Peptoid synthesis involves constructing synthetic peptoids by attaching side chains to the nitrogen atoms in the backbone amide, a distinct approach compared to traditional peptide synthesis, where side chains are linked to the α-carbon. This method, frequently using the submonomer technique on solid supports, facilitates the swift and flexible assembly of peptoids with diverse and tailored properties. These peptoids offer advantages such as greater stability, reduced potential for immunogenic reactions, and customizable features, making them highly suitable for applications in drug development, material sciences, and diagnostic assays. Creative Peptides excels in peptoid synthesis, utilizing advanced platforms and expertise to provide bespoke peptoid libraries and a range of services including solid-phase synthesis, high-throughput screening, and purification. Their capabilities make Creative Peptides an ideal collaborator for pioneering research and industrial projects.
Structure: Peptides are chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Each amino acid has a central carbon atom (α-carbon), an amino group (–NH2), a carboxyl group (–COOH), a hydrogen atom, and a unique side chain (R-group) that defines the amino acid.
Backbone: The backbone of a peptide consists of repeated nitrogen (N) – α-carbon (Cα) – carbonyl carbon (C=O) units. The sequence of amino acids in the peptide determines its structure and function.
Bonds: Peptide bonds are formed through a dehydration reaction between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of another, releasing a molecule of water. This bond is an amide bond and has partial double-bond character, which restricts rotation and contributes to the peptide's structure.
Natural Occurrence: Peptides naturally occur in all living organisms and are crucial for numerous biological processes, including hormone function, enzyme activity, and cell signaling.
Structure: Peptoids (poly-N-substituted glycines) are structural analogs of peptides where the side chains (R-groups) are attached to the nitrogen atom of the backbone amide rather than the α-carbon. This modification results in a structure where the side chains project from the nitrogen atoms in the backbone.
Backbone: The backbone of a peptoid is composed of nitrogen (N) – carbon (C) units, similar to peptides, but without the α-carbon to which side chains are attached in peptides.
Bonds: Peptoids also have amide bonds, but the key difference is the positioning of the side chains on the nitrogen atoms rather than the α-carbons, which gives peptoids distinct structural and functional properties.
Synthetic Nature: Unlike peptides, peptoids are not found in nature and are synthesized chemically. This synthetic nature allows for greater control over their structure and properties, making them useful in various applications.
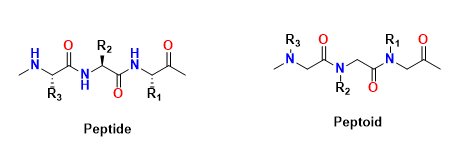 Structural comparison between peptide and peptoid
Structural comparison between peptide and peptoid
The synthesis of peptoids typically employs the submonomer method, which allows for the rapid and efficient construction of peptoid chains with diverse side chains. Here is a detailed overview of the process:
Resin Selection: Peptoid synthesis begins with the selection of an appropriate resin, which serves as the solid support. Common resins include polystyrene beads functionalized with reactive groups.
Attachment: The initial step involves attaching a starting molecule, often an amine, to the resin. This molecule serves as the foundation for the growing peptoid chain.
Acylation: The resin-bound amine is acylated with bromoacetic acid or another electrophilic acylating agent to form a bromoacetamide intermediate.
Displacement: A primary amine is then introduced, which displaces the bromide ion in a nucleophilic substitution reaction, forming an N-substituted glycine unit. This step attaches the side chain to the nitrogen atom of the backbone.
The cycle of acylation and amine displacement is repeated to extend the peptoid chain. Different primary amines can be used in each cycle to introduce a variety of side chains, allowing for the synthesis of peptoids with diverse and customizable properties.
Cleavage: Once the desired peptoid sequence is synthesized, the peptoid is cleaved from the resin using appropriate cleavage reagents.
Purification: The crude peptoid is purified, typically by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), to obtain the final pure product.
Protease Resistance: Peptoids are highly resistant to proteases, enzymes that degrade proteins and peptides. This resistance prolongs their activity in biological systems, making them more effective for therapeutic applications.
Structural Flexibility: The absence of hydrogen bonds typically found in peptides allows peptoids to adopt a variety of secondary structures. This flexibility can be advantageous for designing molecules that need to fit into specific biological targets.
Customizable Side Chains: The ability to incorporate a wide range of side chains allows for the precise tuning of peptoid properties, such as hydrophobicity, charge, and steric bulk. This customization can improve binding affinity and specificity for target molecules.
Low Immunogenicity: Peptoids are less likely to elicit an immune response compared to peptides. This low immunogenicity is beneficial for therapeutic applications, as it reduces the risk of adverse immune reactions.
Ease of Synthesis: The submonomer synthesis method is straightforward and efficient, allowing for rapid production of peptoids. This ease of synthesis facilitates high-throughput screening and the rapid generation of libraries of peptoid molecules for drug discovery.
Cost-Effectiveness: The synthesis of peptoids can be more cost-effective than that of peptides due to the simpler and more scalable chemical processes involved. This can make peptoid-based therapies more affordable and accessible.
Improved Pharmacokinetics: The increased stability and resistance to degradation often result in better pharmacokinetic profiles, including longer circulation times and more sustained therapeutic effects.
Drug Discovery and Development: Peptoids are used to develop new drugs due to their stability, bioavailability, and ability to mimic natural peptides. They are explored as potential treatments for various diseases, including cancer, infectious diseases, and autoimmune disorders.
Antimicrobial Agents: Peptoids have shown promise as antimicrobial agents. Their resistance to proteolytic degradation and customizable side chains allow for the design of molecules that can effectively target and kill bacteria, fungi, and viruses.
