Peptide nucleic acid (PNA) is a DNA mimic with a pseudopeptide backbone composed of N-(2-amino-ethyl)glycine (aeg) units to which the nucleobases are linked through methylene carbonyl linkers. Despite the radical difference in the chemical composition of the backbone, PNA not only retains but also improves the hybridisation characteristics of DNA and RNA. Thus, in most cases PNA oligomers with mixed purine/pyrimidine sequences form duplexes (by Watson-Crick base-pairing) with complementary DNA (and RNA) with higher thermal stability than corresponding DNA-DNA and DNA-RNA complexes and without sacrificing sequence specificity. One approach to improve the performance of PNA is through conjugation, where PNA is linked to other molecules such as proteins, enzymes, or nanoparticles. Creative Peptides can provide many conjugation methods to PNA.
PNA being charge-neutral is hydrophobic and tends to aggregate in aqueous growth media of the cells. The aggregated PNA enters thecell through the endocytosis process where an endosome is formed by encapsulation of the PNA aggregate with an inverted cell membrane. Often the PNA is trapped in the endosome and not available for binding to its target DNA (antigene), mRNA (antisense), and miRNA (anti-miR). For enhanced delivery of the PNA and to avoid endosomal entrapment, PNA is conjugated with cell penetrating peptides (CPP), cationic peptides, Gold nanoparticles (AuNP), and nano graphene oxide (nGO). The conjugated PNA enters the cell mostly through the induced diffusion method and gets detached from its carrier in the cytoplasm to carry out its antigene, antisense, and anti-miR actions.
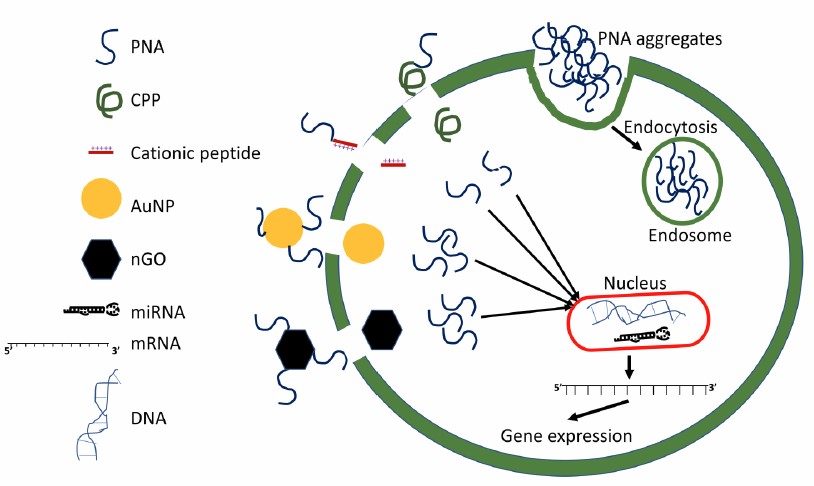 Different strategies for PNA conjugate (Das A, et at. 2021)
Different strategies for PNA conjugate (Das A, et at. 2021)
PNAs can be conjugated to a small molecule at the N- and C-terminus by using standard or modified protocols for peptide synthesis on solid support or in liquid phase. Most PNA modifications have been done at the N-terminus, utilizing the free amino group of the pseudopeptide backbone while the PNA is still attached to the resin and the other reactive groups are protected. The design of PNA N-terminal modification may require a linker between the PNA and the ligand to position the ligand optimally for interaction with DNA or to separate the ligand from the end of the PNA to reduce steric interference.
Peptide nucleic acid-peptide conjugates: This conjugate can combine the sequence-specific recognition of PNA with the biological activities of peptides, such as cell penetration, protease resistance, or targeting to specific tissues or cells. This have various applications, such as gene silencing, antisense therapy, and molecular imaging.
Cell penetrating peptide-PNA conjugates: Covalent conjugation of the PNA to cell penetrating peptide (CPP) decreases the binding affinity of the PNA to its target if the complex is not hydrolyzed in the cell. Mostly the CPP is covalently conjugated with the PNA by a cleavable disulfide linkage. Noncovalent conjugation of the PNA to CPP is developed to overcome the problem of disassociation of the CPP-PNA complex inside the cell.
Nano graphene oxide-PNA conjugates: Fluorophore conjugated PNA (FP-PNA) in complex with nano graphene oxide (nGO) delivered into the cell (upper right panel) and the binding of the PNA to its complementary DNA/RNA is monitored. FP-PNA adsorbed on the nGO sheet (Lower right panel) is used as a probe to detect the target DNA in vitro.
Fluorescently labeled PNAs: It can be used to characterize structural and thermodynamic aspects of the PNA/DNA interactions. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET), absorption hypochromicity (ABS), isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC), and circular dichroism (CD) techniques were employed to evaluate PNA/PNA and PNA/DNA duplex hybridization.
Photoreactive agents-PNA conjugates: It is an attempt to stabilize PNA binding to DNA or as probes of the structure of PNA/DNA complexes.
PNA-lipophilic molecules conjugates: Conjugation of PNAs to lipophilic molecules is motivated by the need to improve PNA transport into the cell.
A PNA conjugate is a peptide nucleic acid linked to another molecule, such as a peptide, nanoparticle, or protein. Conjugation improves PNA delivery, stability, and cellular uptake for research applications.
PNAs are charge-neutral and prone to aggregation, limiting their cellular access. Conjugation with CPPs, cationic peptides, or nanoparticles enhances cellular entry and target binding efficiency.
PNAs can be conjugated to cell-penetrating peptides, gold nanoparticles, nano graphene oxide, lipophilic molecules, or fluorescent labels. Each conjugate type provides specific functional benefits for experimental studies.
Conjugation is usually performed at the N- or C-terminus of the PNA using solid-phase or solution-phase methods. Linkers may be used to reduce steric hindrance and optimize target interactions.
Fluorescent PNA conjugates allow monitoring of PNA binding to complementary DNA or RNA. Techniques such as FRET, ITC, CD, and absorption hypochromicity can be used to evaluate duplex formation and stability.
Conjugating PNAs to lipophilic molecules improves cellular transport and reduces endosomal entrapment. This enhances the availability of PNAs for target recognition and experimental applications.

References