Phage display peptide library technology is to fuse gene expression products of exogenous proteins or peptides with phage coat proteins and display them on their surface, and then obtain a large enrichment by screening phages expressing specific peptides or proteins to obtain the target peptide or protein. In 1985, Smith used genetic engineering to insert exogenous genes into the genome of filamentous phages so that the target genes encoding peptide to be displayed in the form of a fusion protein, thus creating the phage display technology.
The principle of phage display peptide technology is to clone the gene encoding a peptide or protein or a fragment of the target gene into the appropriate position of the phage shell protein structure gene, and to fuse the exogenous peptide or protein with the shell protein without affecting the normal function of other shell proteins in the correct reading frame, and the fusion protein is displayed on the surface of the phage with the reassembly of the daughter phage. The displayed peptide or protein can maintain relatively independent spatial structure and biological activity to facilitate the recognition and binding of target molecules. By repeated affinity elution and amplification, phage display peptides or proteins that can bind to target molecules can be directly obtained, and phages with target genes can be isolated (see figure 1).
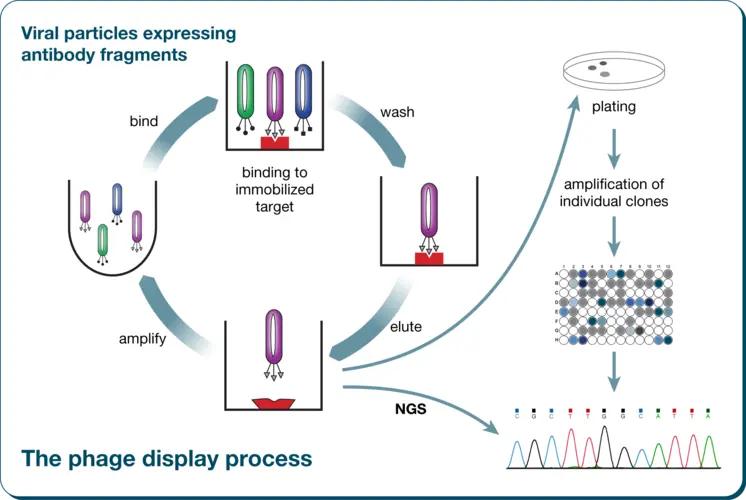 Figure 1. Flow of phage display technology
Figure 1. Flow of phage display technology
The construction of phage display peptide library is mainly applied to M13 phage display system. There are two main ways to construct peptide libraries:organic synthesis method and gene synthesis method. The organic synthesis method is to synthesize short peptides containing various possible sequences directly by solid-phase peptide synthesis technique. The genetic engineering method involves cloning target genes encoding short peptides of various sequence-specific lengths into expression vectors and fusing them with the shell protein genes of phages for expression, resulting in a phage containing a peptide of one sequence on one phage. The screening of phage peptide library is generally done by bio-screening technique, also known as bio-elution, which is the process of screening the desired phage display peptide from the phage random peptide library. Currently, the target molecules are usually purified antibodies, receptors, peptides or enzymes. Depending on the state of the target molecule, the screening methods can be classified as solid phase screening, liquid phase screening, whole cell screening and in vivo screening.
Since its created, phage display technology has become an important research tool in biological research, fundamentally changing the traditional monoclonal antibody preparation process (hybridoma technology), and is widely used in the establishment of antigen antibody libraries, drug design, vaccine research, pathogen detection, gene therapy, antigen epitope research and cell signaling research. With the continuous development and improvement of the technology, it has also evolved into various display technologies, such as ribosome display, mRNA display, bacterial display and yeast display. With the unique advantages and characteristics of phage display peptide library technology, its application prospect is unlimited. As a new technology that is constantly being improved and updated, phage display peptide library technology also has some limitations. For example, the transformation efficiency of E. coli limits the library capacity of the phage display random peptide library, and how to select the desired peptides from the phage display peptide library faster and better. Researchers are currently working on measures to overcome the existing shortcomings by constructing new expression systems and new methods.
Phage display peptide libraries are used to rapidly identify peptide sequences with specific binding properties from extremely large variant pools.
Diversity is generated by inserting randomized peptide-encoding DNA sequences into phage coat protein genes, allowing billions of unique variants to be displayed.
Common formats include linear peptide libraries, cyclic peptide libraries, and motif-focused libraries designed for specific binding interfaces.
Screening is performed through iterative binding and enrichment cycles that selectively retain phage displaying peptides with higher affinity and specificity.
Library size, amino acid distribution, display valency, and phage propagation bias all play key roles in selection performance.
Custom libraries can be designed by adjusting peptide length, cyclization strategy, and sequence constraints to match target characteristics.
Selected phage populations are analyzed by DNA sequencing, enabling rapid identification of dominant and enriched peptide motifs.

References