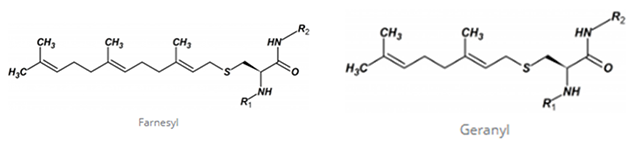
Prenylation (also known as isoprenylation or lipidation) is one of the common post-translational peptide modifications, which involves the addition of a farnesyl (C15) or geranylgeranyl (C20) isoprenoid moiety onto a cysteine residue located near the carboxyl terminal of a peptide. These chemical reactions were catalyzed by farneyl transferase (FTase) and geranylgeranyltransferase (GGTases), respectively. Proteins modified by isoprenylation play an important role in signal transduction in vivo. The role of Ras superfamily guanosine triphosphaterase (GTPases) in tumorigenesis and development has attracted wide attention.
Since discovered in 1978, prenylation has been studied extensively due to its various aspects of cellular physiology and pathology processes by increasing the hydrophobicity of the target protein for efficient anchoring into plasma membranes and/or organellar membranes. These target proteins include the small GTPases in the Ras, Rho, and Rab families, heterotrimeric G proteins, and nuclear lamin proteins. Functions of prenylation are involved in facilitating subcellular localization, promoting protein-protein and protein-membrane interactions. However, the dysregulation of prenylation drives to many severe human diseases such as cancer, cardiac effects, neurodegenerative disorders, retinitis pigmentosa, and premature aging syndromes.
Creative Peptides has developed a reliable procedure for the synthesis of prenylated peptides, we can provide global customers with prenylated peptides based on our excellent technology. It includes farnesylation and geranylgeranylation. Prenylated C-terminus peptide was conjugated to Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin (KLH), and purified by affinity chromatography.
Creative Peptides has extensively developed prenylated peptides structures and is the company of choice to manufacture your prenylated peptides requirements, providing a confidential and efficient service at competitive prices. Every step of peptide synthesis is subject to Creative Peptides’ stringent quality control. Typical delivery specifications include:
Peptide prenylation is a post-translational modification where a farnesyl (C15) or geranylgeranyl (C20) isoprenoid group is added to a cysteine residue near the peptide's carboxyl terminal, catalyzed by farnesyltransferase or geranylgeranyltransferase. This modification increases the hydrophobicity of proteins and helps anchor them to membranes.
Prenylation enhances the hydrophobicity of peptides, facilitating their anchoring to cell membranes and organellar membranes. This modification plays a key role in protein localization and protein-protein or protein-membrane interactions, which are critical in signal transduction and cellular functions.
Prenylation commonly targets small GTPases, such as those in the Ras, Rho, and Rab families, as well as heterotrimeric G proteins and nuclear lamin proteins, all of which are involved in various cellular processes.
Prenylation is involved in subcellular localization, protein interactions, and signal transduction. Dysregulation of this process can lead to several human diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. Understanding prenylation can provide insights into disease mechanisms and cellular physiology.
Creative Peptides uses advanced techniques to synthesize both farnesylated and geranylgeranylated peptides. These peptides are conjugated to Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin (KLH) for purification and analysis. Our methods ensure high-quality, functional prenylated peptides suitable for research and development.
Each batch of prenylated peptides undergoes stringent quality control, including HPLC chromatogram analysis, mass spectrometry, and detailed synthesis reports, ensuring that the peptides meet high standards of purity and functionality.
Prenylated peptides are valuable for studying membrane protein interactions, signal transduction, and cellular localization. They can be used to investigate the role of prenylation in various cellular processes and diseases.

References