GMP-Compliant ProductionHigh Precision&QualityCustom Peptide Design
On the basis of extensive experience in peptide synthesis,Creative Peptides proudly offers the most comprehensive glycopeptides synthesis services to our worldwide clients.Our scientists are committed to deliver high quality glycopeptides which will go through strict mass spectral and HPLC analysis to meet our customers'demands.
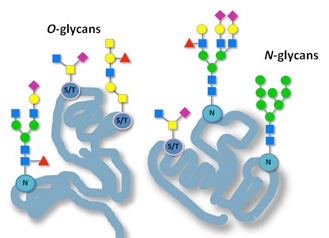
Glycopeptidesare a diverse and intricate class of biomolecules that play crucial roles in various biological processes.Comprising a peptide backbone adorned with complex carbohydrate moieties,glycopeptides exhibit remarkable structural diversity,contributing to their functional versatility.The term"glycopeptide"refers to the combined structure of the peptide/protein and the attached glycans.
Effectiveness Against Resistant Strains
Glycopeptides are particularly valuable in treating infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria that are resistant to other antibiotics.This includes challenging pathogens like methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus(MRSA)and vancomycin-resistant enterococci(VRE).The unique mechanism of glycopeptides,which involves binding to the D-alanyl-D-alanine terminus of bacterial cell wall precursors,makes them effective even against strains that have developed resistance to other antibiotic classes.Their ability to target and disrupt the cell wall synthesis of these resistant bacteria provides a critical option for managing severe and complicated infections.
Broad Spectrum
Glycopeptides possess a broad spectrum of activity against Gram-positive bacteria,including many that are difficult to treat with other antibiotics.They are effective against a range of pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus,Streptococcus pneumoniae,and Enterococcus faecalis.This broad spectrum makes glycopeptides versatile tools in the treatment of various infections,including skin and soft tissue infections,bone and joint infections,and endocarditis.Their broad coverage ensures that they can be used in a variety of clinical situations,especially when other treatment options are limited.
Low Resistance Development
One of the key advantages of glycopeptides is their relatively low rate of resistance development compared to other antibiotic classes.The specific and unique binding mechanism of glycopeptides to bacterial cell wall precursors means that bacteria have fewer mechanisms to counteract their effects.This lower resistance rate is beneficial for maintaining the effectiveness of these antibiotics over time,although vigilance and prudent use are still necessary to prevent the emergence of resistant strains.This characteristic ensures that glycopeptides remain a reliable option in the antibiotic arsenal.
Effective in Serious Infections
Glycopeptides are often reserved for treating serious and life-threatening infections due to their potent activity and efficacy.They are particularly effective in cases where other antibiotics may be inadequate,such as in the treatment of endocarditis(infection of the heart valves),osteomyelitis(bone infection),and complicated skin and soft tissue infections.Their strong antibacterial action and ability to target severe infections make them a crucial component in managing complex clinical scenarios where other treatments may not be effective.
Custom Glycopeptide Synthesis
Glycosylation Site Optimization
Glycopeptide Characterization and Analysis
High-Throughput Glycopeptide Synthesis
Glycopeptide Modification Services
Peptide-Glycan Conjugation
Glycopeptide-based Drug Discovery Support
Quality Assurance and GMP Compliant Production
Glycopeptide Delivery and Formulation
Expertise and Experience
We specialize in the synthesis of complex glycopeptides,bringing years of experience in both academic and industrial applications.
State-of-the-art Technology
Our synthesis platform uses the latest techniques in glycopeptide production,ensuring high-quality results.
Customization
We offer highly flexible services that can be customized to fit your specific research or industrial needs.
Global Reach
Serving researchers,biotech companies,and pharmaceutical labs worldwide.
1
Initial Consultation&Project Scoping
Discuss client needs,define project scope,and agree on peptide sequences and glycosylation patterns.
2
Glycopeptide Design&Planning
Finalize peptide sequence,glycosylation sites,and ensure technical feasibility before synthesis.
3
Synthesis&Glycosylation
Synthesize the peptide using SPPS and integrate glycosylation via enzymatic or chemical methods.
4
Purification&Characterization
Purify the glycopeptide via HPLC and confirm structure using mass spectrometry(MS)and NMR.
5
Quality Assurance&Testing
Perform final quality checks,prepare Certificate of Analysis(COA),and verify biological activity(optional).
6
Delivery&Post-Support
Package and deliver the product with full documentation and offer ongoing technical support if needed.
Creative Peptides also has extensive experience in the design and production of modified peptides.We provide a variety of peptide modifications,labeling,and bioconjugation with other biomolecules,including
In addition,we also provide a variety of optional peptide analysis,including
Creative Peptides provides one-stop peptide solutions,from peptide synthesis,modification,labeling and conjugation to a wide range of biopolymers and surface attachments.Our peptides conjugation services include,but are not limited to
Targeting Gram-Positive Bacteria
Glycopeptides are primarily used to target and eliminate Gram-positive bacteria,which are characterized by their thick peptidoglycan cell wall.This class of antibiotics is particularly effective against a variety of pathogenic Gram-positive organisms,including Staphylococcus aureus,Streptococcus pneumoniae,and Enterococcus faecalis.Their ability to specifically target and disrupt the cell wall of these bacteria makes them crucial in treating infections where other antibiotics may be ineffective.
