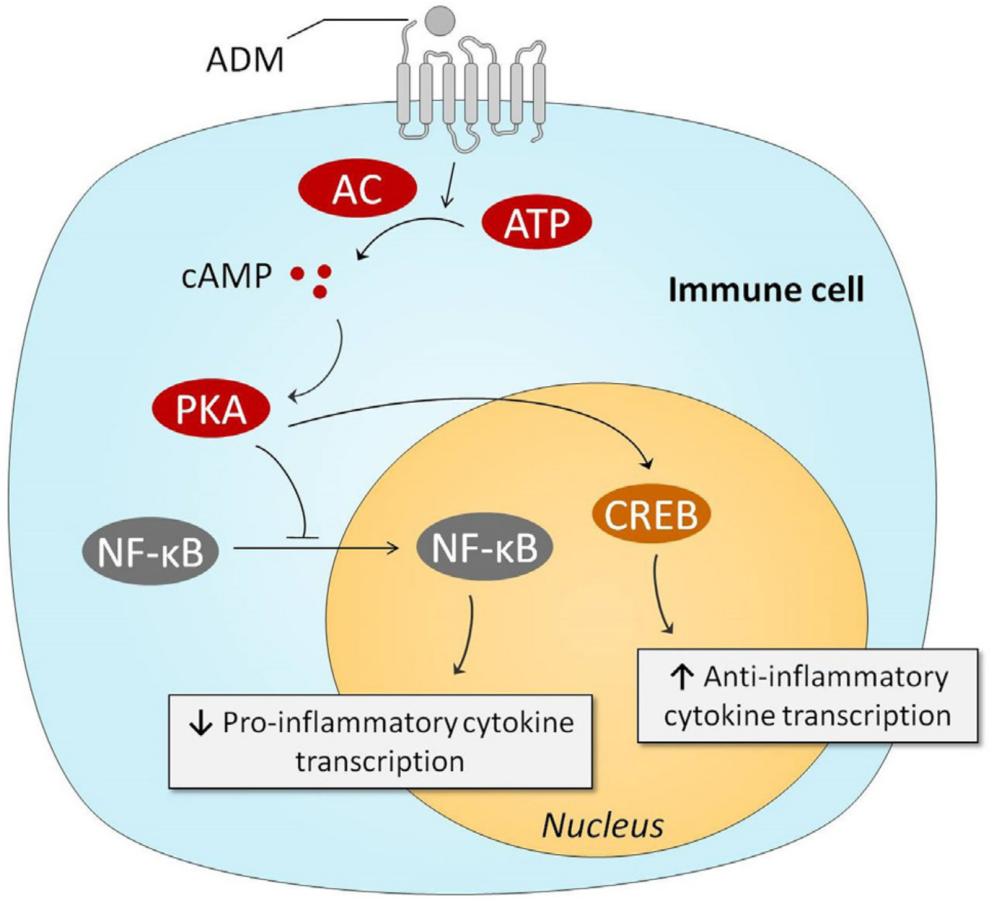
Intracellular mechanisms of ADM-induced anti-inflammatory effects. (Geven C., et al., 2018)
The epithelium is the first line of defense against harmful microbes. Because it is secreted by a wide variety of epithelial cells, ADM is present in numerous body fluids at amounts far greater than those in plasma. ADM has structural and chemical features with other antimicrobial peptides, such as β-defensin-2, such as a positive net charge, a disulfide link between residues 16 and 21, and an amidated tyrosine at the carboxyl terminus. There is also a peptide length similarity. This allows bacteria to intercalate their membranes because it generates an amphipathic structure. Research conducted in a controlled laboratory setting has shown that ADM peptide and smaller ADM fragments may limit bacterial growth.
