Peptide purification refers to the process of isolating and purifying peptides from a mixture. Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. They are synthesized by methods such as solid phase peptide synthesis or recombinant DNA technology. However, these synthesis processes usually result in peptide mixtures containing impurities, by-products, protecting groups and reagents used in the synthesis reaction. Peptide purification is essential to obtain high purity peptides for further characterization, biological research or therapeutic applications. It involves isolating the desired peptide from impurities and obtaining high yield and quality purified peptide samples.
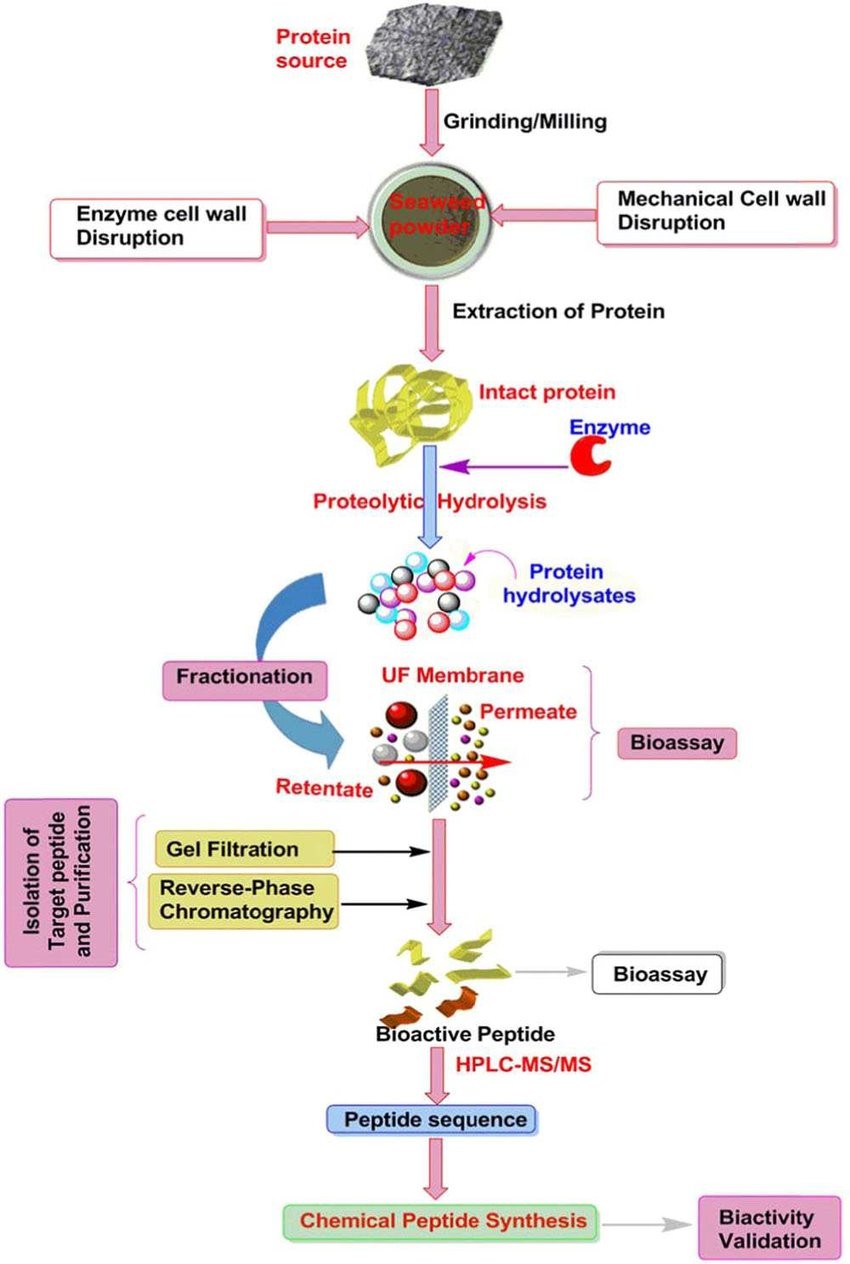 Fig. 1. Extraction, purification and isolation procedures of bioactive peptides (Journal of Food Science. 2018, 83(1): 6-16).
Fig. 1. Extraction, purification and isolation procedures of bioactive peptides (Journal of Food Science. 2018, 83(1): 6-16).
Approaches to Peptide Purification
- High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
Peptides can be purified by preparative or semi-preparative HPLC. Factors such as gradient and flow rate are determined by the size of the column, the sequence of the peptide, and the separation of the desired peptide from impurities. For efficient preparative grade purification, a development process is required in which the gradient and flow rate are optimized for efficient separation. And as the desired product begins to elute from the preparative column, fractions should be collected. These fractions should be tested by analytical HPLC and all fractions with sufficient purity can be combined and lyophilized. Purified fractions should be lyophilized as soon as possible because as a lyophilized powder, the peptides can be stored in a refrigerator for long periods of time, but peptides in solution can deteriorate rapidly. - Affinity Chromatography (AC)
AC is a chromatographic method that separates substances by utilizing the specific affinity between a ligand group attached to a stationary phase matrix and a ligand that can interact with its specificity. Peptides can be purified using Immobilized Metal Affinity Chromatography. The stationary phase matrix chelates some metal ions, such as Cu2+, Ni2+, Fe3+, etc. This column can chelate peptides containing Lys, Met, Asp, Arg, Tyr, Glu and His in the side chain by ligand bonding, especially the structure of peptide sequences containing His-X-X-X-His is most easy to be combined with the metal-ion affinity column, and the purification effect is better. - Capillary Electrophoresis
CE is a separation technique based on the difference in migration rates of substances under the action of an electric field, and can be used to purify peptides. In capillary electrophoresis, peptide molecules migrate through the capillary tube under the action of an electric field based on differences in charge, size and shape, thus enabling the separation and purification of peptides.
Advantages of Peptide Purification
- High Purity
The purification process separates peptides from impurities, resulting in a highly pure peptide sample. High purity peptides are essential for further research, analysis, and applications because the higher the purity, the more reliable and accurate the peptide properties and effects. - Structure Confirmation
Through purification, pure peptide samples can be obtained for structural confirmation and identification. This is essential for understanding the sequence, conformation and function of the peptide, especially in the fields of drug discovery and protein engineering. - Activity Retention
The purification process avoids or minimizes effects on peptide activity. By effectively removing impurities and by-products, purification can help to preserve the natural activity and biological function of peptides, ensuring reliability in research and applications. - Expanded Applications
Purified peptides can be used in a variety of research and application areas, such as biological research, drug discovery, and biomedical applications. High-purity peptide samples provide accurate, reproducible and comparable experimental results. - Improved Stability
The purification process may include some protective measures such as pH adjustment, addition of stabilizers, etc., which help to improve the stability of peptides. - Quantitative Analysis
Purified peptide samples can be analyzed accurately and quantitatively to determine peptide concentration and content. This is important for applications such as formulating solutions, preparing standard curves and determining dosages.
Reference
- Admassu H., et al. Bioactive peptides derived from seaweed protein and their health benefits: antihypertensive, antioxidant, and antidiabetic properties. Journal of Food Science. 2018, 83(1): 6-16.
 Fig. 1. Extraction, purification and isolation procedures of bioactive peptides (Journal of Food Science. 2018, 83(1): 6-16).
Fig. 1. Extraction, purification and isolation procedures of bioactive peptides (Journal of Food Science. 2018, 83(1): 6-16).