Combating Antibiotic Resistance
One of the most significant functions of glycopeptides is their role in managing bacterial infections resistant to other antibiotics.They are essential in treating strains that have developed resistance to commonly used antibiotics,such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus(MRSA)and vancomycin-resistant enterococci(VRE).This ability to address resistant strains underscores the importance of glycopeptides in maintaining effective treatment options for difficult-to-treat infections.
Treating Severe Infections
Glycopeptides are often reserved for severe and life-threatening infections due to their potent antibacterial properties.They are employed in the treatment of serious conditions such as endocarditis(infection of the heart valves),osteomyelitis(bone infections),and complicated skin and soft tissue infections.Their effectiveness in these critical situations highlights their importance in managing severe bacterial infections where other therapies might not suffice.
Supporting Antibiotic Stewardship
By providing an effective treatment option for resistant and severe infections,glycopeptides support broader antibiotic stewardship efforts.Their use helps to preserve the effectiveness of other antibiotics by providing targeted treatment alternatives when first-line therapies fail.This function is vital in controlling the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and ensuring the continued efficacy of existing antibiotics.
Glycopeptides work primarily by targeting and disrupting bacterial cell wall synthesis,which is essential for the structural integrity and survival of Gram-positive bacteria.Here's a detailed explanation of their mechanism of action:
Glycopeptides are a unique class of antibiotics and biomolecules characterized by their peptide backbone coupled with carbohydrate(glycan)moieties.This glycosylation can occur at different sites and involves various linkage types,affecting the structure,function,and biological roles of the glycopeptides.Their ability to bind specifically to bacterial cell walls or other biomolecules makes them crucial in both therapeutic and biological contexts.Understanding the different types of glycopeptides,based on their glycan attachment and location within the peptide chain,provides insights into their diverse functions and applications.
Classification Based on Glycan Attachment Type
N-Linked Glycopeptides:N-linked glycopeptides are distinguished by glycans attached to the nitrogen atom of asparagine residues in the peptide chain.This type of glycosylation is the most prevalent,occurringviaan N-glycosidic bond in the Asn-X-Ser/Thr consensus sequence.The attachment of glycans at asparagine residues influences protein folding,stability,and interactions,making N-linked glycopeptides critical in a variety of biological processes and therapeutic applications.Examples include many glycoproteins such as erythropoietin and antibodies.
O-Linked Glycopeptides:O-linked glycopeptides feature glycans attached to the hydroxyl groups of serine or threonine residues,and occasionally to lysine,proline,or tyrosine.This type of glycosylation involves an O-glycosidic bond without a specific consensus sequence,allowing for diverse attachment sites.O-linked glycosylation is essential for protein functions like mucin production and cellular adhesion.It affects protein stability and interactions,contributing to the biological roles of mucin-type glycoproteins and other cellular proteins.
C-Linked Glycopeptides:C-linked glycopeptides are characterized by glycans attached directly to the carbon atom of tryptophan residues.This less common glycosylation involves a C-glycosidic bond and is observed in specific contexts such as certain bacterial and fungal proteins.The rarity of C-linked glycopeptides and their unique bonding provide specialized functions and structural properties,although they are less well-understood compared to N-and O-linked types.
Classification Based on Glycan Attachment Site
N-Terminal Glycopeptides:N-terminal glycopeptides have glycans attached at the N-terminus of the peptide chain,either directly to the first amino acid or a modified N-terminal residue.This type of glycosylation can influence the peptide’s stability and biological activity.N-terminal modifications are less common but can be critical for specific peptide functions,such as receptor binding and signal transduction,seen in some glycosylated hormones and peptides.
Internal Glycopeptides:Internal glycopeptides feature glycan attachments within the peptide sequence,typically at asparagine,serine,or threonine residues.This internal glycosylation plays a crucial role in protein folding,stability,and functionality.Observed in many glycoproteins like antibodies and membrane proteins,internal glycosylation affects interactions with other cellular components and is vital for proper protein function and immune responses.
C-Terminal Glycopeptides:C-terminal glycopeptides have glycans attached at the C-terminus of the peptide chain.The glycan attachment at the end of the peptide can influence its stability and interactions with other molecules.Although less frequent,C-terminal glycosylation can impact peptide functions in signaling and cellular recognition,contributing to the regulation of protein activity and interactions in various biological contexts.
Yes,we specialize in synthesizing custom glycopeptides with a variety of glycan structures,using both enzymatic and chemical glycosylation methods to meet your specific needs.
We can modify most peptides with glycosylation,including small peptides,monoclonal antibody fragments,and larger polypeptides.
We use high-performance liquid chromatography(HPLC)for purification and perform mass spectrometry(MS)and NMR to confirm the structure and purity of the final product.
Yes, we offer GMP-compliant glycopeptide synthesis for clients requiring clinical-grade products.Our processes meet the highest standards of quality control and regulatory compliance.
Yes,we can perform a variety of functional assays,such as receptor binding,enzymatic activity,and immune response assays,to evaluate the biological activity of your glycopeptide.
Yes, we offer both small-scale research and large-scale production,allowing for scalability to meet the needs of different research phases or industrial applications.