It is also possible that adrenalomedullin has cardioprotective properties. After being exposed to stress-induced cardiac hypertrophy, mice lacking heterozygous ADM showed more fibrosis and increased hypertrophy than their wild-type counterparts. Subsequent in vivo confirmation in a mouse model of the hypothesis showed that ADM-induced inhibition of doxorubicin-induced cardiac myocyte death occurred via a cAMP-dependent pathway. Patients with heart failure have already begun the first stages of ADM therapy. The pulmonary capillary wedge pressure, pulmonary arterial pressure, and cardiac index were all significantly reduced and increased in individuals with stable congestive heart failure who received a short-course ADM infusion. In addition to lowering plasma aldosterone levels, ADM increased urine volume and salt excretion. Combining ADM with human atrial natriuretic peptide led to beneficial hormonal and hemodynamic changes in a pilot study of patients with acute decompensated heart failure. These changes included lower pulmonary arterial pressure, more urine production, and lower plasma concentrations of aldosterone and brain natriuretic peptide. Heart failure patients have not been the subjects of any more research up to this point. Although no measurements of cardiac output (CO) were taken, it was found that isolated ventricular cardiac myocytes exposed to an ADM-receptor antagonist showed an increase in myocyte contractility during the early phase of rat endotoxemia, leading to the conclusion that ADM is a "cardiac depressant factor" in addition to the previously reported data.
Many disease states have been reported to modulate the expression of ADM including cancer. As we mentioned before, ADM was originally isolated from an adrenal gland tumor. A wealth of subsequent studies have found that ADM and its receptor are overexpressed in many human cancers and tumor cell lines establishing an autocrine loop mechanism that tumor cells exploit to maintain an autonomous proliferative state. ADM is intimately intertwined at several levels in the multistep process of tumor development. At the initial stage of tumor growth, rapid accumulation of malignant cells results in the establishment of an avascular nutrient-depleted hypoxic environment. Low oxygen tension within and surrounding the tumor body triggers a number of survival mechanisms which allow neoplastic cells to overcome this inhospitable microenvironment. Many of these encompass the upregulation of ADM's expression. In fact, if not the most important driving force for ADM upregulation in tumor cells is hypoxia. Cellular responses to hypoxia are mediated through a well known hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-dependent mechanism. HIF is a heterodimeric transcription factor which is stabilized under hypoxic conditions and binds to specific DNA sequences denoted hypoxia response elements (HRE) which are present in the promoter regulatory region of the Adrenomedullin gene. Hypoxia also upregulates the expression of the ADM receptor gene in many tumor types hence establishing a rational explanation behind the aforementioned autocrine growth mechanism underlying carcinogenesis.
The release of ADM from tumors into the microenvironment creates a peptide gradient that eventually spreads to a diverse array of cell types—including cancer cells—that are known to react to this peptide and play a role in the tumor's progression. The mitogenic action of ADM and its involvement in an antiapoptotic state both contribute to the growth of tumor cells.
In vitro and in vivo growth is increased to varied degrees by many human cancer cell lines that overexpress ADM. Cells transfected with the Ishikawa gene did not exhibit any growth enhancement, in contrast to the RL95.2 endometrial cancer cell line, which exhibited a significant upregulation of ADM expression. Additionally, in the absence of serum, adrenomedullin sustains the proliferation of the T47D breast carcinoma cell lines. Lastly, U87 glioblastoma cells, which have a high level of endogenous ADM, were shown to have their proliferation drastically reduced in vitro and in vivo when treated with an anti-ADM antibody.
When compared to control cells, transfected tumor cells overexpressing ADM incorporate more bromodeoxiuridine (after serum deprivation) and have greater amounts of oncogenic proteins such Ras, Raf, PKC, and MAPKp49. To some extent, tumor cells can survive hypoxia because of adrenomedullin-mediated overexpression of antiapoptotic proteins or downregulation of pro-apoptotic factors. In addition to its role in enhancing ADM-mediated proliferation in breast cancer cell lines, AMBP-1 has recently been linked to a mechanism that allows tumor cells to survive by avoiding complement-mediated lysis.
