According to the central dogma established by classical naturalists and biologists, proteins/peptides were expected to be exclusively constituted by 20 building blocks, including 19 L-amino acids (L-AAs) and glycine, which is not chiral. At that time, special cases were reported for D-amino acids (D-AAs) containing proteins/peptides such as the presence of D-alanine in octopine derivatives from octopus.
From a functional point of view, these post-translational and chemical modifications in D-AAs containing proteins/peptides confer on them an unusual stereochemistry mostly related to enhanced resistance to enzyme-catalyzed breakdown.
It is worth mentioning the composition of retro-inverso (RI) peptides, also known as all-D-retro peptides or retro-enantio peptides, which are composed of D-AAs assembled in the reverse order to that of their parent L-sequence.
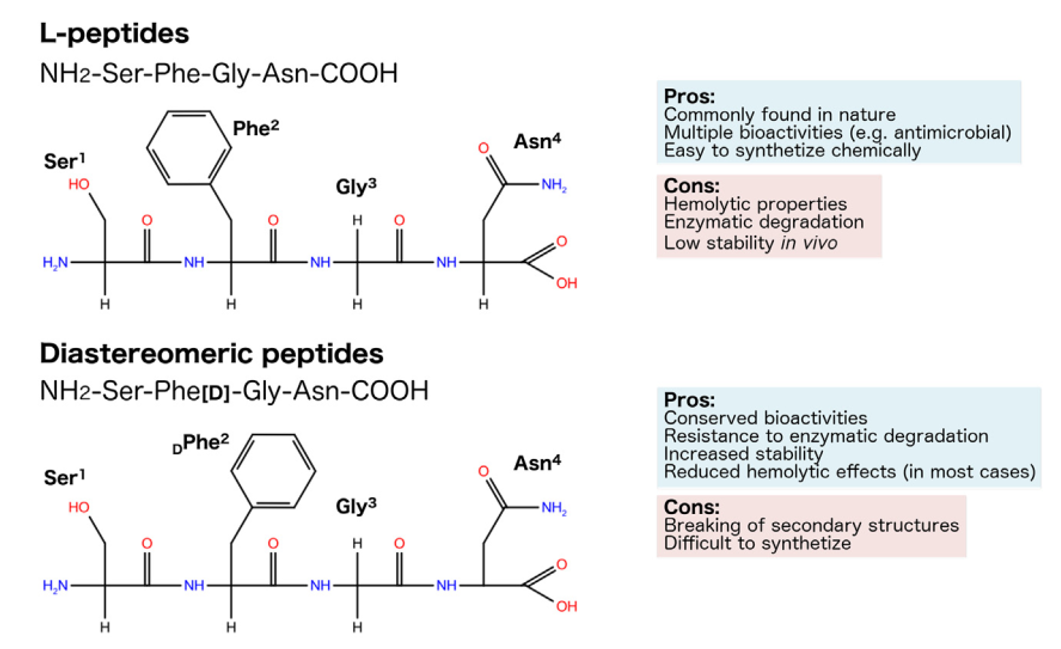
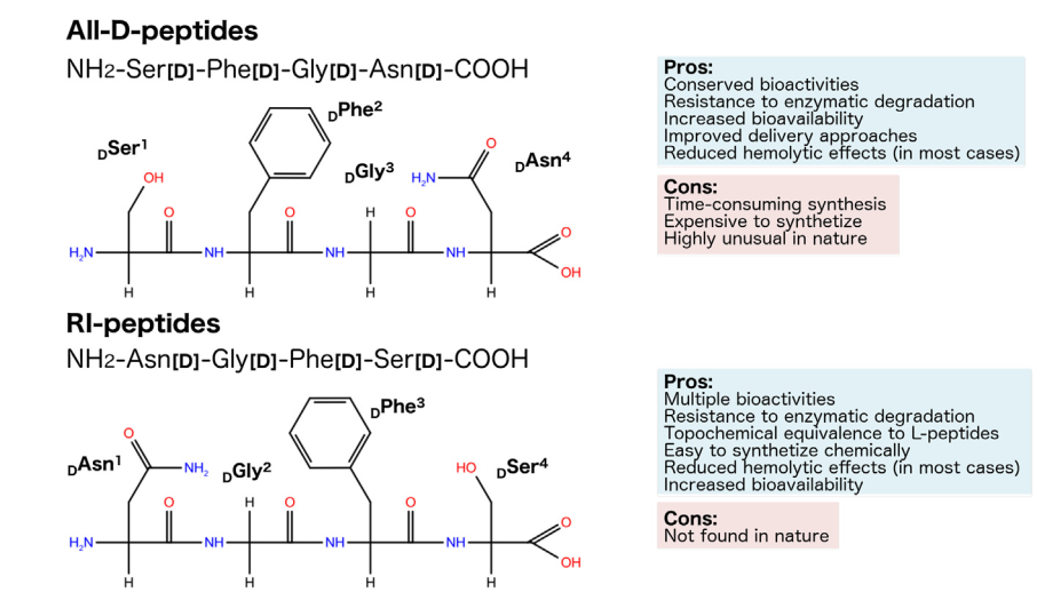
Figure 1 Representation of the planar structure and chirality of hypothetic L-, diastereomeric, all-D- and RI-peptides, also highlighting their pros and cons.
D-amino acids are the mirror image of L-amino acids, providing peptides with enhanced resistance to enzymatic breakdown. They are used to improve peptide stability and bioactivity.
Retro-inverso peptides are composed of D-amino acids in the reverse sequence of the parent peptide. This structure increases stability and resistance to enzymatic degradation.
D-amino acids improve peptide stability and prolong their activity in biological environments. They also enhance resistance to enzymatic degradation, making them ideal for harsh conditions.
D-amino acid peptides are used in anticancer, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial research. They also have applications in drug delivery systems due to their stability.
D-amino acids improve the stability and resistance to enzymatic breakdown in peptide-based delivery agents. This allows for more effective and prolonged drug release.
The main challenge is incorporating D-amino acids without disrupting the peptide's structure. Creative Peptides has advanced methods to overcome these difficulties and ensure high-quality synthesis.
D-amino acids increase the peptide's resistance to degradation, enhancing its bioactivity. In some cases, they improve the peptide's efficacy by stabilizing its functional structure.

Reference