Biosensors and Diagnostic Tools: Peptoids are used in the development of biosensors and diagnostic tools due to their ability to bind specifically to target molecules. They can be engineered to detect biomarkers for diseases, providing valuable tools for early diagnosis and monitoring.
Cell Penetrating Agents: Peptoids can be designed to penetrate cell membranes, making them useful for delivering therapeutic agents directly into cells. This application is particularly valuable for delivering drugs that act on intracellular targets.
Targeted Drug Delivery: Peptoids can be used to create targeted drug delivery systems that deliver therapeutic agents to specific cells or tissues. This targeting can increase the efficacy of treatments while minimizing side effects.
Protein-Protein Interaction Modulators: Peptoids can be designed to modulate protein-protein interactions, which are crucial for many biological processes. This ability makes them valuable tools for studying cellular signaling pathways and for developing therapies that target these interactions.
Material Science and Nanotechnology: Peptoids are used in the design of advanced materials and nanostructures. Their ability to form stable, ordered structures makes them useful for creating functional materials with specific properties, such as self-assembling nanostructures and biocompatible surfaces.
Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine: Peptoids are explored for use in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Their customizable properties and stability make them suitable for developing scaffolds and materials that support tissue growth and repair.
Molecular Imaging: Peptoids can be labeled with imaging agents and used as probes for molecular imaging. This application is valuable for visualizing biological processes in real-time and for studying the distribution and activity of drugs in vivo.
Immune Modulation: Peptoids are being investigated as immune modulators. Their ability to interact with specific immune receptors can be harnessed to develop therapies that modulate immune responses, which is useful in treating autoimmune diseases and for immunotherapy in cancer.
Creative Peptides has developed an innovative peptoid synthesis service to meet the increasing needs in drug target discovery and lead structure discovery research, providing a confidential and efficient service at competitive prices.
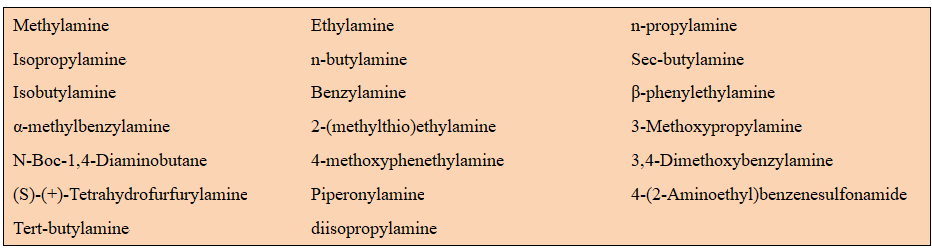 Our available peptoid side chain
Our available peptoid side chain
Advanced Synthesis Platforms: Creative Peptides utilizes state-of-the-art technology for peptoid synthesis, ensuring precise and efficient production of diverse peptoid libraries.
Customization and Versatility: Their services offer extensive customization options, allowing for the creation of peptoids with a wide range of side chains and properties tailored to specific research or industrial needs.
High-Throughput Screening: Creative Peptides provides high-throughput screening capabilities, facilitating the rapid evaluation and optimization of peptoid candidates for various applications.
Expertise in Peptide Chemistry: With a team of experts in peptide and peptoid chemistry, Creative Peptides delivers high-quality, reliable peptoid synthesis with a focus on innovation and precision.
Comprehensive Solutions: Their services encompass the entire peptoid synthesis process, including solid-phase synthesis, purification, and analysis, ensuring well-rounded support for all stages of peptoid development.
Peptoids are synthetic analogs of peptides, where the side chains are attached to the nitrogen atom of the backbone amide. This structural difference gives peptoids enhanced stability, reduced immunogenicity, and greater flexibility for custom applications, making them ideal for drug discovery, material science, and diagnostics.
Peptoid synthesis typically uses the submonomer method, where primary amines are added to a resin-bound intermediate, forming N-substituted glycine units. This process allows for the rapid and flexible assembly of peptoids with diverse side chains, making it ideal for creating large libraries for high-throughput screening.
Peptoids offer greater resistance to proteases, enhanced stability, and customizable side chains, enabling them to bind more effectively to targets. Their reduced immunogenicity makes them safer for therapeutic use, while their structural flexibility allows for the design of molecules that can adopt diverse conformations to interact with biological targets.
Peptoid synthesis has numerous applications, including drug discovery, antimicrobial agents, biosensors, and targeted drug delivery systems. Peptoids can also be used in protein-protein interaction modulation, molecular imaging, tissue engineering, and even in material science for creating self-assembling nanostructures and biocompatible surfaces.
Yes, peptoids can be highly customized with a wide range of side chains, allowing for precise tuning of their properties, such as hydrophobicity, charge, and binding affinity. Creative Peptides offers tailored solutions for various applications, from drug development to biosensors and materials science.
Peptoids play a crucial role in drug discovery by mimicking natural peptides with improved stability and bioavailability. They are used to develop new therapies, create specific binding agents, and design more effective drug delivery systems, especially for targeting difficult or "undruggable" proteins.
High-throughput screening allows for the rapid evaluation of large libraries of peptoids, making it easier to identify the best candidates for specific applications, whether for drug development, diagnostics, or other industrial uses. Creative Peptides leverages this capability to speed up the optimization and selection of peptoid candidates.
Creative Peptides uses advanced purification methods, such as HPLC, to ensure high-quality peptoid production. Each batch undergoes stringent analysis to confirm purity and sequence accuracy, ensuring that the final product meets the required specifications for research and industrial applications.

Reference