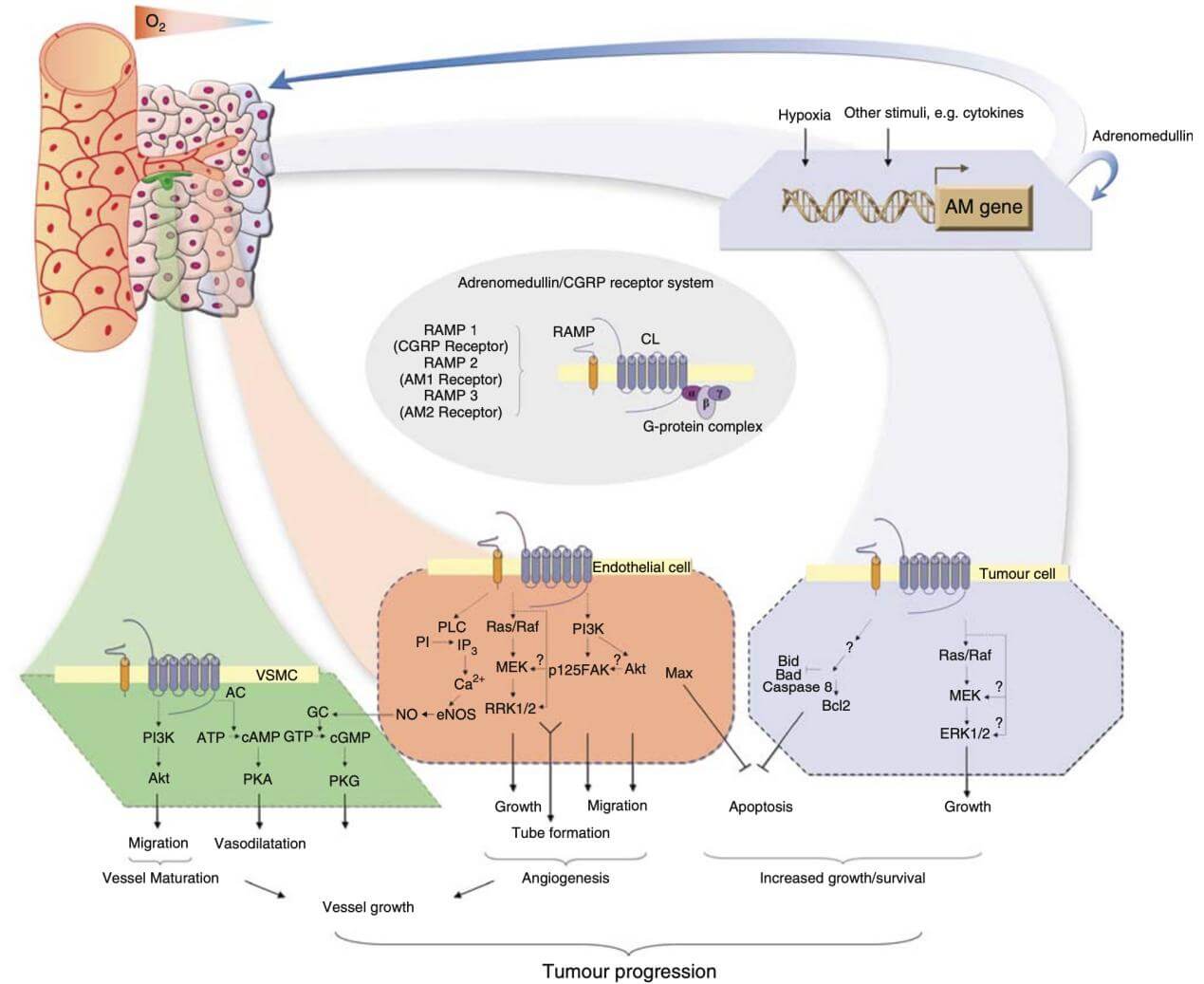
Role of adrenomedullin in tumor progression. (Nikitenko L L., et al., 2006)
References