Peptides are compounds composed of multiple amino acids linked by peptide bonds in a certain order. They have important biological functions and are the basis of life activities and biomaterial development. Self-assembly is a process in which basic units such as molecules and nanostructured materials spontaneously assemble into a stable and compact structure. Peptide self-assembly is the formation of molecular aggregates with a specific order of arrangement by non-covalent forces using molecular recognition between molecules or between one fragment of a molecule and another fragment. The peptide self-assembly technology has become a research hotspot in recent years due to the advantages of clear amino acid sequence, easy synthesis and easy design. Studies have shown that the self-assembly design of some peptide drugs or the use of self-assembled peptide materials as drug delivery carriers can solve the problems of short half-life, poor water solubility and low physiological barrier penetration of the drugs.
Peptides can be used for prevention, treatment and diagnosis of disease, and can be synthesized easily. Because of their properties of both small molecule drugs and protein drugs, peptide drugs have become a hotspot. At present, peptide drugs are mainly used in peptide vaccines, anti-tumor peptides, anti-viral peptides, peptides for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, cytokine mimetic peptides, antibacterial peptides, and diagnostic peptides.
In order to utilize peptide drugs efficiently, people have tried to improve the peptides in many types, such as glycation modification, polyethylene glycol (PEG) modification, conjugated fatty acid chains, etc. Modified peptide are often given the advantage of self-assembly, showing slow release, enhanced stability, and environmental responsiveness.
Antimicrobial peptides are rich in positively charged and hydrophobic residues, which can bind to negatively charged components through electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions and insert into cancer cell membranes, and then quickly kill cancer cells through membrane rupture. This unique mechanism of action makes antimicrobial peptides become potential anticancer drugs. The therapeutic efficiency of antimicrobial peptides can be improved by various strategies such as amino acid substitution, introduction of special amino acids, backbone cyclization, glycosylation, and utilization of drug carriers. Among them, fatty acid modification is a simple and effective method that can affect the potency of antimicrobial peptides by modulating the secondary structure, hydrophobicity, and self-assembly tendency.
The clinical application of free drugs is often limited by some adverse properties, such as low water solubility, poor biological distribution, high degradation rate. In addition, some drugs cannot be administered directly or have the potential risk of inducing an immune response. In order to overcome these undesirable properties and improve the efficiency of treatment, it is necessary to combine the drug with the appropriate drug carrier. In the past few decades, many advances have been made in drug delivery by self-assembling peptides as nanomaterials. Self-assembled peptides have many advantages as drug carriers. In addition to rapid synthesis and controllability, they can also improve cell uptake by providing specific ligands that bind to target cell receptors, ensuring responsive release of drugs at specific targets without toxic effects to other cells and eventually excreted freely from the body.
Peptide self-assembled nanomaterials have a wide range of applications in the field of biomedicine, such as wound repair, tissue engineering scaffolds and biomaterial surface engineering. Compared with other medical materials, self-assembled peptide nanomaterials are not only simple in composition and easy to design, but also provide a nanoscale environment for cells to facilitate cell adhesion, migration, differentiation and proliferation. At present, self-assembled peptide materials have been applied in bone tissue engineering and neural tissue engineering.
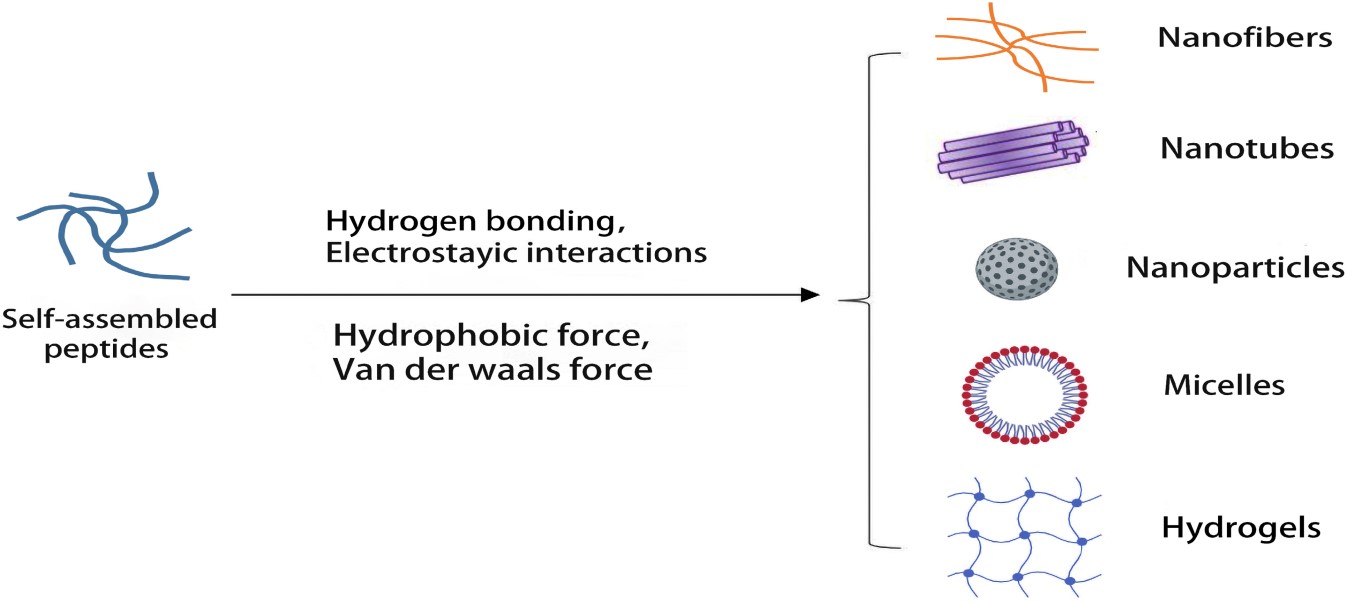 Nanostructures formed by self-assembled peptides (Gao, Y.et al. 2023)
Nanostructures formed by self-assembled peptides (Gao, Y.et al. 2023)
During in vivo molecular imaging, nanoprobes continuously interact with biological barriers before reaching target biomolecules, and then achieve selective molecular recognition in the target microenvironment. Peptide-based nanoprobes for responsive imaging can be constructed by combining contrast agents with peptides due to their targeting and high biocompatibility.
Peptide drugs have significant activity, strong specificity, and good affinity with receptors. However, due to their short half-life, easy enzymolysis in the in vivo environment, and poor penetration of the blood-brain barrier, the clinical application and development of many peptides are hindered. For example, peptide drugs need to be administered for a long time in the treatment of certain chronic diseases such as chronic pain, which are prone to side effects and bring a greater psychological and physical burden to patients. Therefore, reasonable design, reducing the frequency of medication, and changing the dosage form and method of medication are the directions for future efforts of polypeptide drugs. Self-assembled not only has little effect on the activity of peptide drugs, but also produces some excellent properties after self-assembled.